Abstract
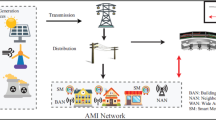
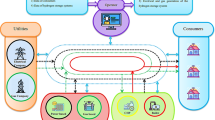
Consumers participation is important for successful implementation of a smart grid. The share of renewable energy sources is ever-increasing Indian power system. As investment required for power generation is quite high, it is important to understand the consumer’s electricity usage pattern for a better planning of resources. It also facilitates energy saving and grid reliability. For a smart grid to operate efficiently and in accordance with the consumer’s preference, real-time power consumption pattern of the consumer is monitored by a Smart Grid Controller for different categories (based on paying capacity). An alert mechanism for voluntary shifting of the consumption to keep the pre-declared budget within limit is suggested.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuballa ML, Abundo ML (2016) A review of the development of Smart Grid technologies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 59:710–725
Brown RE Impact of Smart Grid on distribution system design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting-Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, 20–24 July 2008
Steen D, Le Anh T, Carlson O (2016) Effects of network tariffs on residential distribution systems and price-responsive customers under hourly electricity pricing. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 7(2):617–626
Joe-Wong C, Sen S, Ha S, Chiang M (2012) Optimized day-ahead pricing for smart grids with device-specific scheduling flexibility. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 30(6):1075–1085
Ma J, Chen HH, Song L, Li Y (2016) Residential load scheduling in smart grid: a cost efficiency perspective. IEEE Trans Smart Grid. 7(2):771–784
Mohsenian-Rad A-H, Leon-Garcia A (2010) Optimal residential load control with price prediction in real-time electricity pricing environments. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 1(2):120–133
Samadi P, Mohsenian-Rad A-H, Schober R, Wong VWS, Jatskevich J (2010) Optimal real-time pricing algorithm based on utility maximization for smart grid. In: 2010 1st IEEE international conference on smart grid communications (SmartGridComm), IEEE, 4–6 Oct 2010. doi:10.1109/SMARTGRID.2010.5622077
Ma K, Yao T, Yang J, Guan Xnping (2016) Residential power scheduling for demand response in smart grid. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 78:320–325
Zhou B, Li W, Chan KW, Cao Y, Kuang Y, Liu X, Wang X (2016) Smart home energy management systems: concept, configurations, and scheduling strategies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 61:30–40
Anvari-Moghaddam A, Monsef H, Rahimi-Kian A (2015) Optimal smart home energy management considering energy saving and a comfortable lifestyle. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 6(1):324–332
Pipattanasomporn M, Feroze H, Rahman S (2009) Mul-ti-agent systems in a distributed smart grid: design and implementation. In: Proceedings of IEEE PES 2009 Power Systems Conference and Exposition (PSCE’09), Seattle, Washington, USA, Mar 2009
Gupta R, Jha DK, Yadav VK, Kumar S (2013) A Multi agent framework for operation of a smart grid. Energy Power Eng 5(4B):1330–1336. doi:10.4236/epe.2013.54B252
Gupta R, Jha DK, Nagar S (2015) multi-agent based operation of smart grid for energy management incorporating consumer’s budget. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on recent developments in science, engineering & technology (REDSET-2015), Gurgaon, Oct 2015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Jha, D.K. & Nagar, S. Agent based smart home energy management system. CSIT 4, 103–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0115-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40012-016-0115-y