Abstract
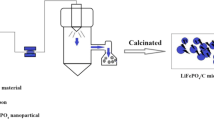
Nanostructured LiFePO4 powder with a narrow particle size (ca. 100 nm) for high rate lithium-ion battery cathode application was obtained by microwave heating and using citric acid as carbon source. The microstructures and morphologies of the synthesized materials were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope while the electrochemical performances were evaluated by galvanostatic charge-discharge. The carbon coating and Ti4+ could improve the conductivity both between the LiFePO4 particles and the intrinsic electronic conductivity. The LiFePO4 doped with 5% C and 1% Ti4+ resulted in a specific capacity of 114·95 mAh·g−1 and 102·4 mAh·g−1 at discharge rates of 0·3C and 1C, respectively, and the cycle performance is very good.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson A S 2001 J. Power Sources 97–98 498
Chung S Y 2002 Nat. Mater. 1 125
Chung S Y 2003 Solid-State Lett. 6 A278
Guo Z P 2005 Synth. Met. 153 114
Huang H 2001 Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 4 A170
MacNeil D D 2002 J. Power Sources 108 8
Padhi A K 1997 J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 1188
Park K S 2004 Solid State Commun. 129 313
Spong A D 2005 J. Electrochem. Soc. 152 A2376
Takahashi M 2002 Solid State Ionics 148 283
Xie H 2006 Electrochim. Acta 51 2064
Yamada A 2001 J. Electrochem. Soc. 148 A224
Zaghib K 2005 Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 8 A207
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Wang, M. & Guo, R. High rate performance of LiFePO4 cathode materials co-doped with C and Ti4+ by microwave synthesis. Bull Mater Sci 32, 579–582 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-009-0088-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-009-0088-7