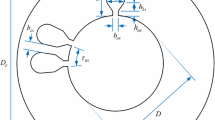
Abstract
The aim of this paper was the design of a three-phase induction motor stator, optimizing its production cost by formulating and solving geometric variables. The stator is a part of the motor and its main function is to generate a magnetic field, thus an interesting research theme, since it is related to the production cost of electric motors. Optimizing techniques are used when the structure of the problem is complex. This generally happens when there is no straightforward procedure. Therefore, optimization techniques can be used in search of a better solution for the problem. These techniques are applied in minimizing the cost, volume and copper loss of the asynchronous machine stator. To solve these problems, the MODE algorithm is used (multiobjective optimization differential evolution) and the outcome is compared to the NSGA II algorithm (non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II).









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ac :
-
Specific electric charge (A/m)
- \(A_\mathrm{c} \) :
-
Area of the stator’s core \((\hbox {mm}^{2})\)
- \(A_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Conductor’s section area \((\hbox {mm}^{2})\)
- \(B_\mathrm{av}\) :
-
Air-gap average flux density (T)
- \(B_\mathrm{c} \) :
-
Flux density in the core (T)
- \(B_\mathrm{cu}\) :
-
Copper density \((8{,}900\,\hbox {kg/m}^{3})\)
- \(B_\mathrm{fe}\) :
-
Iron density \((7{,}600\,\hbox {kg/m}^{3})\)
- \(b_\mathrm{t}^{\prime }\) :
-
Width of the teeth (m)
- \(b_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Width of the stator’s slot (m)
- C :
-
The output coefficient
- \(\cos \varphi \) :
-
Power factor
- \(\textit{Cost}_1\) :
-
Total cost of the weight of copper (\(\hbox {US}\)$)
- \(\textit{Cost}_2\) :
-
Total cost of the weight of iron (\(\hbox {US}\)$)
- \(\textit{Cost}_3 \) :
-
Total cost of the weight of enameled copper (\(\hbox {US}\)$)
- \(\textit{Cost}_4 \) :
-
Total cost of the weight of silicon steel (\(\hbox {US}\)$)
- D :
-
Internal diameter of the stator (m)
- \(d_\mathrm{cs}\) :
-
Depth of the core (m)
- \(D_0 \) :
-
External diameter of the stator (m)
- \(h_\mathrm{ss}\) :
-
Stator slot height (m)
- \(I_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Phase current of the stator (A)
- \(J_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Density current on the stator’s winding \((\hbox {A/mm}^{2})\)
- \(k_\mathrm{w} \) :
-
Winding factor of the stator
- \(k_1 \) :
-
Price of copper per kilo \((\hbox {US}\$/\hbox {kg})\)
- \(k_2\) :
-
Price of iron per kilo \((\hbox {US}\$/\hbox {kg})\)
- \(k_3 \) :
-
Price of enameled copper per kilo \((\hbox {US}\$ /\hbox {kg})\)
- \(k_4\) :
-
Price of silicon steel per kilo \((\hbox {US}\$ /\hbox {kg})\)
- L :
-
Length of the machine (m)
- \(L_\mathrm{i} \) :
-
Actual length of the iron (m)
- \(L_\mathrm{mt}\) :
-
Average turn length (m)
- N :
-
Speed (rpm)
- \(N_\mathrm{ph}\) :
-
Number of turns per phase
- P :
-
Poles
- \(P_\mathrm{cu}\) :
-
Copper loss (W)
- Q :
-
Output equation of the motor (kW)
- \(r_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Winding resistance \((\Omega )\)
- \(S_\mathrm{s} \) :
-
Number of slots in the stator
- \(T_\mathrm{ph}\) :
-
Number of conductors per slot
- \(V_\mathrm{c} \) :
-
Volume of iron in the yoke \((\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(V_\mathrm{cu}\) :
-
Copper volume \((\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(V_\mathrm{d} \) :
-
Volume of iron in the teeth \((\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(V_\mathrm{e} \) :
-
Total volume of the stator \((\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(V_\mathrm{i} \) :
-
Isolation volume \((\hbox {m}^{3})\)
- \(\textit{Weight}_\mathrm{c} \) :
-
Iron weight in the yoke (kg)
- \(\textit{Weight}_\mathrm{cu}\) :
-
Copper weight (kg)
- \(\textit{Weight}_\mathrm{d} \) :
-
Iron weight in the teeth (kg)
- \(\eta \) :
-
Efficiency \((\%)\)
- \(\tau _\mathrm{p} \) :
-
Pole step (m)
- \(\tau _\mathrm{s}^{\prime }\) :
-
Slot step in 1/3 of the height (m)
References
Agarwal, R. K. (2000). Principles of electrical machine design. Katson Books.
Bouzidi, I., Bianchi, N., & Masmoudi, A. (2014). An approach to the sizing of electric motors devoted to aerospace propulsion systems. COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 33(5), 1527–1540.
Carraro, E., Degano, M., Morandin, M., & Bianchi, N. (2014). PM synchronous machine comparison for light electric vehicles. In IEEE international electric vehicle conference (IEVC) (pp. 1–8).
Castro, R. E. (2001). Optimization of structures with multi-objective through genetic algorithms. Tese de Doutorado: Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (In Portuguese).
Cossalter, V., Doria, A., Ferrari, M., Giolo, E., Bianchi, N., Martignoni, C., et al. (2015). Design of a hybrid propulsion system for a three wheeled bicycle. COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 34(1), 189–209.
Cui, G., Liu, L., Li, S., Yang, P., Yang, F., Chen, L., et al. (2014). Optimization design of high efficiency variable frequency induction motor based on finite element analysis. In 17th international conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS) (pp. 701–705).
Deb, K. (2001). Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. Chichester: Wiley.
Fitzgerald, A. E., Kingsley, C, Jr, & Umans, S. D. (2013). Electric machinery. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Hu, X., Coello, C. A. C., & Huang, Z. (2005). A new multi-objective evolutionary algorithm: Neighbourhood exploring evolution strategy. Engineering Optimization, 37(4), 351–379.
Jara, W., Tapia, J. A., Bianchi, N., Pyrhonen, J., & Wallace, R. (2014). Procedure for fast electromagnetic design of axial flux permanent magnet machines. In International conference on electrical machines (ICEM) (pp. 1396–1402).
Kakosimos, P. E., Sarigiannidis, A. G., Beniakar, M. E., Kladas, A. G., & Gerada, C. (2014). Induction motors versus permanent-magnet actuators for aerospace applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 61(8), 4315–4325.
Kimpara, M. L. M., Godoy, R. B., Ribeiro, P. E. J., da Silva, L. E. B., Fahimi, B., & Pinto, J. O. P. (2014). A new synchronous machine modeling using the field reconstruction method. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 25(4), 481–492.
Krause, P. C., et al. (2013). Analysis of electric machinery and drive systems (Vol. 75). Chichester: Wiley.
Krishnan, R. (2001). Electric motor drives: Modeling, analysis, and control. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Lobato, F. S., & Steffen Jr., V. (2007). Engineering system design with multi-objective differential evolution. In Proceedings of the 19th international congress of mechanical engineering.
Malagoli, J. A., Camacho, J. R., & Ferreira da Luz, M. V. (2014a). Three-phase induction machine rotor design using differential evolution algorithm. In Brazilian symposium on microwave and optoelectronic and Brazilian congress electromagnetism (pp. 573–578), Brazil (In Portuguese).
Malagoli, J. A., Lobato, F. S., & Camacho, J. R. (2014b). Multiobjective optimization applied the wound rotor design of three-phase induction motor. In National meeting of computational modeling and meeting materials science and technology (pp. 1–10), Brazil (In Portuguese).
Malagoli, J. A., Lobato, F. S., Camacho, J. R., & Ferreira da Luz, M. V. (2014c). Three-phase induction machine stator design using differential evolution algorithm. In Computational mechanics symposium and state meeting of computational modeling (pp. 1–13), Brazil (In Portuguese).
Malagoli, J. A., Lobato, F. S., Camacho, J. R., Ferreira da Luz, M. V., & Ferreira, J. H. I. (2014d). Multiobjective optimization applied to the three-phase induction motor stator design. In National congress of applied mathematics for industry (pp. 1–9), Brazil (In Portuguese).
Mittle, V. N., & Mittal, A. (2009). Design of electrical machines. Delhi: Standard Publishers Distributors.
Mohammadi, H. R., & Akhavan, A. (2014). Parameter estimation of three-phase induction motor using hybrid of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization. Journal of Engineering, 2014, 1–6.
Pereira, L. A., Haffner, S., Pereira, L. F., Benvenuti, R. A., & da Rosa, R. S. (2015). Parameterized model and performance of five-phase induction machines including losses and saturation. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 26(3), 255–271.
Phuangmalai, W., Konghirun, M., & Chayopitak, N. (2013). A design study of 4/2 switched reluctance motor using particle swarm optimization. ECTI: Transactions on electrical engineering, electronics, and communications (Vol. 11, n1), February.
Raghuram, A., & Shashikala, V. (2013). Design and optimization of three phase induction motor using genetic algorithm. International Journal of Advances in Computer Science and Technology, 2(6), 70–76.
Ranjan, S., & Mishra, S. K. (2015). Multi-objective design optimization of three-phase induction motor using NSGA-II algorithm. In L. C. Jain, H. S. Behera, J. K. Mandal, & D. P. Mohapatra (Eds.), Computational intelligence in data mining (Vol. 2, pp. 1–8). Springer India.
Ramezanian, H., Balochian, S., & Zare, A. (2013). Design of optimal fractional-order PID controllers using particle swarm optimization algorithm for automatic voltage regulator (AVR) system. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 24(5), 601–611.
Rampazzo, P. C. B., Yamakami, A., & de Frana, F. O. (2015). Evolutionary approaches for the multi-objective reservoir operation problem. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 26(3), 297–306.
Shiri, A., & Shoulaie, A. (2012). Design optimization and analysis of single-sided linear induction motor, considering all phenomena. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 27(2), 516–525.
Storn, R., Price, K., & Lampinen, J. A. (2005). Differential evolution-A practical approach to global optimization. Natural computing series. Berlin: Springer.
Terzic, M. V., Mihic, D. S., & Vukosavic, S. N. (2014). Design of high-speed, low-inertia induction machines with drag-cup rotor. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 29(1), 169–177.
Upadhyay, K. G. (2008). Design of electrical machines. New Delhi: New Age International Publishers.
www.infomine.com/investment/metal-prices. Quotation of prices copper and iron. Accessed in September (2015).
Yasodha, S., Ramesh, K., & Ponmurugan, P. (2012). Evolutionary multiobjetive optimization algorithms for induction motor design a study. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering, 2(11), 627-633.
Acknowledgments
The author Juliana Almansa Malagoli is grateful to CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) for the financial support for this research and the Professor Dr. Fran Sérgio Lobato for help with differential evolution algorithms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malagoli, J.A., Camacho, J.R. & da Luz, M.V.F. Optimal Design Variables to Minimize the Cost of Materials the Stator of Asynchronous Machine. J Control Autom Electr Syst 27, 157–168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0227-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-016-0227-5