Abstract
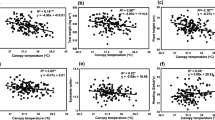
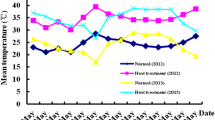
Relationship of canopy temperature (CT) with grain yield and its components were evaluated under terminal heat stress conditions, in Central India, during 2010–2013 growth season, in which 102 durum wheat genotypes were tested under late and very late sown conditions. The genotypes in late sown conditions showed higher grain yield/plant, biomass/plant, harvest index and test grain weight compared to very late sown conditions. The mean grain yield/plant and biomass yield/plant were 18.8 and 55.9 g, respectively, under late sown conditions, compared to 15.1 and 48.9 g under very late sown conditions. Genotypes MACS 3125, HI 8627, HI 8638, HI 8498, WH 896 and HI 8691 showed stable performance under both late and very late sown conditions over the years and hence exhibited high degree of tolerance to terminal heat. CT ranged from 21.0 to 24.7 and 20.2 to 24.9 °C under late and very late sown conditions, respectively. CT showed significant and negative correlation with grain yield/plant and biomass/plant under late and very late conditions and number of grains/spike and 1000 grain weight under very late sown conditions and hence can be successfully used as an important selection parameter in breeding programme at field. The study suggests that CT can be used as one of the important criteria for the selection of stable genotypes under late heat and very late heat stress conditions and can help in improving production and productivity of durum wheat under terminal heat stress conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amani I, Fischer RA, Reynolds MP (1996) Canopy temperature depression association with yield of irrigated spring wheat cultivars in hot climate. J Agron Crop Sci 176:119–129
Bahar B, Yildirim M, Barutcular C, Genc I (2008) Effect of canopy temperature depression on grain yield and yield components in bread. Essays and durum wheat. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Clujnapoca 36:34–37
Balota M, Payne WA, Evet SR, Lazar MD (2007) Canopy temperature depression sampling to assess grain yield and genotypic differentiation in winter wheat. Crop Sci 47:1518–1529
Behera UK, Mishra AN, Pandey HN (2007) Evaluation of heat stress and leaf rust tolerance between very late planted durum and bread wheat cultivars in Central India. Aust J Exp Agri 47:1422–1434
Bilge B, Yildirim M, Barutcular C, Genc I (2008) Effect of canopy temperature depression on grain yield and yield components in bread and durum wheat. Bot Hort Agro Bot Cluj 36:34–37
Fischer RA, Rees D, Sayre KD, Lu ZM, Condon AG, Larque Saavedra A (1998) Wheat yield progress associated with higher stomatal conductance and photosynthetic rate, and cooler canopies. Crop Sci 38:1467–1475
Gautam A, Sai Prasad SV, Jajoo A (2013) Identification of selection parameters for grain yield and its components in durum wheat under terminal heat stress in late sown conditions to combat climate changes. Progres Res 8:55–59
Gutierrez M, Reynolds MP, Raun WR, Stone ML, Klatt AR (2010) Spectral water indices for assessing yield in elite bread wheat genotypes under well-irrigated, water stressed, and high temperature conditions. Crop Sci 50:197–214
Modhej A, Lack S, Naderi A, Emam Y, Normohamadi G (2011) Relationship between canopy temperature and leaf chlorophyll content with grain yield of wheat genotypes at different levels of nitrogen and post-anthesis heat stress condition (in Farsi). Iranian J Field Crops Res 8:946–955
Munjal R, Rana RK (2003) Evaluation of physiological traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) for terminal high temperature tolerance. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Wheat Genetics Symposium, Classical and Molecular Breeding. Poestum. Italy, 2:804–805
Panse VG, Sukhatme PV (1996) Statistical methods for agricultural workers. ICAR, New Delhi
Reynolds PM, Acevedo E, Sayre KD, Fischer RA (1994) Yield potential in modern wheat varieties: its association with a less competitive ideotype. Field Crops Res 37:149–160
Reynolds PM, Nagarajan S, Razzaque MA, Ageeb OAA (2001) Breeding for adaptation to environmental factors, heat tolerance. In: Reynolds PM, Ortiz-Monasterio JI, McNab (eds) Application of physiology in wheat breeding. Cimmyt, Mexico, pp 124–135
Rosyara UR, Vromman D, Duveille E (2008) Canopy temperature depression as an indication of correlative measure of spot blotch resistance and heat stress tolerance in spring wheat. J Plant Pathol 90:103–107
Saxena DC, Sai Prasad SV, Chatrath R, Mishra SC Michelle, Watt Prashar R, Wason A, Gautam A, Malviya P (2014) Evaluation of root characteristics, canopy temperature depression and stay green trait in relation to grain yield in wheat under early and late sown conditions. Ind J Plant Physiol 19:43–47
Smith GRC, Barrs HD, Steiner JL (1986) Alternative models for predicting the foliage-air temperature difference of well irrigated wheat under variable meteorological conditions. Irrig Sci 7:225–236
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:15–42
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the Head, IARI, Regional Station Indore, for providing facilities for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautam, A., Sai Prasad, S.V., Jajoo, A. et al. Canopy Temperature as a Selection Parameter for Grain Yield and Its Components in Durum Wheat Under Terminal Heat Stress in Late Sown Conditions. Agric Res 4, 238–244 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-015-0174-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-015-0174-6