Abstract
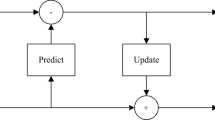
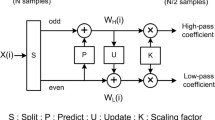
In this paper, an efficient approach to design a 2-D systolic array for high-speed implementation of block-based lifting lossy 9/7 wavelet filter is proposed. The inherent advantage of the in place computation of the lifting-based discrete wavelet transform over the conventional convolution method makes it suitable for efficient hardware implementation with lower computational complexity. The row processor consists of processing elements arranged in a systolic manner, and for column processing, the lifting steps are computed concurrently, by mapping the coefficients to the same systolic arrays, using the cyclic symmetry property of the block of input image coefficients. The advantage of the discussed architecture is that it does not require additional memory for storing the intermediate coefficients. The functionality of the processing element in the systolic array improves the speed, by having the critical path delay of one multiplier and two adders computational time. The area efficient, high-speed design of the lifting algorithm is coded in hardware description language and implemented in Altera cyclone II field programmable gate arrays (FPGA). The implemented results show that the systolic architecture achieves a high speed of 260MHz with a lower accessing time of 0.246μs, when compared to other existing architectures, and reaches a speed performance suitable for real-time multimedia applications. This conceptual design of systolic arrays can be used as IP core in FPGA-based reconfigurable coprocessors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christopoulos C., Skouras A., Ebrahimi T.: The JPEG2000 still image coding system an overview. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 46, 1103–1127 (2000)
Mallat S.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11, 674–693 (1989)
Daubechies I., Sweldens W.: Factoring wavelet transform into lifting steps. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 4, 247–269 (1998)
Singer A.: Colour texture classification using wavelet transform and neural networks ensembles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 34(2B), 145–152 (2009)
Parhi K.K., Nishitani T.: VLSI architectures for discrete wavelet transforms. IEEE Trans. VLSI Syst. 1(2), 191–202 (1993)
Denk, T.C.; Parhi, K.K.: Systolic VLSI architectures for 1-D discrete wavelet transforms. In: Proceedings of Asilomar Conference on signals, systems and Computers, vol 2, pp 1220–1224. Pacific Grove, CA (1998)
Wu P.-C., Chen L.-G.: An efficient architecture for two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 11(4), 536–545 (2001)
Andra K., Chakrabarti C., Acharya T.: A VLSI architecture for lifting-based forward and inverse wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(4), 966–977 (2002)
Dillen G., Georis B., Legat J.-D., Cantineau O.: Combined line-based architecture for the 5/3 and 9/7 wavelet transform of JPEG2000. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 13(9), 944–950 (2003)
Shi G., Liu W., Zhang L.: An efficient folded architecture for lifting based discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst II Express Briefs 56(4), 290–294 (2009)
Huang C.-T., Tseng P.-C., Chen L.-G.: Flipping structure—an efficient VLSI architecture for lifting-based discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52(4), 1080–1089 (2004)
Usha Bhanu, N.; Chilambuchelvan, A.: Efficient VLSI architecture for discrete wavelet transform. IJCSI Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues, Special Issue, ICVCI-2011, 1(1), 2011 ISSN (Online), 1694–0814 (2011)
Xiong C., Tian J., Liu J.: Efficient architectures for Two dimensional wavelet transform using lifting scheme. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(3), 607–614 (2007)
Cheng C., Parhi K.K.: High-speed VLSI implementation of 2-D discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(1), 393–403 (2008)
Tian X., Wu L., Tan Y.-H., Tian J.-W.: Efficient multi-input/multi-output VLSI architecture for two-dimensional lifting-based DWT. IEEE Trans. Comput. 60(8), 1207–1211 (2011)
Kilic I., Yilmaz R.: A hybrid video compression based on zero tree wavelet structure. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 34(1B), 187–196 (2009)
Salehi S.A., Sadri S.: Investigation of lifting-based hardware architectures for DWT. J. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 28, 41–55 (2009)
Acharya T., Chakrabarti C.: A survey on lifting-based discrete wavelet transforms architectures. J. VLSI Signal Process. 42, 321–339 (2006)
Usha Bhanu N., Chilambuchelvan A.: A detailed survey on VLSI architectures for lifting based DWT for efficient hardware implementation. Int. J. VLSI Des. Commun. Syst. (VLSICS) 3(2), 143–164 (2012)
Parhi K.K.: VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation. Wiley, New York (1999)
Kung H.T.: Why systolic architectures. Comput. Mag. 15, 37–45 (1982)
Pan S.B., Park R.H.: Unified systolic array for computation of DCT/DST/DHT. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 7, 413–419 (1997)
Chiper D.F., Swamy M.N.S., Ahamad O., Stouraitis T.: A systolic array architecture for discrete sine transforms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(9), 2347–2354 (2002)
Meher P.K., Chandrasekaran S., Amira A.: FPGA realization of FIR filters by efficient and flexible systolization using distributed arithmetic. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3009–3017 (2008)
Meher P.K., Mohanty B.K., Patra J.C.: Hardware efficient systolic like modular design for 2D DWT. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 55(2), 151–155 (2008)
Alwan N.A.S.: Efficient systolic sinusoidal sequence generation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 33(1B), 179–186 (2008)
Mohanty B.K., Meher P.K.: Memory efficient modular VLSI architecture for high-throughput and low-latency implementation of multilevel lifting 2-D DWT. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2072–2084 (2011)
Mohanty B.K., Mahajan A., Meher P.K.: Area and power efficient architecture for high throughput implementation of lifting 2D DWT’. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Brief. 59(7), 434–438 (2012)
Salehi, S.A.; Amirfattahi, R.: A block based 2D discrete wavelet transform structure with new scan method for overlapped sections. In: Proceedings of the First Middle East Conference on Biomedical Engineering, pp 126–129. Sharjah (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usha Bhanu, N., Chilambuchelvan, A. High-Speed Systolic VLSI Architecture for 2-D Forward Lifting-Based DWT. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6125–6135 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1208-2