Abstract
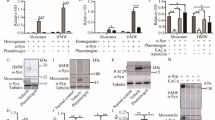
Berberine and palmatine exhibit a mild and competitive inhibition on bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.2; TH). In this study, the inhibitory effects of protoberberine alkaloids (such as berberine, palmatine and coptisine) on dopamine biosynthesis in PC12 cells were investigated. Treatment with berberine and palmatine showed 53.7% and 61.0% inhibition of dopamine content in PC12 cells at a concentration of 20 μM for 24 hr, respectively. However, coptisine did not reduce dopamine content. The IC50 values of berberine and palmatine were 18.6 μM and 7.9 μM. Dopamine content was lowered at 6 hr and reached the minimal level at 24 hr after exposure to berberine and palmatine at 20 μM. The decreased dopamine level was maintained up to 48 hr, and then recovered to the control level at about 72 hr. TH activity was inhibited at 6 hr following treatment with berberine and palmatine, and was maintained at a reduced level up to 36 hr in PC12 cells (21–27% inhibition at 20 μM), whereas TH mRNA level was not found to alter for 24 hr. However, the intracellular Ca2+ concentration decreased by treatment with berberine and palmatine at 20 μM by 22–26% inhibition relative to the control level in PC12 cells. These results give evidence that berberine and palmatine lead to decreased dopamine content by inhibition of TH activity but not by regulation of TH gene expression in PC12 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Tang, W., and Eisenbrand, G. 1992. Coptis supp. 362-371, in Chinese drugs of plant origin. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Sethi, M. L. 1983. Inhibition of reverse transcriptase activity by protoberberine alkaloids and structure-activity relationship. J. Pharm. Sci. 72:538–541.
Kuo, C. L., Chou, C. C., and Yung, B. Y. 1995. Berberine complexes with DNA in the berberine-induced apoptosis in human leukemic HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 93:193–200.
Taira, Z., Matsumoto, M., Ishida, S., Ichikawa, T., and Sakiya, Y. 1994. Aggregation of DNA enhanced by the protoberberine alkaloids, coralyne and berberine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 42: 1556–1561.
Hiller, K. O., Ghorbani, M., and Schilcher, H. 1998. Antispasmodic and relaxant activity of chelidonine, protopine, coptisine, and Chelidonium majus extracts on isolated guinea-pig ileum. Planta Med. 64:758–760.
Shin, D.-H., Yu, H., and Hsu, W. H., 1993. A paradoxical stimulatory effect of berberine on guinea-pig ileum contractility: Possible involvement of acetylcholine release from the postganglionic parasymphathetic nerve and cholinesterase inhibition. Life Sci. 53:1495–1500.
Oelmez, E., and Ilhan, M. 1992. Evaluation of the ?-adrenoreceptor antagonistic action of berberine in isolated organs. Arzneim.-Forsch /Drug Res. 42:1095–1097.
Hsieh, M. T., Su, S. H., Tsai, H. Y., Peng, W. H., Hsieh, C. C., and Chen, C. F. 1993. Effects of palmatine on motor activity and the concentration of central monoamines and its metabolites in rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 61:1–5.
Greene, L. A., and Rein, G. 1977. Short-term regulation of catecholamine biosynthesis in a nerve growth factor responsive clonal line of rat pheochromocytoma cells. J. Neurochem. 30: 549–555.
Tischler, A. S., Perlman, R. L., Morse, G. M., and Sheard, B. E. 1983. Glucocorticoids increase catecholamine synthesis and storage in PC12 pheochromocytoma cell cultures. J. Neurochem. 40:364–370.
Byrd, J. C., Hadjiconstantinou, M., and Cavalla, D. 1986. Epinephrine synthesis in the PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 127:139–142.
Gebreyesus, K., Kilbourne, E. J., and Sabban, E. L. 1993. Bradykinin elevates tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine ?-hydroxylase mRNA in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 608:345–348.
Nagatsu, T., Levitt, M., and Udenfriend, S. 1964. Tyrosine hydroxylase, The initial step in norepinephrine biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 239:2910–2917.
Lee, M. K., and Kim, H. S. 1996. Inhibitory effects of protoberberine alkaloids from the the root of Coptis japonica on catecholamine biosynthesis in PC12 cells. Planta Med. 62:31–34.
Shin, J. S., Kim, K. T., and Lee, M. K. 1998. Inhibitory effects of bulbocapnine on dopamine biosynthesis in PC12 cells. Neurosci. Lett. 244:161–164.
Kim, H. S., Zhang, Y. H., Fang, L. H., and Lee, M. K. 1998. Inhibitory effect of fangchinoline on dopamine biosynthesis in PC12 cells. Med. Sci. Res. 26:475–476.
Lee, M. K., and Zhang, Y. H. 1996. Inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase by berberine. Med. Sci. Res. 24:561–562.
Lee, M. K., Zhang, Y. H., and Kim, H. S. 1996. Inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase by palmatine. Arch. Pharm. Res. 19:258–260.
Zhang, Y. H., Shin, J. S., Lee, S. S., Kim, S. H., and Lee, M. K. 1997. Inhibition of tyrosine hydroxylase by bulbocapnine. Planta Med. 63:362–363.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Mitsui, A., Nohta, H., and Ohkura, Y. 1985. High-performance liquid chromatography of plasma catecholamines using 1,2-diphenylethylenediamine as precolumn fluorescence derivatization reagent. J. Chromatogr. 344:61–70.
Nagatsu, T., Oka, K., and Kato, K. 1979. Highly sensitive assay for tyrosine hydroxylase activity by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 163:247–252.
Lee, M. K., Nohta, H., and Ohkura, Y. 1986. Occurrence of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in human plasma and its assay by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. 378:329–336.
Chomczynski, P., and Sacchi, N. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156–159.
Kim, K. S., Park, D. H., Wessel, T. C., Song, B., Wagner, J. A., and Joh, T. H. 1993. A dual role for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase in tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:3471–3475.
Grynkiewicz, G., Poeni, M., and Tsien, R. Y. 1985. A new generation of Ca???indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260:3440–3450.
Shin, J. S., Kim, E. I., Kai, M., Kim, H. S., and Lee, M. K. 1998. Inhibitory effects of coralyne on dopamine content in PC12 cells. Med. Sci. Res. 26:745–747.
Shin, J. S., Yun-Choi, H. S., Kim, E. I., and Lee, M. K. 1999. Inhibitory effects of higenamine on dopamine content in PC12 cells. Planta Med. 65:452–455.
Dunkley, P. R., Cote, A., Harrison, S. M., Herd, L., Hall, A., and Powis, D. A. 1996. Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 51: 239–245.
Haycock, J., Bennett, W. F., George, R. J., and Waymire, J. C. 1982. Multiple site phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 257:13699–13703.
Kim, K. S., Lee, M. K., Carroll, J., and Joh, T. H. 1993. Both basal and inducible transcription of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene are dependent upon a cAMP response element. J. Biol. Chem. 268:15689–15695.
Kim, K. S., Tinti, C., Song, B., Cubells, J. F., and Joh, T. H. 1994. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase regulated basal and cyclic-AMP-stimulated but not phorbol ester-stimulated transcription of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene. J. Neurochem. 63:834–842.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.S., Kim, E.I., Kai, M. et al. Inhibition of Dopamine Biosynthesis by Protoberberine Alkaloids in PC12 Cells. Neurochem Res 25, 363–368 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007541020736
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007541020736