Abstract
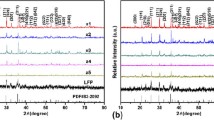
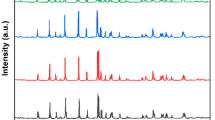
Iron-based cathode material, iron phosphate, was prepared by homogeneous co-precipitation followed by spray drying method, where Ce3+doping modifications were carried out to improve the electrical conductivity. Considering that the relationship between structures and performances, calcining temperature and doping concentration were investigated. The physicochemical property of the precursor was analyzed using TG–DSC, the structures and morphologies of samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical behaviors of samples were analyzed using charge–discharge tests and electrochemical impedance spectrum tests. Results show that the electrochemical performance of iron phosphate was improved by the synthesis condition optimization and doping modification. Fe0.98Ce0.02PO4 calcined at 460°C showed the highest discharge capacity of 100.3 mAh/g for the initial cycle at 0.05C. In addition, the doping mechanism for FePO4 was discussed in this paper.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dileep C., Kumar B.: Influence of metham sodium on suppression of collar rot disease of peanut, in vitro antibiosis, siderophore production and root colonization by a fluorescent pseudomonad strain FPO4, Indian J. Exp. Biol. 38, 1245–1250 (2000)
Patience G.S., Farrie Y., Devaux J.F., Dubois J.L.: Oxidation kinetics of carbon deposited on cerium-doped fepo4 during dehydration of glycerol to acrolein. Chem. Eng. Technol. 35, 1699–1706 (2012)
Kim S.W., Ryu J., Park C.B., Kang K.: Carbon nanotube-amorphous FePO4 core–shell nanowires as cathode material for Li ion batteries. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 46, 7409–7411 (2010)
Shi Z., Li Y., Ye W., Yang Y.: Mesoporous FePO4 with Enhanced Electrochemical Performance as Cathode Materials of Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Electrochem. solid-state Lett. 8, A396–A399 (2005)
Padhi A., Nanjundaswamy K., Goodenough J.B.: Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144, 1188–1194 (1997)
Song Y., Yang S., Zavalij P.Y., Whittingham M.S.: Temperature-dependent properties of FePO4 cathode materials. Mater. Res. Bull. 37, 1249–1257 (2002)
Yin Y., Hu Y., Wu P., Zhang H., Cai C.: A graphene–amorphous FePO4 hollow nanosphere hybrid as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 48, 2137–2139 (2012)
Tang P., Holzwarth N.: Electronic structure of FePO4, LiFePO4 and related materials. Phys. Rev. B. 68, 165107 (2003)
Scaccia S., Carewska M., Prosini P.P.: Thermoanalytical study of iron(III) phosphate obtained by homogeneous precipitation from different media. Thermochim. Acta. 413, 81–86 (2004)
Song, Y.; Zavalij, P.Y.; Chernova, N.A.; Whittingham, M.S.; Synthesis, crystal structure, and electrochemical and magnetic study of new iron (III) hydroxyl-phosphates, isostructural with lipscombite. Chem. Mater. 17, 1139–1147 (2005)
Song Y., Zavalij P.Y., Suzuki M., Whittingham M.S.: New iron (III) phosphate phases: crystal structure and electrochemical and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 41, 5778–5786 (2002)
Whittingham M.S., Song Y., Lutta S., Zavalij P.Y., Chernova N.A.: Some transition metal (oxy) phosphates and vanadium oxides for lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 15, 3362–3379 (2005)
Okada S., Yamamoto T., Okazaki Y., Yamaki J.-i., Tokunaga M., Nishida T.: Cathode properties of amorphous and crystalline FePO4. J. Power Sour. 146, 570–574 (2005)
Cui Y., Wang M., Guo R.: High rate performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials co-doped with C and Ti4+ by microwave synthesis. Bull. Mater. Sci. 32, 579–582 (2009)
Cho Y.-D., Fey G.T.-K., Kao H.-M.: Physical and electrochemical properties of La-doped LiFePO4/C composites as cathode materials for lithium–ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 12, 815–823 (2008)
Croce F., D’Epifanio A., Reale P., Settimi L., Scrosati B.: Ruthenium oxide-added quartz iron phosphate as a new intercalation electrode in rechargeable lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, A576–A581 (2003)
Fedorková A., Wiemhöfer H.D., Oriòáková R., Oriòňák A., Kaniansky D.: Surface modification of FePO4 particles with conductive layer of polypyrrole. Solid State Sci. 12, 924–928 (2010)
Oxley J., Hiskey M., Naud D., Szekeres R.: Thermal decomposition of nitramines: dimethylnitramine, diisopropylnitramine, and N-nitropiperidine. J Phys. Chem, 96, 2505–2509 (1992)
Scaccia S., Carewska M., Bartolomeo A.D., Prosini P.P.: Thermoanalytical investigation of iron phosphate obtained by spontaneous precipitation from aqueous solutions. Thermochim. Acta. 383, 145–152 (2002)
Okawa H., Yabuki J., Kawamura Y., Arise I., Sato M.: Synthesis of FePO4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries by a sonochemical method. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 1203–1208 (2008)
Shi Z.C., Attia A., Ye W.L., Wang Q., Li Y.X., Yang Y.: characterization and electrochemical performance of mesoporous FePO4 as cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta. 53, 2665–2673 (2008)
Prosini P.P., Lisi M., Zane D., Pasquali M.: Determination of the chemical diffusion coefficient of lithium in LiFePO4. Solid State Ion. 148, 45–51 (2002)
Ong S.P., Jain A., Hautier G., Kang B., Ceder G.: Thermal stabilities of delithiated olivine MPO4(M= Fe, Mn) cathodes investigated using first principles calculations. Electrochem. Commun. 12, 427–430 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, S.M. & Zhang, J.X. Synthesis and Modification of Iron-based Cathode Materials: Iron Phosphate for Lithium Secondary Batteries. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 6687–6691 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1185-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1185-5