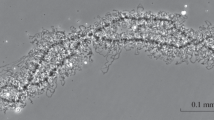
Abstract
The lampbrush chromosomes and assorted nuclear bodies of amphibian and avian oocytes provide uniquely advantageous and amenable experimental material for cell biologists to study the structure and function of the eukaryotic nucleus, and in particular to address the processes of nuclear gene expression. Recent findings discussed here include the molecular analysis of the actively elongating RNA polymerase complexes associated with lampbrush chromosome loops and of the association between loop nascent transcripts and RNA processing components. In addition, several types of chromosome structure that do not outwardly resemble simple extended loops and that may house novel nuclear functions have recently been studied in detail. Among these a type of chromosomal body that can also exist free in the oocyte nucleus, the Cajal body, has been shown to possess a range of characteristics that suggest it is involved in the assembly of macromolecular complexes required for gene expression. Homologous structures have also been described in somatic nuclei. Fundamental aspects of the looped organization exhibited by lampbrush as well as other chromosomes have also been addressed, most notably by the application of a technique for de-novo chromosome assembly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott J, Marzluff WF, Gall JG (1999) The stem-loop binding protein (SLBP1) is present in coiled bodies of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Mol Biol Cell 10: 487–499.
Angelier N, Penrad-Mobayed M, Billoud B, Bonnanfant-Jais ML, Coumailleau P (1996) What role might lampbrush chromosomes play in maternal gene expression? Int J Dev Biol 40: 645–652.
Barsacchi G, Bussoti L, Mancino G (1970) The maps of the lampbrush chromosomes of Triturus (Amphibia Urodela) IV. Triturus vulgaris meridionalis. Chromosoma 31: 255–270.
Bellini M, Lacroix JC, Gall JG (1993) A putative zinc-binding protein on lampbrushc hromosome loops. EMBO J 12: 107–114.
Bentley D (1999) Coupling RNA polymerase II transcription withpr e-mRNA processing. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11: 347–351.
Bromley SE, Gall JG (1987) Transcription of the histone loci onlampbrush chromosomes of the newt Notophthalmus viridescens. Chromosoma 95: 396–402.
Bucci S, Giani L, Mancino G, Pellegrino M, Ragghianti M (2001) TAFII70 protein in Cajal bodies of the amphibian germinal vesicle. Genome 44: 1100–1103.
Bustin M (2001) Chromatin unfolding and activation by HMGN chromosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 26: 431–437.
Callan HG (1966) Chromosomes and nucleoli of the axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum. J Cell Sci 1: 85–108.
Callan HG (1982) The Croonian Lecture, 1981. Lampbrush chromosomes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 214: 417–448.
Callan HG (1986) Lampbrush Chromosomes. Berlin, Springer-Verlag.
Callan HG, Gall JG, Berg CA (1987) The lampbrush chromosomes of Xenopus laevis: preparation, identification, and distribution of 5S DNA sequences. Chromosoma 95: 236–250.
Callan HG, Gall JG, Murphy C (1988) The distribution of oocyte 5S, somatic 5S and 18S+28S rDNA sequences in the lampbrush chromosomes of Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 97: 43–54.
Callan HG, Gall JG, Murphy C (1991) Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of Xenopus lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 101: 245–251.
Casimir CM, Gates PB, Ross-Macdonald PB, Jackson JF, Patient RK, Brockes JP (1988) Structure and expression of a newt cardio-skeletal myosin gene. Implications for the C value paradox. J Mol Biol 202: 287–296.
Dahmus ME (1996) Reversible phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 271: 19009–19012.
Davidson EH (1986) Gene Activity in Early Development. 3rd edn. Orlando, Fl., Academic Press.
Diaz MO, Gall JG (1985) Giant readthrough transcription units at the histone loci on lampbrush chromosomes of the newt Notophthalmus. Chromosoma 92: 243–253.
Eckmann CR, Jantsch MF (1997) Xlrbpa, a double-stranded RNA-binding protein associated withr ibosomes and heterogeneous nuclear RNPs. J Cell Biol 138: 239–253.
Eckmann CR, Jantsch MF (1999) The RNA-editing enzyme ADAR1 is localized to the nascent ribonucleoprotein matrix on Xenopus lampbrushc hromosomes but specifically associates witha n atypical loop. J Cell Biol 144: 603–615.
Fischer D, Hock R, Scheer U (1993) DNA topoisomerase II is not detectable on lampbrush chromosomes but enriched in the amplified nucleoli of Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res 209: 255–260.
Flemming W (1882) Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung. Leipzig, F.C.W. Vogel.
Frey MR, Matera AG (1995) Coiled bodies contain U7 small nuclear RNA and associate withs pecific DNA sequences in interphase human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 5915–5919.
Gaginskaya E (1972) The nuclear structures of oocytes in adult birds. II. Protein bodies and karyosphere. Cytology 14: 568–578.
Gall JG (2000) Cajal bodies: the first 100 years. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16: 273–300.
Gall JG, Murphy C (1998) Assembly of lampbrush chromosomes from sperm chromatin. Mol Biol Cell 9: 733–747.
Gall JG, Stephenson EC, Erba HP, Diaz MO, Barsacchi-Pilone G (1981) Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrushch romosomes. Chromosoma 84: 159–171.
Gall JG, Diaz MO, Stephenson EC, Mahon KA (1983) The transcription unit of lampbrushc hromosomes. Symp Soc Dev Biol 41: 137–146.
Gall JG, Murphy C, Callan HG, Wu ZA (1991) Lampbrush chromosomes. Meth Cell Biol 36: 149–166.
Gall JG, Tsvetkov A, Wu Z, Murphy C (1995) Is the sphere organelle/coiled body a universal nuclear component? Dev Genet 16: 25–35.
Gall JG, Bellini M, Wu Z, Murphy C (1999) Assembly of the nuclear transcription and processing machinery: Cajal bodies (coiled bodies) and transcriptosomes. Mol Biol Cell 10: 4385–4402.
Grande MA, van der Kraan I, de Jong L, van Driel R (1997) Nuclear distribution of transcription factors in relation to sites of transcription and RNA polymerase II. J Cell Sci 110: 1781–1791.
Hirose Y, Manley JL (2000) RNA polymerase II and the integration of nuclear events. Genes Dev 14: 1415–1429.
Hock R, Moorman A, Fischer D, Scheer U (1993) Absence of somatic histone H1 in oocytes and preblastula embryos of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol 158: 510–522.
Hock R, Carl M, Lieb B, Gebauer D, Scheer U (1996) A monoclonal antibody against DNA topoisomerase II labels the axial granules of Pleurodeles lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 104: 358–366.
Jantsch MF, Gall JG (1992) Assembly and localization of the U1-specific snRNP C protein in the amphibian oocyte. J Cell Biol 119: 1037–1046.
Kezer J, Macgregor HC (1973) The nucleolar organizer of Plethodon cinereus cinereus (Green) II. The lampbrush nucleolar organizer. Chromosoma 42: 427–444.
Kurek R, Trapitz P, Bunemann H (1996) Strukturdifferenzierungen in Y-chromosom von Drosophila hydei: the unique morphology of the Y chromosomal lampbrush loops Threads results from ‘coaxial shells’ formed by different satellitespeci fic subregions within megabase-sized transcripts. Chromosome Res 4: 87–102.
Lacroix JC, Azzouz R, Boucher D, Abbadie C, Pyne CK, Charlemagne J (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to lampbrush chromosome antigens of Pleurodeles waltlii. Chromosoma 92: 69–80.
Ladomery M, Wade E, Sommerville J (1997) Xp54, the Xenopus homologue of human RNA helicase p54, is an integral component of stored mRNP particles in oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 965–973.
Leon P, Kezer J (1990) Loop size in newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 99: 83–86.
Macgregor HC (1980) Recent developments in the study of lampbrush chromosomes. Heredity 44: 3–35.
Mais C, Scheer U (2001) Molecular architecture of the amplified nucleoli of Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Sci 114: 709–718.
Marko JF, Siggia ED (1997) Polymer models of meiotic and mitotic chromosomes. Mol Biol Cell 8: 2217–2231.
Matera AG (1999) Nuclear bodies: multifaceted subdomains of the interchromatin space. Trends Cell Biol 9: 302–309.
Mayeda A, Zahler AM, Krainer AR, Roth MB (1992) Two members of a conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1301–1304.
Morgan GT, Macgregor HC, Colman A (1980) Multiple ribosomal gene sites revealed by in situ hybridization of Xenopus rDNA to Triturus lampbrushc hromosomes. Chromosoma 80: 309–330.
Morgan GT, Doyle O, Murphy C, Gall JG (2000) RNA polymerase II in Cajal bodies of amphibian oocytes. J Struct Biol 129: 258–268.
Myer VE, Young RA (1998) RNA polymerase II holoenzymes and subcomplexes. J Biol Chem 273: 27757–27760.
Olson MOJ, Dundr M, Szebeni A (2000) The nucleolus: an old factory withun expected capabilities. Trends Cell Biol 10: 189–196.
Patturajan M, Schulte RJ, Sefton BM et al. (1998) Growthrelated changes in phosphorylation of yeast RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 273: 4689–4694.
Pinol-Roma S, Swanson MS, Gall JG, Dreyfuss G (1989) A novel heterogeneous nuclear RNP protein with a unique distribution on nascent transcripts. J Cell Biol 109: 2575–2587.
Proudfoot N (2000) Connecting transcription to messenger RNA processing. Trends Biochem Sci 25: 290–293.
Pyne CK, Simon F, Loones MT, Geraud G, Bachmann M, Lacroix JC (1994) Localization of antigens PwA33 and La on lampbrushc hromosomes and on nucleoplasmic structures in the oocyte of the urodele Pleurodeles waltl: light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies. Chromosoma 103: 475–485.
Reugels AM, Kurek R, Lammermann U, Bunemann H (2000) Mega-introns in the dynein gene DhDhc7(Y) on the heterochromatic Y chromosome give rise to the giant threads loops in primary spermatocytes of Drosophila hydei. Genetics 154: 759–769.
Roth MB (1995) Spheres, coiled bodies and nuclear bodies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7: 325–328.
Roth MB, Gall JG (1987) Monoclonal antibodies that recognize transcription unit proteins on newt lampbrush chromosomes. J Cell Biol 105: 1047–1054.
Roth MB, Gall JG (1989) Targeting of a chromosomal protein to the nucleus and to lampbrush chromosome loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 1269–1272.
Roth MB, Murphy C, Gall JG (1990) A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a phosphorylated epitope stains lampbrush chromosome loops and small granules in the amphibian germinal vesicle. J Cell Biol 111: 2217–2223.
Roth MB, Zahler AM, Stolk JA (1991) A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol 115: 587–596.
Ryan J, Llinas AJ, White DA, Turner BM, Sommerville J (1999) Maternal histone deacetylase is accumulated in the nuclei of Xenopus oocytes as protein complexes with potential enzyme activity. J Cell Sci 112: 2441–2452.
Scheer U (1978) Changes of nucleosome frequency in nucleolar and non-nucleolar chromatin as a function of transcription: an electron microscopic study. Cell 13: 535–549.
Scheer U (1981) Identification of a novel class of tandemly repeated genes transcribed on lampbrushch romosomes of Pleurodeles waltlii. J Cell Biol 88: 599–603.
Scheer U (1982) A novel type of chromatin organization in lampbrushc hromosomes of Pleurodeles waltlii: visualization of clusters of tandemly repeated, very short transcriptional units. Biol Cell 44: 213–220.
Scheer U (1987) Structure of lampbrush chromosome loops during different states of transcriptional activity as visualised in the presence of physiological salt concentrations. Biol Cell 59: 33–41.
Schul W, van Driel R, de Jong L (1998) Coiled bodies and U2 snRNA genes adjacent to coiled bodies are enriched in factors required for snRNA transcription. Mol Biol Cell 9: 1025–1036.
Solovei I, Gaginskaya E, Allen T, Macgregor H (1992) A novel structure associated witha lampbrushc hromosome in the chicken, Gallus domesticus. J Cell Sci 101: 759–772.
Solovei I, Gaginskaya ER, Macgregor HC (1994) The arrangement and transcription of telomere DNA sequences at the ends of lampbrushc hromosomes of birds. Chromosome Res 2: 460–470.
Solovei I, Macgregor H, Gaginskaya E (1995) Specifically terminal clusters of telomere DNA sequences are transcribed from the C-rich strand on chicken lampbrush chromosomes. In: Proceedings of The Kew Chromosome Conference IV: pp. 323–330, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Press.
Solovei IV, Joffe BI, Gaginskaya ER, Macgregor HC (1996) Transcription of lampbrushc hromosomes of a centromerically localized highly repeated DNA in pigeon (Columba) relates to sequence arrangement. Chromosome Res 4: 588–603.
Sommerville J, Ladomery M (1996) Transcription and masking of mRNA in germ cells: involvement of Y-box proteins. Chromosoma 104: 469–478.
Sommerville J, Crichton C, Malcolm DB (1978) Immuno-fluorescent localization of transcriptional activity on lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 66: 99–114.
Sommerville J, Baird J, Turner BM (1993) Histone H4 acetylation and transcription in amphibian chromatin. J Cell Biol 120: 277–290.
Tuma RS, Roth MB (1999) Induction of coiled body-like structures in Xenopus oocytes by U7 snRNA. Chromosoma 108: 337–344.
Turner BM (1991) Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci 99: 13–20.
Uhlman F (2001) Chromosome condensation: Packaging the genome. Curr Biol 11: R384-R387.
Varley JM, Morgan GT (1978) Silver staining of the lampbrush chromosomes of Triturus cristatus carnifex. Chromosoma 67: 233–244.
Varley JM, Macgregor HC, Nardi I, Andrews C, Erba HP (1980) Cytological evidence of transcription of highly repeated DNA sequences during the lampbrush stage in Triturus cristatus carnifex. Chromosoma 80: 289–307.
Weber T, Schmidt E, Scheer U (1989) Mapping of transcription units on Xenopus laevis lampbrushc hromosomes by in situ hybridization with biotin-labeled cDNA probes. Eur J Cell Biol 50: 144–153.
Wu CH, Gall JG (1993) U7 small nuclear RNA in C snurposomes of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 6257–6259.
Wu CH, Murphy C, Gall JG (1996) The Sm binding site targets U7 snRNA to coiled bodies (spheres) of amphibian oocytes. RNA 2: 811–823.
Wu ZA, Murphy C, Callan HG, Gall JG (1991) Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol 113: 465–483.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, G.T. Lampbrush chromosomes and associated bodies: new insights into principles of nuclear structure and function. Chromosome Res 10, 177–200 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015227020652
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015227020652