Abstract
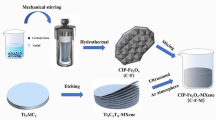
The signal crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) problems direly need to be resolved in the rapid development of modern microwave communication technology for a better working frequency and transmission power of electronic systems. Where the new absorbing materials such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)/titania (TiO2)/Ti2CTx and MoS2/Ti2CTx composites could meet the requirement of “thin, strong, light weight, and wide band” for excellent absorbing performance. In this work, a lighter Ti2CTx material was selected as the matrix, and MoS2 was in-situ grown on Ti2CTx matrix by traditional hydrothermal method and microwave solvothermal method. The fabricated composite exhibited synergic effect of two-dimensional heterostructural interface and double dielectric elements, where a small amount of TiO2 and a certain proportion of MoS2 jointly improve the impedance matching of the composite material. In here, the extreme reflection loss (RLmin) can reach − 54.70 dB (with a frequency of 7.59 GHz, 3.39 mm thickness), and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EABmax) can reach 4 GHz. Polyethylene glycol 200 was used as the solvent instead of water to make Ti2CTx less oxidized during the composite process, where the microwave heating would attain fast speed, short time, high efficiency, and uniform product. Since, the MoS2/Ti2CTx composite without oxidizing possessed a wider effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) at a thinner thickness, thus resulting in the excellent microwave absorption performance and confirming the validity and rationality of new microwave absorption materials.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z, Xu C, Ma C, Ren W, Cheng H (2013) Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 25(9):1296–1300
Yousefi N, Sun X, Lin X, Shen X, Jia J, Zhang B, Tang B, Chen M, Kim J (2014) Highly aligned graphene/polymer nanocomposites with excellent dielectric properties for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 26(31):5480–5487
Guo J, Chen Z, El-Bahy ZM, Liu H, Abo-Dief HM, Abdul W, Abualnaja KM, Alanazi AK, Zhang P, Huang M, Hu G, Zhu J (2022) Tunable negative dielectric properties of magnetic CoFe2O4/graphite-polypyrrole metacomposites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:899–906
Li F, Li Q, Kimura H, Xie X, Zhang X, Wu N, Sun X, Xu B, Algadi H, Pashameah RA, Alanazi AK, Alzahrani E, Li H, Du W, Guo Z, Hou C (2022) Morphology controllable urchin-shaped bimetallic nickel-cobalt oxide/carbon composites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J Mater Sci Technol 148(10):250–259
Guo Y, Wang D, Wang J, Tian Y, Liu H, Liu C, Shen C (2022) Hierarchical HCF@NC/Co derived from hollow Loofah fiber anchored with metal−organic frameworks for highly efficient microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:2038–2050
Pan D, Yang G, Abo-Dief HM, Dong J, Su F, Liu C, Li Y, Xu B, Murugadoss V, Naik N, El-Bahy SM, El-Bahy ZM, Huang M, Guo Z (2022) Vertically aligned silicon carbide nanowires/boron nitride cellulose aerogel networks enhanced thermal conductivity and electromagnetic absorbing of epoxy composites. Nano-Micro Lett 14:118–137
Yao F, Xie W, Ma C, Wang D, El-Bahy ZM, Helal HM, Liu H, Du A, Guo Z, Gu Z (2022) Superb electromagnetic shielding polymer nanocomposites filled with 3-dimensional p-phenylenediamine/aniline copolymer nanofibers@copper foam hybrid nanofillers. Compos Part B-Eng 245
Feng S, Zhai F, Su H, Sridhar D, Algadi H, Xu B, Pashameah RA, Alzahrani E, Abo-Dief HM, Ma Y, Li T, Guo Z (2022) Progress of metal organic frameworks-based composites in electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater Today Phys 30
Naguib M, Kurtoglu M, Presser V, Lu J, Niu J, Min H, Hultman L, Gogotsi Y, Barsoum MW (2011) Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv Mater 23(37):4248–4253
Wan L, Chua DHC, Sun H, Chen L, Wang K, Lu T, Pan L (2021) Construction of two-dimensional bimetal (Fe-Ti) oxide/carbon/ MXene architecture from titanium carbide MXene for ultrahigh rate lithium-ion storage. J Colloid Interf Sci 588:147–156
Miao B, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Cao Y, Bai Z, Chen L (2022) Highly enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of hetero structured Ti3C2/TiO2/rGO composites. Langmuir 38:15579–15591
Sivasankarapillai VS, Sharma TSK, Hwa KY, Wabaidur SM, Angaiah S, Dhanusuraman R (2022) MXene based sensing materials: current status and future perspectives. ES Energy Environ 15:4–14
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhou D (2016) Titanium carbide (MXene) nanosheets as promising microwave absorbers. Ceram Int 42(14):16412–16416
Han M, Yin X, Wu H, Hou Z, Chen L (2018) Ti3C2 MXenes with modified surface for high-performance electromagnetic absorption and shielding in the X-Band. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(32):21011–21019
Asia S, Alessia P, Liu Y, Dandekar K, Anasori B (2018) 2D titanium carbide (MXene) for wireless communication. Sci Adv 4(9)
Guo R, Fan Y, Wang L, Jiang W (2020) Core-rim structured carbide MXene/SiO2 nanoplates as an ultrathin microwave absorber. Carbon 169:214–224
Li X, Yin X, Han M, Song C, Sun X, Xu H, Cheng L, Zhang L (2017) A controllable heterogeneous structure and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Ti2CTX MXene. J Mater Chem C 5(30):7621–7628
Yang Y, Umrao S, Lai S, Lee S (2017) Large-area highly conductive transparent two-dimensional Ti2CTx film. J Phys Chem Lett 8(4):859–865
Li J, Du Y, Huo C, Wang S, Chong C (2015) Thermal stability of two-dimensional Ti2C nanosheets. Ceram Int 41(2):2631–2635
Rakhi RB, Ahmed B, Hedhil MN, Anjum DH, Alshareef HN (2015) Effect of post etch annealing gas composition on the structural and electro-chemical properties of Ti2CTx MXene electrodes for super capacitor applications. Chem Mater 27(15):5314–5323
Li X, Wen C, Yang L, Zhang R, Li Y, Che R et al (2021) Enhanced visualizing charge distribution of 2D/2D MXene/MoS2 heterostructure for excellent microwave absorption performance. J Alloy Compd 869:159365
Wang J, Liu L, Jiao S, Ma K, Lv J, Yang J (2020) Hierarchical carbon Fiber@MXene@MoS2 core‐sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave Absorptio. Adv Funct Mater 30(45):2002595.1–2002595.10
Liu Z, Cui Y, Li Q, Zhang Q, Zhang B (2022) Fabrication of folded MXene/MoS2 composite microspheres with optimal composition and their microwave absorbing properties. J Colloid Interf Sci 607:633–644
Fan B, Muhammad T, Chen Q, Wei F, Du H, Ouyang B, Kan E, Chen Y, Zhao B, Zhang R (2022) Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of 2D/2D MoS2/Ti3C2Tx heterostructure for enhanced microwave absorbing performance. J Alloy Compd 923(25)
Mondal K, Ghosh P (2019) Exfoliation of Ti2C and Ti3C2 Mxenes from bulk trigonal phases of titanium carbide: a theoretical prediction. Solid State Commun 299:113657
Yu H, Xu K, Zhang Z, Weng J, Wu J (2021) Oxygen functionalization-induced crossover in the tensile properties of the thinnest 2D Ti2C MXene. Mater Chem C 9(7):2416–2425
Liu N, GuoY YX, Lin H, Yang L, Shi Z, Zhong Z, Wang S, Tang Y, Gao Q (2015) Microwave-assisted reactant-protecting strategy toward efficient MoS2 electrocatalysts in hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23741–23749
Zhou J, Zhang, G, Luo, J, Hu Y, Hao G, Guo H, Guo F, Wang S, Jiang W (2021) A MOFs-derived 3D superstructure nanocomposite as excellent microwave absorber. Chem Eng J 426
Li Q, Zhong B, Zhang W, Jia Z, Jia D, Qin S, Wang J, Razal JM, Wang X (2019) Ti3C2 MXene as A new nanofiller for robust and conductive elastomer composites. Nanoscale 11:14712–14719
Wang H, Zhao R, Hu H, Fan X, Zhang D (2020) Wang D (2020) 0D/2D Heterojunctions of Ti3C2 MXene QDs/SiC as an efficient and robust photocatalyst for boosting the visible photocatalytic NO pollutant removal ability. Acs Appl Mater 12:40176–40185
Kim SJ, Koh HJ, Ren CE, Kwon O, Maleski K, Cho SY, Anasori B, Kim CK, Choi YK, Kim J, Gogotsi Y, Jung HT (2018) Ti3C2Tx MXene gas sensors with ultrahigh signal-to-noise ratio. ACS Nano 12:986–993
Ahmed R, Si R, Rehman SU, Yu Y, Li, Q, Wang C (2021) High dielectric constant and low temperature ferroelectric-phase-transition in Ca, Pb co-doped BiFeO3. Results Phys 20
Ahmed R, Wang J, Si R, Rehman SU, Li T, Bi H, Yu Y, Li Q, Li Y, Huang S, Guo Y, Wang C (2021) Jahn-Teller assisted polaronic electron hopping in LiCuNb3O9. Eur Ceram Soc 41:2625–2632
Aslam MA, Ding W, Rehman, SU, Hassan A, Bian YC, Liu, Q, Sheng Z (2021) Low cost 3D bio-carbon foams obtained from wheat straw with broadened bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Appl Surf Sci 543
Liu Y, Zhang S, Su X, Xu J, Li Y (2020) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2 MXene powders decorated with Ni particles. J Mater Sci 55:10339–10350
Th A, Qi L, Zhang Y, Zhu W, Yu K, Wang S, Xu Q, Liang S, Wang L (2020) Near-infrared light-driven photofixation of nitrogen over Ti3C2Tx/TiO2 hybrid structures with superior activity and stability - ScienceDirect. Appl Catal B 273
Wu N, Zhao B, Chen X, Hou C, Huang M, Alhadhrami A, Mersal GAM, Ibrahim MM, Tian J (2022) Dielectric properties and electromagnetic simulation of molybdenum disulfide and ferric oxide-modified Ti3C2TX MXene hetero-structure for potential microwave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1548–1556
Zhang Z, Liu M, Ibrahim MM, Wu K, Li Y, Mersal GAM, Azab IHE, El-Bahy SM, Huang M, Jiang Y, Liang G, Xie P, Liu C (2022) Flexible polystyrene/graphene composites with epsilon-near-zero properties. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1054–1066
Xie P, Shi Z, Feng M, Sun K, Liu Y, Yan K, Liu C, Moussa TAA, Huang M, Meng S, Liang G, Hou H, Fan R, Guo Z (2022) Recent advances in radio-frequency negative dielectric metamaterials by designing heterogeneous composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:679–695
Han M, Yin X, Kong L, Li M, Duan W, Zhang L, Cheng L (2014) Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater 2:16403–16409
Liu Z, Wu C, Wang Y, Xian G, Zhu Z, Xie N, Wang Y, Liu Y, Kong L (2022) MXene/CoS heterostructures self-assembled through electrostatic interaction as superior microwave absorber. J Alloy Compd 900
Wang P, Cheng L, Zhang L (2017) One-dimensional carbon/SiC nanocomposites with tunable dielectric and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Carbon 125:207–220
Chen Y, Gao P, Zhu C, Wang R, Wang L, Cao M, Fang X (2009) Synthesis, magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous Fe3O4/Fe/SiO2 core/shell nanorods. Appl Phys 106
Zhang X, Dong X, Huang H, Liu Y, Wang W, Zhu, X, Lv, B, Lei J, Lee C (2006) Microwave absorption properties of the carbon-coated nickel nano capsules. Appl Phys Lett 89
Zhao B, Guo X, Zhao W, Deng J, Shao G, Fan B, Bai Z, Zhang R (2016) Yolk-Shell Ni@SnO2 Composites with a designable interspace to improve electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater 8:28917–28925
Hassan A, Aslam MA, Bilal M, Khan MS, Rehman SU, Ma K, Wang J, Sheng Z (2021) Modulating dielectric loss of MoS2@Ti3C2Tx Nanoarchitectures for electromagnetic wave absorption with radar cross section reduction performance verified through simulations. Ceram Int 47:20706–20716
Cao M, Cai Y, He P, Shu J, Cao W, Yuan J (2019) 2D MXenes: electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 359:1265–1302
Ning M, Lu M, Li J (2015) Two-dimensional nanosheets of MoS2: a promising material with high dielectric properties and microwave absorption performance[J]. Nanoscale 7:15734
Wang Y, Chen D, Yin X, Xu P, Wu F, He M (2015) Hybrid of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide: a lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl Mater 7:26226–26234
Li X, Yin X, Han M, Song C, Xu H, Hou Z, Zhang L, Cheng L (2017) Ti3C2 MXenes modified with in situ grown carbon nanotubes for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. RSC 5:4068–4074
Liu P, Yao Z, Ng V, Zhou J, Kong L, Yue K (2018) Facile synthesis of ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles on MXenes for high microwave absorption performance. Compos Part A-Appl S 115:371–382
Wang H, Ma H (2019) The electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of MoS2 modified Ti3C2Tx nanocomposites. J Mater Sci-Mater EL 30:15250–15256
Yang J, Wang J, Li H, Wu Z, Xing Y, Chen Y, Liu L (2022) MoS2/MXene aerogel with conformal heterogeneous interfaces tailored by atomic layer deposition for tunable microwave absorption. Adv Sci 9
Xu H, Yin X, Li X, Li M, Zhang L, Cheng L (2019) Thermal stability and dielectric properties of 2D Ti2C MXenes via annealing under a gas mixture of Ar and H2 atmosphere. Funct Compos Struct 1(1)
Zhang S, Cheng B, Jia X, Zhao Z, Jin X, Zhao Z, Wu G (2022) The art of framework construction: hollow-structured materials toward high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:1658–1698
Funding
The research was supported by the Key Scientific Research projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (21A430009), Henan Provincial Science and Technology R&D Plan Joint Fund (Application Research) Project (222103810045), and Natural science Project of Zhengzhou Science and Technology Bureau (Special project of collaborative innovation) (22ZZRDZX02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Baoji Miao, Yange Cao, and Qingsong Zhu conceived the idea, designed the experiments, and wrote the paper. Muhammad Asif Nawaz, Jose Antonio Ordiozola, Tomas Ramirez Reina, and Zhiming Bai planned and performed the experiments and collected and analyzed the data. Junna Ren and Fengchun Wei helped with characterization of the materials and discussed data. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, B., Cao, Y., Zhu, Q. et al. Scalable synthesis of 2D Ti2CTx MXene and molybdenum disulfide composites with excellent microwave absorbing performance. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6, 61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-023-00643-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-023-00643-2