Abstract
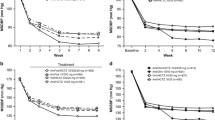
Lowering blood pressure (BP) in patients with high blood pressure reduces cardiovascular risk. Studies support health benefits when BP goals are achieved earlier in the course of treatment. Many patients require combination therapy to achieve BP goals; initial use of combination therapy may improve earlier BP goal attainment. This analysis reports the results of a search of the Boehringer Ingelheim clinical trial database for randomized, double-blind studies of telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide (T/H) combination therapy compared with blood pressure monotherapies. Nine studies were identified. This report examined six separate analyses of these nine studies (three analyses of individual trials; three analyses for which two trials each were pooled). The focus of this report is the BP effects of combination T/H therapy compared with respective monotherapies at the earliest available time points (Weeks 1, 2, 3 and/or 4). These analyses included a total of 5,358 patients. During these earlier time periods, combination T/H reduced systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP) significantly more than placebo or respective monotherapies in most treatment comparisons for patients initiated on monotherapy. Combination T/H also allowed significantly more patients to achieve BP (<140/90 mmHg), SBP (<140 mmHg), and DBP (<90 mmHg) goal attainment rates compared with placebo (p < 0.0002), and numerically higher compared with T or H monotherapy. In patients uncontrolled by monotherapy, combination T/H significantly reduced SBP/DBP more than monotherapy (p < 0.0001). Similarly, BP, SBP and DBP goal attainment rates were significantly higher with combination T/H therapy (p < 0.0022). Reported adverse events with T/H therapy were generally similar to monotherapy, and placebo. In summary, the six separate analyses of nine different trials demonstrated that T/H significantly lowered BP as early as 1–4 weeks after initiation of therapy, with greater BP lowering, and greater BP goal attainment than with monotherapies or placebo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–357.
Dahlof B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:895–906.
Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M, et al. Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomised trial. Lancet. 2004;363:2022–31.
Weber MA, Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, et al. Blood pressure dependent and independent effects of antihypertensive treatment on clinical events in the VALUE Trial. Lancet. 2004;363:2049–51.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–52.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Hypertension: Clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. CG127 August 2011. NICE website. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG127.
Gradman AH, Basile JN, Carter BL, et al. Combination therapy in hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011;13:146–54.
Mallat SG. What is a preferred angiotensin II receptor blocker-based combination therapy for blood pressure control in hypertensive patients with diabetic and non-diabetic renal impairment? Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012;11:32.
Kjeldsen SE, Schmieder RE, Unger T, et al. Telmisartan and hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy for the treatment of hypertension. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26:879–87.
Schumacher H, Mancia G. The safety profile of telmisartan as monotherapy or combined with hydrochlorothiazide: a retrospective analysis of 50 studies. Blood Press Suppl. 2008;1:32–40.
Kjeldsen S, Mancia G, Schmieder R, et al. An update on telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide combinations for the management of hypertensive patients with additional cardiovascular risk factors. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2013;11:673–82.
Neldam S, Dahlof B, Oigman W, et al. Early combination therapy with telmisartan plus amlodipine for rapid achievement of blood pressure goals. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67:843–52.
Egan BM, Bandyopadhyay D, Shaftman SR, et al. Initial monotherapy and combination therapy and hypertension control the first year. Hypertension. 2012;59:1124–31.
Brown MJ, McInnes GT, Papst CC, et al. Aliskiren and the calcium channel blocker amlodipine combination as an initial treatment strategy for hypertension control (ACCELERATE): a randomised, parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2011;377:312–20.
Bangalore S, Ley L. Improving treatment adherence to antihypertensive therapy: the role of single-pill combinations. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012;13:345–55.
Acknowledgements
The authors were fully responsible for all content and editorial decisions, were involved at all stages of manuscript development and have approved the final version. Medical writing assistance, supported financially by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG., was provided by Emma Fulkes, PhD, of PAREXEL, during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bays, H., Zhu, D. & Schumacher, H. Single-Pill Combination of Telmisartan and Hydrochlorothiazide: Studies and Pooled Analyses of Earlier Hypertension Treatment. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 21, 119–126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-014-0041-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-014-0041-8