Abstract
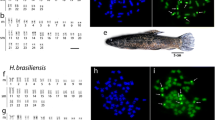
Comparative karyotype analyses of five diploid, two tetraploid, and three hexaploid species of Helianthuswere performed using Feulgen staining, Giemsa C and CMA3 (C-CMA) staining, and FISH with 45S rDNA probe. The karyotypes are composed by a basic number of x = 17 with a predominance of meta- and submetacentric chromosome types. A polyploid series is associated with the basic number. Giemsa C- and C-CMA banding revealed terminal or interstitial heterochromatin according to the species, suggesting the existence of a mechanism that may be acting in the dispersion of heterochromatic segments in Helianthus. The nucleolar organizer regions were located at terminal chromosome positions by FISH with 45S rDNA probe. Diploid species presented four, six, and eight rDNA sites, tetraploid species showed eight sites and hexaploid species presented 12 rDNA sites. Karyomorphological differences include variation in number, size and chromosome morphology, suggesting that rearrangements involving small heterochromatic and rDNA segments played a major role in karyotype evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R. & R.L. Honeycutt, 1986. Evolution over a billion years, pp. 81–125 in DNA Systematics II. Plant DNA, edited by S.K. Dutta. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Chandler J.M., C.C. Jan & B.H. Beard, 1986. Chromosomal differentiation among the annual Helianthus species. System Bot. 11: 354–371.
Cuéllar T., E. Belhassen, B. Fernández-Calvín, J. Orellana & J.L. Bella, 1996. Chromosomal differentiation in Helianthus annuus var. macrocarpus: heterochromatin characterization and rDNA location. Heredity 76: 586–591.
Cuéllar T., J. Orellana, E. Belhassen & J.L. Bella, 1999. Chromosomal characterization and physical mapping of the 5S and the 18S-5.8S-25S ribosomal DNA in Helianthus argophyllus, with new data from Helianthus annuus. Genome 42: 110–115.
Cuadrado A. & N. Jouve, 1994. Mapping and organization of highly-repeated DNA sequences by means of simultaneous and sequential FISH and C-banding in 6x-Triticale. Chrom. Res. 2: 231–238.
Dorado O., L.H. Rieseberg & D. Arias, 1992. Chloroplast DNA introgression in southern California sunflowers. Evolution 46: 566–572.
Gerlach W.L. & J.R. Bedbrook, 1979. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucl. Acids Res. 7: 1869–1885.
Heiser Jr. C.B., 1965. Species crosses in Helianthus. III. Delimitation of sections. Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard. 52: 364–370.
Heslop-Harrison J.S., T. Schwarzacher, K. Anamthawat-Jonsson, A.R. Leitch, M. Shi & I.J. Leitch, 1991. In situ hybridization with automated chromosome denaturation. Technique 3: 106–109.
Jackson R.C. & B.G. Murray, 1983. Colchicine induced quadrivalent formation in the Helianthus: evidence of ancient polyploidy. Theor. Appl. Genet. 64: 219–222.
Kulshreshtha V.B. & P.K. Gupta, 1981. Cytogenetic studies in the genus Helianthus L. II. Karyological studies in 12 species. Cytologia 46: 279–289.
Leggett J.M. & G.S. Markand, 1995. The genomic identification of some monosomics of Avena sativa L. cv. Sun II using genomic in situ hybridization. Genome 38: 747–751.
Messina R. & M. Biagetti, 1999. Chromosomal localization of rDNA in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by fluorescent in situ hybridization. J. Genet. Breed. 53: 259–261.
Pedersen C. & I. Linde-Laursen, 1994. Chromosomal locations of four minor rDNA loci and a marker microsatellite sequence in barley. Chrom Res. 2: 65–71.
Raicu, V.V., A. Mihãilescu, C. Popescu & M.K. Motz, 1976. Research of the chromosome complement in Helianthus L. genus. Caryol 29: 307–316.
Schilling E.E. & C.B. Heiser Jr., 1981. Infrageneric classification of Helianthus compositae. Taxon 30: 393–403.
Schrader O., R. Ahne, J. Fuchus & I. Schubert, 1997. Karyotype analysis of Helianthus annuus using Giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Chrom. Res. 5: 451–456.
Schwarzacher T., P. Ambros & D. Schweizer, 1980. Application of Giemsa banding to orchid karyotype analysis. Plant Syst. Evol. 134: 293–297.
Schweizer D. & F. Ehrendorfer, 1983. Evolution of C-band patterns in Asteraceae-Anthemideae. Biol. Zbl. 102: 637–655.
Schweizer D. & J. Loidl, 1987. A model for heterochromatin dispersion and the evolution of C-band patterns. Chrom. Today 9: 61–74.
Vaughan H.E., M. Jamilena, C. Ruiz-Rejon, J.S. Parker & M.A. Garrido-Ramos, 1993. Loss of nucleolus-organizer regions during polyploid evolution in Scilla autumnalis. Heredity 71: 574–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanzela, A.L., Ruas, C.F., Oliveira, M.F. et al. Characterization of Diploid, Tetraploid and Hexaploid Helianthus Species by Chromosome Banding and FISH with 45S rDNA Probe. Genetica 114, 105–111 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015171625890
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015171625890