Abstract
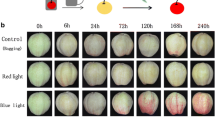
The rare ever-red crabapple (Malus spp.) leaves have importantly ornamental and medicinal traits, and their coloration is regulated by light conditions. However, little is known about the molecular mechanism of the red color formation via anthocyanin biosynthesis mediated by upstream regulators of light signaling under different light conditions. We selected the ever-red leaf cultivar, M.cv. ‘Royalty,’ to investigate the expression profile of various factors under dark conditions. The factors studied include the photoreceptors McphyA and McphyB, the ubiquitin E3 ligase McCOP1, the transcription factor McMYB10, the MBW complex, the main structural genes in anthocyanin biosynthesis, and the photomorphogenesis transcription factors McbZIP and McHY5. Our results indicated that under dark conditions McCOP1 expression was up-regulated, while the expression of other factors studied was down-regulated, leading to decreased expression of the structural genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and reduction in anthocyanin content. Interestingly, when McCOP1 was silenced in the leaves, the expression of McMYB10, McbHLH, McWD40, McbZIP, and McHY5 was markedly up-regulated, resulting in the up-regulation of the structural genes including McF3H, McFLS, McDFR, and McUFGT and the subsequent accumulation of anthocyanins compared with leaves treated with empty vector. These data demonstrate that darkness negatively regulates the coloration of the ever-red leaves by regulating McCOP1 expression, further inhibiting the expression of McMYB10 and the structural genes in anthocyanin biosynthesis. These results may provide important insight into the breeding of color-leafed plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan AC, Hellens RP, Laing WA (2008) MYB transcription factors that colour our fruit. Trends Plant Sci 13:99–102
Ang LH, Deng XW (1994) Regulatory hierarchy of photomorphogenic loci: allele-specific and light-dependent interaction between the HY5 and COPl loci. Plant Cell 6:613–628
Casal JJ, Candia AN, Sellaro R (2014) Light perception and signalling by phytochrome A. J Exp Bot 65:2835–2845
Cavallini E, Matus JT, Finezzo L, Zenoni S, Loyola R, Guzzo F, Schlechter R, Ageorges A, Arce-Johnson P, Tornielli GB (2015) The phenylpropanoid pathway is controlled at different branches by a set of R2R3-MYB C2 repressors in grapevine. Plant Physiol 167:1448–1470
Chen S, Xiang Y, Deng J, Liu Y, Li S (2013) Simultaneous analysis of anthocyanins and non-anthocyanins flavonoid in various tissues of different lotus (nelumbo) cultivars by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n). PLoS One 8:e62291
Cocciolone SM, Cone KC (1993) Pl-Bh, an anthocyanins regulatory gene of maize that leads to variegated pigmentation. Genetics 135:575–588
Davies KM (2015) Swapping one red pigment for another. Nat Genet 47:5–6
Debrieux D, Trevisan M, Fankhauser C (2013) Conditional involvement of CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 in the degradation of phytochrome A. Plant Physiol 161:2136–2145
Deluc L, Barrieu F, Marchive C, Lauvergeat V, Decendit A, Richard T, Carde JP, Merillon JM, Hamdi S (2006) Characterization of a grapevine R2R3-MYB transcription factor that regulates the phenylpropanoid pathway. Plant Physiol 140:499–511
Deng XW, Caspar T, Quail PH (1991) COPl: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 5:1172–1182
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15:573–581
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty AS, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49:414–427
Feng S, Wang Y, Yang S, Xu Y, Chen X (2010) Anthocyanins biosynthesis in pears is regulated by a R2R3-MYB transcription factor PyMYB10. Planta 232:245–255
Hatlestad GJ, Akhavan NA, Sunnadeniya RM, Elam L, Cargile S, Hembd A, Gonzalez A, McGrath JM, Lloyd AM (2015) The beet Y locus encodes an anthocyanins MYB-like protein that activates the betalain red pigment pathway. Nat Genet 47:92–96
Hoecker U, Xu Y, Quail PH (1998) Spa1: a new genetic locus involved in phytochrome a–specific signal transduction. Plant Cell 10:19–33
Holm M, Ma LG, Qu LJ, Deng XW (2002) Two interacting bZIP proteins are direct targets of COP1-mediated control of light-dependent gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 16:1247–1259
Hsieh HL, Okamoto H (2014) Molecular interaction of jasmonate and phytochrome a signalling. J Exp Bot 65:2847–2857
Jang IC, Yang JY, Hak SS, Chua NH (2005) Hfr1 is targeted by COP1 E3 ligase for post-translational proteolysis during phytochrome a signaling. Genes Dev 19:593–602
Jang IC, YangSW Yang JY, Chua NH (2007) Independent and interdependent functions of LAF1 and HFR1 in phytochrome a signaling. Genes Dev 21:2100–2111
Justin OB, Xia YJ, Jack B, Richard AD, Chris L (2000) Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 12:2383–2393
Kwok SF, Solano R, Tsuge T, Chamovitz DA, Ecker JR, Matsui M, Deng XW (1998) Arabidopsis homologs of a C-jun coactivator are present both in monomeric form and in the COP9 complex, and their abundance is differentially affected by the pleiotropic cop/det/fus mutations. Plant Cell 10:1779–1790
Laubinger S, Fittinghoff K, Hoecker U (2004) The SPA quartet: a family of WD-repeat proteins with a central role in suppression of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2293–2306
Li YY, Mao K, Zhao C, Zhao XY, Zhang HL, Shu HR, Hao YJ (2012) MdCOP1 Ubiquitin E3 ligases interact with MdMYB1 to regulate light-induced anthocyanins biosynthesis and red fruit coloration in apple. Plant Physiol 160:1011–1022
Llorente B, D’Andrea L, Ruiz-Sola MA, Botterweg E, Pulido P, Andilla J, Loza-Alvarez P, Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2016) Tomato fruit carotenoid biosynthesis is adjusted to actual ripening progression by a light dependent mechanism. Plant J 85:107–119
Luo Q, Lian HL, He SB, Li L, Jia KP, Yang HQ (2014) COP1 and Phyb physically interact with PIL1 to regulate its stability and photomorphogenic development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:2441–2456
McNellis TW, Arnim AG, Deng XW (1994) Overexpression of Arabidopsis COP1 results in partial suppression of light-mediated development: evidence for a light-inactivable repressor of photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 6:1391–1400
Meng LS, Liu A (2015) Light signaling induces anthocyanins biosynthesis via AN3 mediated COP1 expression. Plant Signal Behav. doi:10.1080/15592324.2014.1001223
Osterlund MT, Wei N, Deng XW (2000) The roles of photoreceptor systems and the COP1-Targeted destabilization of HY5 in light control of Arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Physiol 124:1520–1524
Pacin M, Legris M, Casal JJ (2014) Rapid decline in nuclear CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 abundance anticipates the stabilization of its target elongated hypocotyl5 in the light. Plant Physiol 164:1134–1138
Pacín M, Legris M, Casal JJ (2013) COP1 Re-accumulates in the nucleus under shade. Plant J 75:631–641
Pinto E, Ferreira IM (2015) Changes in the content of free and conjugated polyamines during Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) growth. J Agric Food Chem 63:440–446
PokhilkoA RamosJA, Holtan H, Maszle DR, Khanna R, Millar AJ (2011) Ubiquitin ligase switch in plant photomorphogenesis: a hypothesis. J Theor Biol 270:31–41
Rahim MA, Busatto N, Trainotti L (2014) Regulation of anthocyanins biosynthesis in peach fruits. Planta 240:913–929
Seo HS, Etsuko W, Satoru T, Akira N, Chua NH (2004) Photoreceptor ubiquitination by COP1 E3 ligase desensitizes phytochrome a signaling. Genes Dev 18:617–622
Shen HX, Zhang J, Yao YC, Tian J, Song TT, Geng J, Gao JP (2012) Isolation and expression of McF3H gene in the leaves of crabapple. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1353–1361
Shi H, Zhong S, Mo X, Liu N, Nezames CD, Deng XW (2013) HFR1 sequesters PIF1 to govern the transcriptional network underlying light-initiated seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3770–3784
Shinomiya R, Fujishima H, Muramoto K, Shiraishi M (2015) Impact of temperature and sunlight on the skin coloration of the ‘Kyoho’ table grape. Sci Hort 193:77–83
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50:660–677
Telias A, Lin-Wang K, Stevenson DE, Cooney JM, Hellens RP, Allan AC, Hoover EE, Bradeen JM (2011) Apple skin patterning is associated with differential expression of MYB10. BMC Plant Biol 11:93
Wang JG, Chen CH, Chien CT, Hsieh HL (2011) FAR-RED INSENSITIVE219 modulates CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 activity via physical interaction to regulate hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:631–646
Xu D, Lin F, Jiang Y, Huang X, Li J, Ling J, Hettiarachchi C, Tellgren-Roth C, Holm M, Deng XW (2014a) The RING-Finger E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 SUPPRESSOR1 negatively regulates COP1 abundance in maintaining COP1 homeostasis in dark-grown Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 26:1981–1991
Xu W, Grain D, Bobet S, Le Gourrierec J, Thévenin J, Kelemen Z, Lepiniec L, Dubos C (2014b) Complexity and robustness of the flavonoid transcriptional regulatory network revealed by comprehensive analyses of myb-bhlh-wdr complexes and their targets in Arabidopsis seed. New Phytol 202:132–144
Xu X, Paik I, Zhu L, Bu Q, Huang X, Deng XW, Huq E (2014c) PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR1 enhances the E3 ligase activity of CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 to synergistically repress photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:1992–2006
Yamamoto YY, Matsui M, Ang LH, Deng XW (1998) Role of a Cop1 interactive protein in mediating light-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1083–1094
Yao JL, Cohen D, Atkinson R, Richardson K, Morris B (1995) Regeneration of transgenic plants from the commercial apple cultivar Royal Gala. Plant Cell Rep 14:407–412
Yu J, Rubio V, Lee N, Bai S, Lee S, Kim S, Liu L, Zhang Y, Irigoyen ML, Sullivan JA, Zhang Y, Lee I, Xie Q, Paek N, Deng XW (2008) COP1 and Elf3 control circadian function and photoperiodic flowering by regulating Gi stability. Mol Cell 32:617–630
Yuan Y, Sagawa JM, Frost L, Vela JP, Bradshaw HD (2014) Transcriptional control of floral anthocyanins pigmentation in Monkeyflowers (Mimulus). New Phytol 204:1013–1027
Zhang XJ, Wang LX, Liu YL, Chen XX, Yang YZ, Zhao ZY (2013) Differential gene expression analysis of ‘Granny Smith’ apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) during fruit skin coloration. S Afr J Bot 88:125–131
Acknowledgments
We thank the Beijing Key Laboratory for Agricultural Application and New Technique and the Beijing Nursery Engineering Research Center for Fruit Crops for providing basic experimental conditions. We are grateful to all of the technicians at the BUA Crabapple Germplasm Resource Garden. Financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31200213), the Project of Construction of Innovative Teams and Teacher Career Development for Universities and Colleges Under Beijing Municipality (IDHT20140509), the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education Science and Technology Promotion Plan (PXM2014-014207-000081), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program) (2011AA100204), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Project of Beijing Municipal Commission of Rural Affairs (No. 20150121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yanfen Lu, Suxiao Hao and Na Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Hao, S., Liu, N. et al. Light affects anthocyanin biosynthesis via transcriptional regulation of COP1 in the ever-red leaves of crabapple M.cv. ‘Royalty’. Braz. J. Bot 39, 659–667 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0277-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0277-8