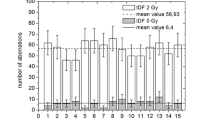
Abstract
WE have previously shown1 that ultraviolet irradiation of normal human lymphocytes immediately before or after X irradiation gives an approximately two-fold increase of the frequency of dicentric chromosomes as compared with the yield induced by X rays alone. Ultraviolet light itself induces very few dicentrics. One interpretation of this synergistic reaction might be that lesions induced by X rays are transformed into chromosome breaks by the ultraviolet treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmberg, M., and Jonasson, J., Mutat. Res. (in the press).
Sasaki, M. S., and Tonomura, A., Jap. J. Human Genet., 14(2), 81 1969.
Evans, H. J., in Advances in Physical and Biological Radiation Detectors, 593–609 (Proceedings of a Symposium, IAEA, Vienna 1971).
Bender, M. A., and Brewen, J. G., Mutat. Res., 8, 383 (1969).
Evans, R. G., and Norman, A., Nature, 217, 455 (1968).
Evans, R. G., and Norman, A., Rad. Res., 36, 287 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOLMBERG, M. No interaction between ultraviolet and X irradiation on chromosome aberrations in cells with trisomy 21. Nature 249, 448–449 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/249448a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/249448a0
- Springer Nature Limited