Abstract
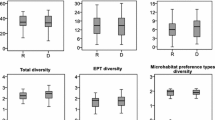
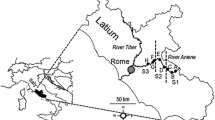
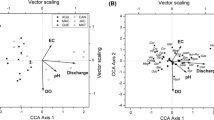
Structure and composition of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages were investigated in seven sampling sites with a gradient of environmental integrity and water quality conditions. Composite samples of the four most representative substrates were collected in order to characterize the riffle-pool dynamic in each sampling site. Spatial and temporal variability of macroinvertebrate assemblages were analyzed at two scales: using substrates and grouping samples for comparing sampling sites. Distribution of macroinvertebrates was influenced primarily by substrate type, but also by environmental integrity, water quality and sampling period. Species occurrence was highly dependent on substrate type. At local spatial scale, environmental degradation measured by the Riparian Channel Environmental Inventory and water chemistry were the determinants of assemblage patterns. We evaluated to which extent the substrates were influenced by environmental integrity and water chemistry, and we found that degradation influenced significantly the macroinvertebrate fauna on the four substrate types, although they were not responding to the same variables. Our results show that qualitatively communities were not influenced by seasonal changes, but abundance was stochastically dependent on rainfall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angradi, T. R., 1996. Inter-habitat variation in benthic community structure, function, and organic matter storage in 3 Appalachian headwater streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15: 42–63.
Angrisano, E.B., 1995. Insecta Trichoptera. In: Lopretto, E.C. & G., Tell (eds), Ecosistemas de Aguas Continentales. Metodologias para su estudio (vol III). Ediciones Sur, La Plata: 1199–1237.
APHA, 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. APHA, AWWA, WEF, 20th edn.
Baptista, D. F., L. F. M. Dorvillé, D. F. Buss & J. L. Nessimian, 2001. Spatial and temporal organization of aquatic insect assemblages in the longitudinal gradient of a tropical river. Brazilian Journal of Biology 61: 295–304.
Brown, A. V. & P. P. Brussock, 1991. Comparisons of benthic invertebrates between riffles and pools. Hydrobiologia 220: 99–108.
Buss, D. F., D. F. Baptista, M. P. Silveira, J. L. Nessimian & L. F. M. Dorvillé, 2002. Influence of water chemistry and environmental degradation on macroinvertebrate assemblages in a river basin in south-east Brazil. Hydrobiologia 481: 125–136.
Death, R. G. & M. J. Winterbourn, 1995. Diversity patterns in stream benthic invertebrate communities: the influence of habitat stability. Ecology 76: 1446–1460.
De Marmels, J., 1990. Key to the ultimate instar larvae of the Venezuelan odonate families. Opuscula Zoologica Fluminenesia 50: 1–6.
Dominguez, E., M. D. Hubbard & W. D. Peters, 1992. Clave para ninfas y adultos de las familias y generos de Ephemeroptera Sudamericanos. Biologia Acuatica 16: 5–39.
Dorvillé, L.F.M. & C. G. Froehlich, 1999. Additional characters to distinguish the nymphs of the Perlidae genera from Southeastern Brazil (Insecta, Plecoptera). Aquatic Insects 21: 281–284.
Flecker, A. S. & B. Feifarek, 1994. Disturbance and the temporal variability of invertebrate assemblages in two Andean streams. Freshwater Biology 31: 131–142.
Flint, O. S. Jr., 1991. Studies of neotropical caddisflies, XLV: The taxonomy, phenology and faunistics of the Trichoptera of Antioquia, Colombia. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology 52: 1–113.
Froehlich, C.G., 1984. Brazilian Plecoptera 4. Nymphs of perlid genera from southeastern Brazil. Annales de Limnologie 20: 43–48.
Grasshoff, K., M. Erhardt & K. Kremling (eds), 1983. Methods of Seawater Analysis, 2nd edn, Verlag-Chemie, Weinheim: 411 pp.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970. The ecology of stream insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 15: 25–42.
Jackson, J. K. & B. W. Sweeney, 1995. Egg and larval development times for 35 species of tropical stream insects from Costa Rica. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 14: 115–130.
Jacobsen, D. & A. Encalada, 1998. The macroinvertebrate fauna of Ecuadorian high-land streams in the wet and dry season. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 142: 53–70.
Kikuchi, R. M. & V. S. Uieda, 1998. Composição da comunidade de invertebrados de um ambiente lótico tropical e sua variação espacial e temporal. In Nessimian, J. L. & A. L. Carvalho (eds), Ecologia de Insetos Aquáticos. Series Oecologia Brasiliensis, vol. V. PPGE-UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro: 157–173.
Lemly, A. D., 1982. Modification of benthic insect communities in polluted streams: combined effects of sedimentation and nutrient enrichment. Hydrobiologia 87: 229–245.
Logan, P. & M. P. Brooker, 1983. The macroinvertebrate faunas of riffles and pools. Water Research 17: 263–270.
Manly, B. F. J., 1986. Multivariate Statistical Methods: A Primer. Chapman & Hall, London: ix+159 pp.
McClelland, W. T. & M. A. Brusven, 1980. Effects of sedimentation on the behaviour and distribution of riffle insects in a laboratory stream. Aquatic Insects 2: 161–169.
McCulloch, D. L., 1986. Benthic macroinvertebrate distributions in the riffle-pool communities of two east Texas streams. Hydrobiologia 135: 61–70.
Melo, A. S. & C. G. Froehlich, 2001.Macroinvertebrates in neotropical streams: richness patterns along a catchment and assemblage structure between 2 seasons. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 1–16.
Merritt, R.W. & K. W. Cummins, 1996. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 3rd edn. Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque.
Minshall, G. W. & J. N. Minshall, 1977. Microdistribution of benthic invertebrates in a Rocky Mountain (USA) stream. Hydrobiologia 55: 231–249.
Minshall, G.W. & R. C. Petersen, 1985. Towards a theory of macroinvertebrate community structure in stream ecosystems. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 104: 49–76.
Nieser, N. & A. L. de Melo, 1997. Os heterópteros aquáticos de Minas Gerais, guia introdutório com chave de identificação para as espécies de Nepomorpha e Gerromorpha. Editora UFMG, Belo Horizonte: 180 pp.
Oliveira, L. G., 1996. Aspectos da biologia de comunidades de insetos aquáticos da ordem Trichoptera Kirby, 1813, em córregos de cerrado do município de Pirenópolis, Estado de Goiás. Dissertação de doutorado Instituto de Biologia da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo: 120 pp.
Parsons, T. R., Y., Maita & C. M. Lalli, 1984. AManual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. Pergamon Press, Oxford: 173 pp.
Petersen, R. C., 1992. The RCE: a Riparian, Channel, and Environmental Inventory for small streams in the agricultural landscape. Freshwater Biology 27: 295–306.
Power, M. E., 1992. Habitat heterogeneity and the functional significance of fish in river food webs. Ecology 73: 1675–1688.
Ramírez, A. & C. M. Pringle, 2001. Spatial and temporal patterns of invertebrate drift in streams draining a Neotropical landscape. Freshwater Biology 46: 47–62.
Resh, V. H., A. V. Brown, A. P. Covich, M. E. Gurtz, H. G. Li, G. W. Minshall, S. R. Reice, A. L. Sheldon, J. B. Wallace & R. C. Wissmar, 1988. The role of disturbance in stream ecology. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7: 433–455.
Robinson, C. T. & G. W. Minshall, 1986. Effects of disturbance frequency on stream benthic community structure in relation to canopy cover and seasons. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 5: 237–248.
Scrimgeour, G. J. & M. J. Winterbourn, 1989. Effects of floods on epilithon and benthic macroinvertebrate populations in an unstable New Zealand river. Hydrobiologia 171: 33–44.
Sokal, R. R. & F. J. Rohlf, 1995. Biometry. W.H. Freeman & Company, New York, 887 pp.
Statzner, B., J. A. Gore & V. H. Resh, 1988. Hydraulic stream ecology: Observed patterns and potential applications. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7: 307–360.
Statzner, B. J. & B. Higler, 1986. Stream hydraulics as a major determinant of benthic invertebrate zonation patterns. Freshwater Biology 16: 127–139.
Thomson, J. R., P. S. Lake, & B. J. Downes, 2002. The effect of hydrological disturbance on the impact of a benthic invertebrate predator. Ecology 83: 628–642.
Townsend, C. R., A. G. Hildrew, & K. Schofield, 1987. Persistence of stream invertebrate communities in relation to environmental variability. Journal of Animal Ecology 56: 597–613.
Wallace, J. B. & J. R. Webster, 1996. The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annual Review of Entomology 41: 115–139.
Wiggins, G.B., 1996. Larvae of the North American Caddisfly Genera (Trichoptera), 2nd edn. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, xiii+457 pp.
Wohl, D. L., J. B. Wallace & J. L. Meyer, 1995. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure, function and production with respect to the habitat type, reach and drainage basin in the southern Appalachians (USA). Freshwater Biology 34: 447–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buss, D.F., Baptista, D.F., Nessimian, J.L. et al. Substrate specificity, environmental degradation and disturbance structuring macroinvertebrate assemblages in neotropical streams. Hydrobiologia 518, 179–188 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025067.66126.1c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000025067.66126.1c