Abstract
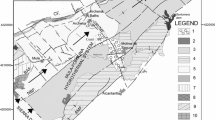
We revisited the historical and instrumental period records and recognized that due to Gölbaşı-Türkoğlu and Türkoğlu-Antakya segments of the East Anatolian Fault System (EAFS), densely populated Kahramanmaraş district is at great seismic risk. Therefore, in this study, Gölbaşı-Türkoğlu segment of East Anatolian Fault was continuously monitored by collecting data of different geochemical parameters of spring waters emanating from major fault segments (pH, temperature, conductivity, anion and cation concentrations) and correlating with seismicity. For this purpose, three online spring water observation stations located on the Gölbaşı-Türkoğlu segment of EAFS which is the most important source of earthquakes for Kahramanmaraş and its surroundings were established. Physical and chemical changes of the spring waters which are thought to be directly related to the fault were monitored. Spring water temperature and electrical conductivity and pH were measured on an hourly basis, whereas anion-cation concentrations were determined daily from bottled spring water samples. Dense seismology network run under the TURDEP Project (EOS Transactions, 88, 333–334, 2007) in the area provided means for monitoring earthquakes down to magnitude 1. We show that a magnitude 4.2 event (20 August 2008) caused significant changes in the geochemical parameters of a nearby spring. From the geochemical transients determined we conclude that there is a close relation between earthquakes and geochemical parameters of spring waters in the region. In order to see this correlation better, measurements of geochemical parameters should continue in the future.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
İnan S., Ergintav S., Saatçılar R., Tüzel B., İravul Y.: Turkey Makes Major Investments in Earthquake Research. EOS Trans. 88, 333–334 (2007)
Şengör A.M.C., Yılmaz Y.: Tethyan evolution of Turkey: a plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 75, 181–241 (1981)
Koçyiğit, A.: Intra-plate neotectonic development in Southwestern Turkey and adjacent areas. Bull. Geol. Soc. Turkey. 27, 1–16 (1984, Ankara)
Allen, C.R.: Active Faulting in Northern Turkey, Division of Geological Science, California Institute of Technology Contribution No. 1577 (1969)
Arpat E., Şaroğlu F.: The East, Anatolian fault system: thoughts on its development. Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. Inst. 78, 33–39 (1972)
Arpat E., Şaroğlu F.: Some recent tectonic events in Turkey. Bull. Geol. Soc. Turkey 18/1, 91–101 (1975)
Mc Kenzie D.P.: The East Anatolian Fault, a major Structure in Eastern Turkey. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 29, 189–193 (1976)
Yalçın, N.: Characters of East Anatolian fault between Türkoğlu and Karaağaç (K.Maraş) in relation to settlement problems. Bulletin of the Altınlı Symposium of Geological Society of Turkey, pp. 49–56 (1979)
Hempton M.R., Dewey J.F., Şaroğlu F.: The East Anatolian transform fault: along strike variations in geometry and behaviour. EOS Trans. 62, 393 (1981)
Şengör, A.M.C.; Görür, N.; Şaroğlu, F.: Strike-slip faulting and related basin formation in zones of tectonic escape: Turkey as a case study. In: Biddle, K.T.; Christie-Blick, N. (eds.) Strike-slip Faulting and Basin Formation, Society of Economic Paleontology Mineralogists, vol. 37. Special Publication, pp. 227–264 (1985)
Dewey, J.F.; Hempton, M.R.; Kidd, W.S.F.; Şaroğlu, F.; Şengör, A.M.C.: Shortening of continental lithosphere: the neotectonics of eastern Anatolia—a young collision zone. In: Coward, M.O.; Ries, A.C. (eds.) Collisional Tectonics, Geological Society Special Publication, vol. 19. Geological Society, London, pp. 3–36 (1986)
Hempton M.R.: Constraints on Arabian plate motion and extensional history of the Red Sea. Tectonics 6, 687–705 (1987)
Perinçek, D.; Günay, K.; Kozlu, H.: New observations on strike-slip faults in east and south Anatolia, 7. Biannual Petroleum Congress of Turkey, UCTEA Chamb. Pet. Eng. Turk. Assoc. Pet. Geol., 89–103 (1987)
Çemen, İ.; Perinçek, D.: Extensional origin of the northern part of the Hatay-Karasu half-graben. In: 7th Turkish Geological Society Annual Meeting, Abstracts with Programs, pp. 10–11 (1987)
Muehlberger R.W., Gordon M.B.: Observations on the complexity of the East Anatolian Fault. Turkey. J. Struct. Geol. 9, 899–903 (1987)
Lybéris N., Yürür T., Chorowicz J., Kasapoğlu E., Gündoğdu N.: The East Anatolian fault: an oblique collisional belt. Tectonophysics 204, 1–15 (1992)
İmamoğlu, M.Ş.: Neotectonic investigation of the East Anatolian fault in the area between Gölbaşı (Adıyaman), Pazarcık-Narlı (K. Maraş). Ank. University., Enstitude of Natural and Applied Sciences, Department of Geological Engineering, PhD Thesis, (Unpublished) (1993)
Westaway R.: Present-day kinematics of the Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 12071–12090 (1994)
Ambraseys N.N.: Temporary seismic, quiescence: SE Turkey. Geoph. J. 96, 311–331 (1989)
Rikitake T.: Earthquake Prediction. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1976)
Wakita H.: Geochemical challenge to earthquake prediction. Proceed.Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 3781–3786 (1996)
King J.Y.: Gas geochemistry applied to earthquake prediction: A, review. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 12,269–12,281 (1986)
King J.Y., Koizumi Y., Kitagawa Y.: Hydrogeochemical anomalies and the 1995 Kobe earthquake. Science 269, 38–39 (1995)
Toutain J. P., Baubron J.C.: Gas geochemistry and seismotectonics:A review. Tectonophysics 304, 1–27 (1999)
Claesson L., Skelton A., Graham C., Dietl C., Moerth M., Torssander P., Kockum I.: Hydrogeochemical changes before and after a major earthquake. Geology 32, 641–644 (2004)
Hartmann J., Levy J.K.: Hydrogelogical and gasgeochemical earthquake precursors—A review for application. Nat. Hazards 34, 279–304 (2005)
Freund F., Takenchi A., Lau B.: Electric currents streaming out of stresses igneous rocks—a step towards understanding pre-earthquake low frequency EM emissions. Phys. Chem. Earth 31, 389–396 (2006)
İnan, S.; Akgül, T.; Seyis, C.; Saatçılar, R.; Baykut, S.; Ergintav, S.; Baş, M.: Geochemical monitoring in the Marmara region (NW Turkey): A search for precursors of seismic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 113, B03401 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JB005206
İnan, S.; Ertekin, K.; Seyis, C.; Şimşek, Ş.; Kulak, F.; Dikbaş, A.; Tan, O.; Ergintav, S.; Çakmak, R.; Yörük, A.; Çergel, M.; Yakan, H.; Karakuş, H.; Saatçılar, R.; Akçiğ, Z.; İravul, Y.; Tüzel, B.: Multi-Disciplinary Earthquake Researches in Western Turkey: Hints to Select Sites to Study Geochemical Transients Associated to Seismicity. Acta Geophysica 58, 1–47 (2008). doi:10.2478/s11600-010-0016-7
İnan, S.; Kop, A.; Çetin, H.; Kulak, F.; Pabuçcu; Seyis, C.; Ergintav, S.; Tan, O.; Saatçılar, R.; Bodur, M.N.: Seasonal variations in soil radon emanation: Long term continuous monitoring in light of seismicity. Natural Hazard (2012). doi:10.1007/s11069-012-0096-6
Erees, F.S.; Aytas, S.; Saç, M.M.; Yener, G.; Salk, M.: Radon concentrations in thermal waters related to seismic events along faults in the Denizli Basin, Western Turkey. Radiat. Meas. 42, 80–86 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.radmeas.2006.06.003
Saç, M.M.; Harmansah, C.; Camgöz, B.; Sozbilir, H.: Radon Monitoring as the Earthquake Precursor in Fault Line in Western Turkey. Ekoloji (2011). doi:10.5053/Ekoloji7912
Bolca M., Saç M.M., Altınbaş Ü., Camgöz B.: Chemical and radioactivity effects of geothermal springs on environmental pollution in Seferihisar region in Western Turkey. Asian J. Chem. 19(3), 2265–2276 (2007)
Camgöz, B.; Saç, M.M.; Bolca, M.; Özen, F.; Oruç, Ö.E.; Demirel, N.: Investigation of Radioactive and Chemical Contents of Thermal Waters; Izmir Seferihisar Region Representative İzmir, Ekoloji, pp. 78–87 (2010), doi:10.5053/Ekoloji769
Kop, A.: Importance of soil radon gas measurement on geothermal areas related to faults: an example from hartlap thermal water, Kahramanmaraş. İstanbul Yerbilimleri Dergisi 23(1), 39–52 (2010)
http://www.ydbae.mam.gov.tr TUBITAK Marmara Research Center, Earth And Marine Sciences Institute, Multi-Disciplinary Earthquake Researches in High Risk Regions of Turkey Representing Different Tectonic Regimes (TURDEP) (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kop, A., Ezer, M., Bodur, M.N. et al. Geochemical Monitoring Along the Türkoğlu (Kahramanmaraş)-Gölbaşı (Adıyaman) Segments of the East Anatolian Fault System. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 5521–5536 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0912-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0912-7