Abstract
Purpose. To investigate the potential of chitosan (CS) to enhance buccal peptide and protein absorption, the TR146 cell culture model, a model of the buccal epithelium, was used.
Methods. The sensitivity of TR146 cells to several CS solutions (different salts with different MW) was investigated by using the MTS/PMS assay. Permeability studies were performed to determine the enhancing effect of CS glutamate (1, 20, 40, 60, and 100 μg/mL) on the permeability of 3H-mannitol and fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled dextrans (FD) with various MW (4.4-19.5 kD) across the cell culture model.
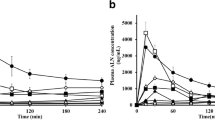
Results. Sensitivity of TR146 cells to CS solutions depended on the concentration, the pH, and the type of CS salt. CS glutamate solutions (pH 6.0) were found to be the least harmful. CS glutamate was able to increase the permeability of model substances with MW up to 9.5 kD across the cell model. An enhancing effect was found for CS concentrations of 20 μg/mL and higher, correlating with a decrease in TEER values. The 20 μg/mL CS concentration had a negligible effect on the enzyme activity of the cells as determined by the MTS/PMS assay.
Conclusions. CS glutamate is effective in enhancing the transport of macromolecules across the buccal TR146 cell culture model. Therefore, it might be a promising vehicle for peptide and protein buccal administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. H. L. Lee. Peptidase activities in absorptive mucosae. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 17:937–940 (1989).
F. Veuillez, Y. N. Kalia, Y. Jacques, J. Deshusses, and P. Buri. Factors and strategies for improving buccal absorption of peptides. Eur. J. Pharm. BioPharm. 51:93–109 (2001).
H. E. Junginger, A. J. Hoogstraate, and J. C. Verhoef. Recent advances in buccal drug delivery and absorption-in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Control. Release 62:49–159 (1999).
B. J. Aungst. Oral mucosal permeation enhancement: possibilities and limitations. In: M. J. Rathbone (ed.). Oral Mucosal Drug Delivery. 1st ed. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, 1996, pp. 65–83.
T. J. Aspden, L. Illum, and O. Skaugrud. Chitosan as a nasal delivery system: evaluation of insulin absorption enhancement and effect on nasal membrane integrity using rat models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 22:23–31 (1996).
R. Fernández-Urrusuno, P. Calvo, C. Remuñán-López, J. L. Vila-Jato, and M. J. Alonso. Enhancement of nasal absorption of insulin using chitosan nanoparticles. Pharm. Res. 16:1576–1581 (1999).
P. Artursson, T. Lindmark, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum. Effect of chitosan on the permeability of monolayers of intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2).Pharm. Res. 11:1358–1361 (1994)
N. G. M. Schipper, K. M. Varum, and P. Artursson. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly water absorbable drugs. I. Influence of molecular weight and degree of acetylation on drug trans-port across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Pharm. Res. 13:1686–1692 (1996).
N. G. M. Schipper, S. Olson, J. A. Hoogstraate, A. G. De Boer, K. M. Varum, and P. Artursson. Chitosans as absorption enhancers for poorly absorbable drugs 2: mechanism of absorption enhancement. Pharm. Res. 14:923–929 (1997).
A. F. Kotze, B. J. Leeuw, H. L. Lueßen, A. G. De Boer, J. C. Verhoef, and H. E. Junginger. Chitosans for enhanced delivery of therapeutic peptides across intestinal epithelia: in vitro evaluation in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int. J. Pharm. 159:243–253 (1997).
J. Jacobsen, B. van Deurs, M. Pedersen, and M. R. Rassing. TR146 cells grown on filters as a model for human buccal epithelium. I. Morphology, growth, barrier properties and permeability. Int. J. Pharm. 125:165–184 (1995).
T. H. Rupniak, C. Rowlatt, E. B. Lane, J. G. Steele, L. K. Trejdosiewicz, B. Laskiewicz, S. Povey, and B. T. Hill. Characterization of four new human cell lines derived from squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 75:621–635 (1985).
H. M. Nielsen and M. R. Rassing. TR146 cells grown on filters as a model of human buccal epithelium. IV. Permeability of water, mannitol, testosterone and b-adrenoceptor antagonists: comparison to human, monkey and porcine buccal mucosa. Int. J. Pharm. 194:155–167 (2000).
H. M. Nielsen and M. R. Rassing. TR146 cells grown on filters as a model of human buccal epithelium. III. Permeability enhancement by different pH values, different osmolality values, and bile salts. Int. J. Pharm. 185:215–225 (1999).
J. Jacobsen, M. Pedersen, and M. R. Rassing. TR146 cells as a model for human buccal epithelium. II. Optimisation and use of a cellular sensitivity MTS/PMS assay. Int. J. Pharm. 141:217–225 (1996).
B. Carreño-Gómez and R. Duncan. Evaluation of biological properties of soluble chitosan and chitosan microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 148:231–240 (1997).
A. F. Kotze, H. L. Lue?en, A. G. De Boer, J. C. Verhoef, and H. E. Junginger. Chitosan for enhanced intestinal permeability: prospects for derivatives soluble in neutral and basic environments. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 7:145–151 (1998).
L. J. Filar and M. G. Wirick. Bulk and solution properties of chitosan. In: R. A. A. Muzzarelli and E. R. Parisier (eds.). Proceedings of the First International Conference on Chitin/Chitosan. Massachusetts, 1987, pp. 169–181.
H. M. Nielsen, J. C. Verhoef, M. Ponec, and M. R. Rassing. TR146 cells grown on filters as a model of human buccal epithelium: permeability of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labelled dextrans in the presence of sodium glycocholate. J. Control. Release 60:223–233 (1999).
D. K. Powell. Barrier function of epithelia. Am. J. Physiol. 241:G275–G288 (1981).
C. A. Squier, P. Cox, and P. W. Wertz. Lipid content and water permeability of skin and oral mucosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 96:123–126 (1991).
D. Harris and J. R. Robinson. Drug delivery via the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. J. Pharm. Sci. 81:1–10 (1992).
I. Henriksen, G. Smistad, and J. Karsten. Interactions between liposomes and chitosans. Int. J. Pharm. 101:227–236 (1994).
S. Senel, M. J. Kremer, S. Kas, P. W. Wetz, A. A. Hincal, and C. A. Squier. Enhancing effect of chitosan on peptide drug delivery across buccal mucosa. Biomaterials 21:2067–2071 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Portero, A., Remuñán-López, C. & Nielsen, H.M. The Potential of Chitosan in Enhancing Peptide and Protein Absorption Across the TR146 Cell Culture Model—An in Vitro Model of the Buccal Epithelium. Pharm Res 19, 169–174 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014220832384
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014220832384