Abstract
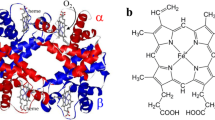
Cooperative functioning of many protein systems depends on communication between different subunits of those systems. Perhaps the best understood cooperative protein system is the vertebrate haemoglobin tetramer, in which the subunits share a similar tertiary structure (the myoglobin fold) with each other and with myoglobins and haemoglobins from at least four different animal phyla and leguminous plants. Blood clams have cooperative tetrameric haemoglobin and, in addition, a cooperative homodimeric haemoglobin 1–6. In view of previous reports7,8 concerning the role of dimers in the vertebrate tetramer, the clam haemoglobins represent a very interesting model system. We report here the low-resolution three-dimensional crystal structures of the dimeric and turmeric cooperative hemoglobins from the blood clam Scapharca inaequivalvis. We find that clam haemoglobins are made of myoglobin-like subunits but their assembly to form dimers and tetramers is quite different from that of vertebrate haemoglobin. The arrangement of the subunits provides a simple structural explanation for haem-haem interaction in the dimer and tetramer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohnoki, S., Mitomi, Y., Hata, R. & Satake, K. J. Biochem., Tokyo 73, 717–725 (1973).
Djangmah, J. S., Gabbott, P. A. & Wood, E. J. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 60 B, 245–250 (1978).
Furuta, H., Ohe, M. & Kajita, A. J. Biochem., Tokyo 82, 1723–1730 (1977).
Como, P. F. & Thompson, E. O. P. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 33, 643–652 (1980).
Chiancone, E., Vecchini, P., Verzili, D., Ascoli, F. & Antonini, E. J. molec. Biol 152, 577–592 (1981).
Ikeda-Saito, M. et al. J. molec. Biol. 170, 1009–1018 (1983).
Antonini, E. Science 158, 1417–1425 (1967).
Mills, F. C., Johnson, M. L. & Ackers, G. A. Biochemistry 15, 5350–5362 (1976).
Como, P. F. & Thompson, E. O. P. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 33, 653–664 (1980).
Furuta, H. & Kajita, A. Biochemistry 22, 917–922 (1983).
Baldwin, J. & Chothia, C. J. molec. Biol. 129, 175–220 (1979).
Phillips, S. E. V. J. molec. Biol. 142, 531–554 (1980).
Crowther, R. A. in The Molecular Replacement Method (ed. Rossmann, M. G.) 173–178 (Gordon & Breach, New York, 1972).
Crowther, R. A. & Blow, D. M. Acta crystallogr. 23, 544–548 (1967).
Ward, K. B., Wishner, B. C., Lattman, E. E. & Love, W. E. J. molec. Biol. 98, 161–177 (1975).
Wishner, B. C., Ward, K. B., Lattman, E. E. & Love, W. E. J. molec. Biol. 98, 179–194 (1975).
Rossmann, M. G. Acta crystallogr. 14, 383–388 (1961).
Bernstein, F. C. et al. J. molec. Biol. 112, 535–542 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Royer, W., Love, W. & Fenderson, F. Cooperative dimeric and tetrameric clam haemoglobins are novel assemblages of myoglobin folds. Nature 316, 277–280 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/316277a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/316277a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Two-domain hemoglobin from the blood clam,Barbatia lima. The cDNA-derived amino acid sequence
Journal of Protein Chemistry (1995)
-
The amino acid sequence of hemoglobin III from the symbiont-harboring clamLucina pectinata
Journal of Protein Chemistry (1993)
-
Amino acid sequence of the coelomic C globin from the sea cucumberCaudina (Molpadia) arenicola
Journal of Protein Chemistry (1992)
-
Primary structure of chain I of the heterodimeric hemoglobin from the blood clamBarbatia virescens
Journal of Protein Chemistry (1992)
-
Molecular inventiveness
Nature (1990)