Abstract
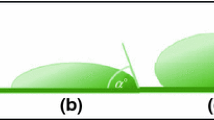
The micromorphologies of surfaces of several typical plant leaves were investigated by scanning electron microscopy(SEM). Different non-smooth surface characteristics were described and classified. The hydrophobicity and anti-adhesion of non-smooth leaf surfaces were quantitatively measured. Results show that the morphology of epidermal cells and the morphology and distribution density of epicuticular wax directly affect the hydrophobicity and anti-adhesion. The surface with uniformly distributed convex units shows the best anti-adhesion, and the surface with regularly arranged trellis units displays better anti-adhesion. In contrast, the surface with randomly distributed hair units performs relatively bad anti-adhesion. The hydrophobic models of papilla-ciliary and fold-setal non-smooth surfaces were set up to determine the impacts of geometric parameters on the hydrophobicity. This study may provide an insight into surface machine molding and apparent morphology design for biomimetics engineering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren L Q, Wang Y P, Li J Q, Tong J. Flexible unsmoothed cuticles of soil animals and their characteristics of reducing adhesion and resistance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43, 166–169.
Ren L Q, Yan B Z, Tong J. Experimental study on bionic non-smooth surface soil electroosmosis. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 1999, 8, 185–196.
Ren L Q, Deng S Q, Wang J C, Han Z W. Design principles of the non-smooth surface of bionic plow moldboard. Journal of Bionics Engineering, 2004, 1, 9–19.
Sun J R, Li J Q, Cheng H, Dai Z D, Ren L Q. Restudies on body surface of dung beetle and application of its bionics flexible technique. Journal of Bionics Engineering, 2004, 1, 53–60.
Lin Z Q, Meng R X, Zhou Z Z, Xu R X, Lin H. The micro-morphological characters of leaf epidermis of some species in Polygonum under. Journal of Anhui University Natural Science Edition, 1997, 21, 67–80, in Chinese.
Ma W L, Gao Y C. Studies on ultrastructure of achene epidermis and its taxonomic implications to Carex (cvperaceae). Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1998, 18, 66–71, in Chinese.
Shui Y M, Li Q R, Huang S H. Observation of leaf epidermis and its hair of Begonia from Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 1999, 21, 309–316, in Chinese.
Baker E A. Chemistry and morphology of plant epicuticular waxes. In: Cutler D F, Alvin K L, Price C E(eds). The Plant Cuticle, Academic Press, London, 1982, 139–166.
Barthlott W. Epicuticular wax ultrastructure and systematics. In: Behnke H D, Mabry T J (eds.) Evolution and Systematics of the Caryophyllales, Springer, Berlin, 1993, 75–86.
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C. Purity of the sacred lotus or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta, 1997, 202, 1–8.
Cassie A, Baxter S. Wettability of porous surface. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1994, 40, 546–551.
Wenzel R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1936, 28, 988–994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Lq., Wang, Sj., Tian, Xm. et al. Non-smooth morphologies of typical plant leaf surfaces and their anti-adhesion effects. J Bionic Eng 4, 33–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(07)60010-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(07)60010-9