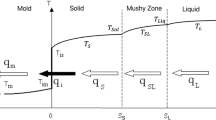
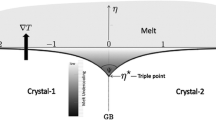
Abstract
Using the framework of modern continuum thermomechanics, we develop sharp- and diffuse-interface theories for coherent solid-state phase transitions. These theories account for atomic diffusion and for deformation. Of essential importance in our formulation of the sharp-interface theory are a system of “configurational forces” and an associated “configurational force balance.” These forces, which are distinct from standard Newtonian forces, describe the intrinsic material structure of a body. The configurational balance, when restricted to the interface, leads to a generalization of the classical Gibbs–Thomson relation, a generalization that accounts for the orientation dependence of the interfacial energy density and also for a broad spectrum of dissipative transition kinetics. Our diffuse-interface theory involves nonstandard “microforces” and an associated “microforce balance.” These forces arise naturally from an interpretation of the atomic densities as macroscopic parameters that describe atomistic kinematics distinct from the motion of material particles. When supplemented by thermodynamically consistent constitutive relations, the microforce balance yields a generalization of the Cahn–Hilliard relation giving the chemical potentials as variational derivatives of the total free energy with respect to the atomic densities. A formal asymptotic analysis (thickness of the transition layer approaching zero) demonstrates the correspondence between versions of our theories specialized to the case of a single mobile species for situations in which the time scale for interface propagation is small compared to that for bulk diffusion. While the configurational force balance is redundant in the diffuse-interface theory, when integrated over the transition layer, the limit of this balance is the interfacial configurational force balance (i.e., generalized Gibbs–Thomson relation) of the sharp-interface theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Ågren, Diffusion in phases with several components and sublattices, Journal of the Physics and Chemistry of Solids 43:421–430 (1982).
R. Abeyaratne and J. K. Knowles, On the driving traction acting on a surface of strain discontinuity in a continuum, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 38:345–360 (1990).
J. I. D. Alexander and W. C. Johnson, Thermomechanical equilibrium in solid-fluid systems with curved interfaces, Journal of Applied Physics 58:816–824 (1985).
S. S. Antman and J. E. Obsborn, The principal of virtual work and integral laws of motion, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 69:231–262 (1979).
J. W. Cahn, Free energy of a nonuniform system. II. Thermodynamic basis, Journal of Cherubical Physics 30:1121–1124 (1959).
J. W. Cahn, On spinodal decomposition, Acta Metallurgica 9:795–801 (1961).
J. W. Cahn, On spinodal decomposition in cubic crystals, Acta Metallurgica 10:179–183 (1962).
J. W. Cahn, Surface stress and the equilibrium of small crystals––I. The case of the isotropic surface, Acta Metallurgica 28:1333–1338 (1980).
J. W. Cahn and J. E. Hilliard, Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy, Journal of Chemical Physics 28:258–267 (1958).
J. W. Cahn and J. E. Hilliard, Free energy of a nonuniform system. III. Nucleation in a two-component incompressible fluid, Journal of Chemical Physics 31:688–699 (1959).
J. W. Cahn and J. E. Hilliard, Spinodal decomposition: a reprise, Acta Metallurgica 19:151–161 (1971).
J. W. Cahn and D. W. Hoffman, A vector thermodynamics for anisotropic surfaces––II. Curves and faceted surfaces, Acta Metallurgica 22:1205–1214 (1974).
J. W. Cahn and F. C. Larché, Surface stress and the equilibrium of small crystals––II. Solid particles embedded in a solid matrix, Acta Metallurgica 30:51–56 (1980).
J. W. Cahn and F. C. Larché, An invariant formulation of multicomponent diffusion in crystals, Scripta Metallurgica 17:927–932 (1983).
G. Capriz, Continua with Microstructure (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1989).
G. Capriz and P. Podio-Guidugli, Structured continua from a Lagrangian point of view, Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata 135:1–25 (1983).
P. Cermelli and M. E. Gurtin, The dynamics of solid-solid phase transitions 2. Incoherent interfaces, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 127:41–99 (1994a).
P. Cermelli and M. E. Gurtin, On the kinematics of incoherent phase transitions, Acta Metallurgica et Materialia 42:3349–3359 (1994b).
F. Davì and M. E. Gurtin, On the motion of a phase interface by surface diffusion, Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 41:782–811 (1990).
J. L. Ericksen, Anisotropic fluids, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 4:231–237 (1960).
J. L. Ericksen, Conservation laws for liquid crystals, Transactions of the Society of Rheology 5:23–34 (1961).
J. L. Ericksen, Liquid crystals with variable degree of orientation, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 113:97–120 (1991).
J. D. Eshelby, The force on an elastic singularity, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A 244:87–112 (1951).
J. D. Eshelby, The continuum theory of lattice defects, in Progress in Solid State Physics 3, (F. Seitz and D. Turnbull, eds. (Academic Press, 1956), pp. 79–144.
J. D. Eshelby, Energy relations and the energy-momentum tensor in continuum mechanics, in Inelastic Behavior of Solids, M. F. Kanninen, W. F. Alder, A. R. Rosenfield and R. I. Jaffe, eds. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1970).
J. D. Eshelby, The elastic energy-momentum tensor, Journal of Elasticity 5:321–335 (1975).
I. Fonseca, Variational methods for elastic crystals, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 107:195–224 (1989).
F. C. Frank, On the kinematic theory of crystal growth and dissolution processes, in Growth and Perfection of Crystals, R. H. Doremus, B. W. Roberts and D. Turnbull, eds. (Wiley, New York. 1958).
M. Frémond, Adhérence des solides, Journal de Mécanique théorique et appliquée 6:383–407 (1987).
M. Frémond, Endommagement et principe des puissances virtuelles, Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, série II 317:857–863 (1993).
E. Fried, Continua described by a microstructural field, Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 47:168–175 (1996).
E. Fried, Correspondence between a phase-field theory and a sharp-interface theory for crystal growth, Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics 9:33–60 (1997).
E. Fried, Introduction. Fifty years of research on evolving phase interfaces, in Evolving Phase Interfaces in Solids, J. M. Ball, D. Kinderlehrer, P. Podio-Guidugli and M. Slemrod, eds. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1999).
E. Fried and G. Grach, An order-parameter based theory as a regularization of a sharp-interface theory for solid-solid phase transitions, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 138:355–404 (1997).
E. Fried and M. E. Gurtin, Continuum theory of thermally induced phase transitions based on an order parameter, Physica D 68:326–343.
E. Fried and M. E. Gurtin, Dynamic solid-solid transitions with phase characterized by an order parameter, Physica D 72:287–308 (1994).
E. Fried and M. E. Gurtin, A phase-field theory for solidification based on a general anisotropic sharp-interface theory with interfacial energy and entropy, Physica D 91:143–181 (1996).
E. Fried and S. Vedantam, Phase-field theory for stress-induced diffusional solid-solid phase transitions. (Unpublished manuscript.)
K. Fuchs, Uber die Mischungsschicht zweier Flüssigkeiten, Repertorium der Physik 24:614–647 (1888).
P. Germain, Sur l'application de la méthode des puissances virtuelles en mécanique des milieux continus, Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, série A 274:1051–1055 (1973).
M. A. Goodman and S. C. Cowin, A continuum theory for granular materials, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 44:249–266 (1972).
J. W. Gibbs, On the equilibrium of heterogeneous substances, Transactions of the Connecticut Academy of Arts and Sciences 3:108–248. Reprinted in The Scientific Papers of J. Willard Gibbs, Vol. 1 (Dover, New York, 1961).
M. E. Gurtin, On the two-phase Stefan problem with interfacial energy and entropy, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 96:199–241 (1986).
M. E. Gurtin, Multiphase thermomechanics with interfacial structure 1. Heat conduction and the capillary balance law, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 104:195–221 (1988).
M. E. Gurtin, On a nonequilibrium thermodynamics of capillarity and phase, Quarterly of Applied Mathematics 47:129–145 (1989).
M. E. Gurtin, On the thermomechanical laws for the motion of a phase interface, Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 42:370–388 (1991).
M. E. Gurtin, Thermomechanics of Evolving Phase Boundaries in the Plane (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1993).
M. E. Gurtin, The dynamics of solid-solid phase transitions 1. Coherent interfaces, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 123:305–335 (1993).
M. E. Gurtin, The characterization of configurational forces, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 126:387–394 (1994).
M. E. Gurtin, The nature of configurational forces, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 131:67–100 (1995).
M. E. Gurtin, Generalized Ginzburg–Landau and Cahn–Hilliard equations based on a microforce balance, Physica D 92:178–192 (1996).
M. E. Gurtin, Configurational Forces as Basic Concepts of Continuum Physics (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1999).
M. E. Gurtin and A. Struthers, Multiphase thermormechanics with interfacial structure 3. Evolving phase boundaries in the presence of bulk deformation, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 112:97–160 (1990).
M. E. Gurtin and P. W. Voorhees, The continuum mechanics of coherent two-phase elastic solids with mass transport, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A 440:323–343 (1993).
W. Heidug and F. K. Lehner, Thermodynamics of coherent phase transformations in non-hydrostatically stressed solids, Pure and Applied Geophysics 123:91–98 (1985).
C. Herring, Surface tension as a motivation for sintering, in The Physics of Powder Metallurgy, W. E. Kingston, ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1951).
C. Herring, The use of classical macroscopic concepts in surface-energy problems, in Structure and Properties of Solid Surfaces, R. Gomer and C. S. Smith, eds. (University of Chicago, Chicago, 1953).
D. W. Hoffman and J. W. Cahn, A vector thermodynamics for anistotropic surfaces––I. Fundamentals and applications to plane surface junctions, Surface Science 31, 368–388 (1972).
W. C. Johnson and J. I. D. Alexander, Interface conditions for thermomechanical equilibrium in two-phase crystals, Journal of Applied Physics 59:2735–2746 (1986).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, A linear theory of thermochemical equilibrium of solids under stress, Acta Metallurgica 21:1051–1063 (1973).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, A nonlinear theory of thermochemical equilibrium of solids under stress, Acta Metallurgica 26:53–60 (1978a).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, Thermochemical equilibrium of multiphase solids under stress, Acta Metallurgica 26:1579–1589 (1978b).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, The effect of self-stress on diffusion in solids, Acta Metallurgica 30:1835–1845 (1982).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, The interactions of composition and stress in crystalline solids, Acta Metallurgica 33:331–357 (1983).
F. C. Larché and J. W. Cahn, Phase changes in a thin plate with non-local self-stress effects, Acta Metallurgica 40:947–955 (1992).
P. Leo, J. S. Lowengrub, and H. J. Jou, A diffuse interface model for microstructural evolution in elastically stressed solids, Acta Materiala 47:2113–2130 (1998).
P. Leo and R. F. Sekerka, The effect of surface stress on crystal-melt and crystal-crystal equilibrium, Acta Metallurgica 37:3119–3138 (1989).
F. M. Leslie, Some constitutive equations for liquid crystals, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis 28:265–283 (1968).
G. A. Maugin, Material Inhomogeneities in Elasticity (Chapman and Hall, London, 1993).
T. Miyazaki, T. Kozakai, and S. Mizuno, A theoretical analysis of the phase-decompositions based upon the two-dimensional non-linear diffusion equaiton, Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals 24:799–808 (1983).
W. W. Mullins, Two-dimensional motion of idealized grain boundaries, Journal of Applied Physics 27:900–904 (1956).
W. W. Mullins, Grain boundary grooving by surface diffusion, Transactions of the American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers 218:354–361 (1960).
W. W. Mullins, The thermodynamics of critical phases with curved interfaces: specific case of interfacial isotropy and hydrostatic Pressure, in Proceedings of an International Conference on Solid → Solid Phase Transformations, H. I. Aaronson, D. E. Laughlin, R. F. Sekerka, and C. M. Wayman, eds. (American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, New York, 1982).
W. W. Mullins, Thermodynamic equilibrium of a crystalline sphere in a fluid, Journal of Chemical Physics 81:1436–1442 (1984).
W. W. Mullins and R. F. Sekerka, Morphological stability of a particle growing by diffusion or heat flow, Journal of Applied Physics 34:323–329 (1963).
W. W. Mullins and R. F. Sekerka, Stability of a planar interface during solidification of a binary alloy, Journal of Applied Physics 35:444–451 (1964).
W. W. Mullins and R. F. Sekerka, On the thermodynamics of crystalline solids, Journal of Chemical Physics 82:5192–5202 (1985).
H. Nishimori and A. Onuki, Pattern formation in phase-separating alloys with cubic symmetry, Physical Review B 42:980–983 (1990).
H. Nishimori and A. Onuki, Freezing of domain growth in cubic solids with elastic misfit, Journal of the Physical Society of Japan 60:1208–1211 (1991).
A. Onuki, Ginzburg–Landau approach to elastic effects in the phase separation of solids, Journal of the Physical Society of Japan 58:3065–3068 (1989a).
A. Onuki, Long-range interactions through elastic fields in phase-separating solids, Journal of the Physical Society of Japan 58:3069–3072 (1989b).
C. W. Oseen, The theory of liquid crystals, Transactions of the Faraday Society 29:883–899 (1933).
R. L. Pego, Front migration in the nonlinear Cahn-Hilliard equation, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A 422:261–278 (1989).
Lord Rayleigh, On the theory of Surface forces––II. Compressible fluids, Philosophical Magazine 33:209–220 (1892).
J. S. Rowlison, Van der Waals and the physics of liquids, in J. D. van der Waals: On the Continuity of the Gaseous and Liquid States, J. S. Rowlison, ed. (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1988).
C. H. Su and P. W. Voorhees, The dynamics of precipitate evolution in elastically stressed solids––I. Inverse coarsening, Acta Metallurgica et Materiala 44:1987–1999 (1996a).
C. H. Su and P. W. Voorhees, The dynamics of precipitate evolution in elastically stressed solids––II. Particle alignment, Acta Metallurgica et Materiala 44:2001–2016 (1996b).
M. E. Thompson, C. S. Su, and P. W. Voorhees, The equilibrium shape of a misfitting precipitate, Acta Metallurgica et Materiala 42:2107–2122 (1994).
M. E. Thompson and P. W. Voorhees, Equilibrium particle morphologies in elastically stressed solids, in Mathematics of Microstructure Evolution, L. Q. Chen, B. Fultz, J. W. Cahn, J. R. Manning, J. E. Morral, and J. Simmons, eds. (SIAM, Philadelphia, 1996).
C. Truesdell and W. Noll, The Non-Linear Field Theories of Mechanics, in (Handbuch der Physik III–3, S. Flügge, ed.) (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1965).
C. Truesdell and R. A. Toupin, The Classical Field Theories, in (Handbuch der Physik III–1, S. Flügge, ed.) (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1960).
L. M. Truskinovsky, Dynamics of nonequilibrium phase boundaries in a heat conducting nonlinearly elastic medium, Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (PMM) 51:777–784 (1987).
L. M. Truskinovsky, Kinks versus shocks, in Shock Induced Transitions and Phase Structures in General Media, J. E. Dunn, R. L. Fosdick, and M. Slemrod, eds. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1993).
J. D. van der Waals, Thermodynamische Theorie de Capillariteit in de Onderstelling van Continue Dichteidsverandering, Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen, Afdeeling Natuurkunde, Deel 1, 1893. See also J. S. Rowlison, Translation of J. D. van der Waals’ “The thermodynamic theory of capillarity under the hypothesis of a continuous variation of density, ” Journal of Statistical Physics 20:197–244 (1979).
Y. Wang, L. Q. Chen, and A. G. Khachaturyan, Kinetics of strain-induced morphological transformation in cubic alloys with a miscibility gap, Acta Metallurgica et Materiala 41:279–296 (1993).
Y. Wang and A. G. Khachaturyan, Shape instability during precipitate growth in coherent solids, Acta Metallurgica et Materiala 43:1837–1857 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fried, E., Gurtin, M.E. Coherent Solid-State Phase Transitions with Atomic Diffusion: A Thermomechanical Treatment. Journal of Statistical Physics 95, 1361–1427 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004535408168
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004535408168