Abstract
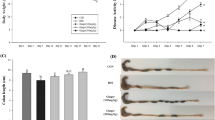
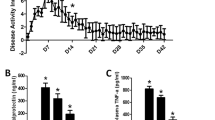
Aim of this study was to assess the structural,ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and clinicalaspects in Sprague-Dawley rats with dextrane sulfatesodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Colitis was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by seven days of DSSoral administration followed by seven days of tap wateronly (for one, two and three cycles). Controls were fedwith water only. Segments of proximal, mid-, and distal colon of each animal were adequatelyprepared for light and scanning electron microscopeobservations. The severity of the lesions was scoredhistologically. For immunohistochemical study, acocktail of S-100, NSE, and antineurofilament antibodieswas used. Symptoms such as weight, feces consistency,diarrhea, hematochezia were recorded daily. From aclinical point of view symptoms appeared significantly later after the first cycle than after thesecond and third cycles and lasted significantly longerin the second and third cycles. Treated rats showed aslower weight gain rate by 20% compared to controls, and the whole colon length appeared to besignificantly shorter after colitis induction comparedto controls. Structural observations by light microscopyshowed prominent involvement of the distal colon. Immunohistochemical study of both submucosaland myoenteric nerve plexuses was similar to controls.Scanning electron microscope observations of the colonicmucosal surface in colitis rats showed a complete subversion of its architecture, characterizedby dilatations of gland crypt openings, dropout ofgoblet cells, and inhomogeneous distribution or lack ofmicrovilli. These were most evident after the third cycle. In conclusion, experimental DSS colitisin SD rats appeared to be highly reproducible and sharedmost features with human UC, not only from a structuraland clinical but also from an ultrastructural point of view.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Duerr RH: Genetics of inflammatory bowel disease Inflam Bowel Dis 2:48–60, 1996
Sartor RB: Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: Pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology 106:533–539, 1994
Jarnerot G: Dietary factors in inflammatory bowel disease. In Inflammatory Bowel Disease. G Jarnerot (ed). Malmo, Corona Astra, 1992, pp 37–47
Sartor B: Microbial agents in the pathogenesis, differential diagnosis, and complications of inflammatory bowel disease. In Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract. MJ Blaser, PD Smith, JI Ravdin, HB Greenberg, RL Guerrant (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1995, pp 435–458
Strober W: Animal models in inflammatory bowel disease—an overview. Dig Dis Sci 12:35, 1985
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS, Riddel RH: Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 109:1344–1367, 1995
Dieleman LA, Pena AS, Meuwissen SGM, Van Rees EP: Role of animal models for the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 32( suppl 223):66–104, 1997
Familiari G, Familiari A, Machiarelli G, Didio LJA, Motta PM: The use of sonic frequencies as a cleaning agent of specimens to be observed by scanning electron microscopy. Scan Microsc 7:107–114, 1993
Gibson PR, Anderson RP, Mariadason JM, Wilson AJ: Protective role of the epithelium of the mall intestine and colon. Inflam Bowel Dis 2:279–302, 1996
Okayasu I, Hatakeyama S, Yamada M, Okhusa T, Inagaki Y, Nakaya R: A novel method of reliable experimental acute and chronic ulcerative colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 98:694–702, 1990
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS, Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest 69:238–249, 1993
Dieleman LA, Ridwan BU, Tennyson GS, Beagley KW, Busy RP, Elson CO: Dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced colitis occurs in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Gastroenterology 107:1643–1652, 1994
Roediger WEW, Duncan A, Kapanaris O, Millard S: Sulphide impairment of substrate oxydation in rat colonocytes: A biochemical basis of ulcerative colitis? Clin Sci 85:623–627, 1993
Roediger WEW, Moore J, Babidge W: Colonic sulfide in pathogenesis and treatment of ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 42:1571–1579, 1997
Collins SM, Van Assche G, Hageboam C: Alterations in enteric nerve and smooth muscle function in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflam Bowel Dis 3:38–48, 1997
Collins SM: The immunomodulation of enteric neuromuscular function: Implications for motility and inflammatory disorders. Gastroenterology 111:1683–1699, 1996
Fedorak RN: Naturally occurring and experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. In Inflammatory Bowel Disease. JB Kirshner, RG Shorter (eds). Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1995, pp 71–94
Okhusa T: Production of experimental colitis in hamsters by dextran sulfate sodium and change in intestinal microflora. Gastroenterol Jpn 82:1327–1336, 1985 ( in Japanese, abstract in English)
Iwanaga T, Hoshi O, Han H, Fujita T: Morphological analysis of acute ulcerative colitis experimentally induced by dextran sulfate sodium in the guinea pig: Some possible mechanisms of cecal ulcerations. Gastroenterol Jpn 29:430–438, 1994 ( in Japanese, abstract in English)
Kishimoto S, Kobayashi H, Shimizu S, Haruma K, Tamaru T, Kijiyama G, Myoshi A: Changes of colonic vasoactive intestinal peptide and cholinergic activity in rats with chemical colitis. Dig Dis Sci 37:1729–1737, 1992
Tamaru T, Kobayashi H, Kishimoto S, Kajiyama G, Shimamoto F, Brown WR: Histochemical study of colonic cancer in experimental colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 38:529–537, 1993
Bjorck S, Jennische E, Dahlstrom A, Ahlman H: Influence of topical rectal application of drugs on dextran sulfate-induced colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 42:824–832, 1997
Kimura I, Kamiya A, Nagahama S, Yoshida J, Tanigawa H, Kataoka H: Study on the experimental ulcerative colitis model induced by the alcian-blues taining method. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 102:343–350, 1993 ( in Japanese, abstract in English)
Kimura I, Nagahama S, Kawasaki M, Kamiya A, Kataoka M: Study on the experimental ulcerative colitis (UC) model induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in rats. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 105:145–152, 1995 ( in Japanese, abstract in English)
Jewel DP: Ulcerative colitis. In Gastrointestinal Diseases, MH Sleisenger, JS Fordtran (eds). Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1993, pp 1305–1330
Goldman H: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis. In Pathology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, SC Ming, H Goldman (eds). Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1992, pp 643–688
Shields HH, Bates ML, Goldman H, Zuckerman GR, Mills BA, Best CJ, Bair FA, Goran DA, De Schryver-Kecskemeti K: Scanning electron microscopic appearance of chronic ulcerative colitis with and without dysplasia. Gastroenterology 89:62–72, 1985
Myllaremi H, Nickels J: Scanning electron microscopy of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis of the colon. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 385:343–350, 1980
Trabucchi E, Mukenge S, Baratti C, Colombo R, Fregoni F, Montorsi W. Differential diagnosis of Crohn' s disease of the colon from ulcerative colitis: Ultrastructure study with the scanning electron microscope. Int J Tissue React 8:79–84, 1986
Trabucchi E, Pace M, Micheletto G, Abelli P, Radaelli E, Foschi D: Colite ulcerosa: Aspetti ultrastrutturali e di diagnostica differenziale. Minerv Chir 47:461–467, 1992
Marin ML, Geller SA, Greenstein AJ, Marin RH, Gordon RE, Aufses AH Jr: Ultrastructural pathology of Crohn's disease: Correlated transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and freeze fracture studies. Gastroenterology 78:355–364, 1983
Stanisz A, Collins SM: Increased levels of substance P in myenteric plexus in Trichinella-infected rats. Gastroenterology 102:1913–1919, 1992
Miller MJS, Sodowska-Krowicka H, Jena AY, Chotinarnemal S, Wong M, Clark DA, Ho W, Sharkey KA: Substance P levels in experimental ileitis in guinea pigs: effects of misoprostol. Am J Physiol 265:G321-G330, 1993
Reinshagen M, Egger B, Procaccino F, Eysselein VE: Neuropeptides in inflammatory bowel disease: An update. JBD 3:303–317, 1997
Holzer P, Holzer-Petsche U: Tachykinins in the gut. Part II. Roles in neural excitation, secretion and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther 73:219–263, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudio, E., Taddei, G., Vetuschi, A. et al. Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) Colitis in Rats (Clinical, Structural, and Ultrastructural Aspects). Dig Dis Sci 44, 1458–1475 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026620322859
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026620322859