Abstract
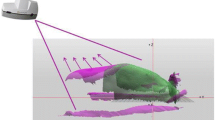
The purpose of this study was to quantify the effect of treatment area and treatment distance on dose distributions for geometrically optimised surface mould plans in order to provide guidance in choosing treatment parameters and constructing moulds for individual patients. Geometrically optimised plans were generated with a typical brachytherapy planning system and measurements were taken with radiochromic film over depths of 5–32 mm with an 192Ir high dose rate source. Films were calibrated with a cylindrical geometry technique utilising the 192Ir source and readout was performed with a flatbed scanner. The rate of dose fall-off about the prescription plane, as well as the magnitude and extent of local dose maxima superficial to the prescription plane, increased with decreasing treatment areas when inter-catheter spacing and treatment distance were kept constant. The dose fall-off was highly dependent on treatment distance, with a 16 % reduction in dose 4 mm superficial to the treatment depth occurring when the distance was increased from 10 to 20 mm while maintaining a 10 mm inter-catheter spacing. The table generated using the measured planar geometry data, can be used as an initial guide for mould construction and planning. The properties of high dose regions near to the catheter plane are highly dependent on the treatment area, which must be considered when normal tissue dose tolerances are a concern. Treatment distance is a key variable influencing the overall dose distribution and should be adjusted as a function of the desired tumour to skin dose ratio, controlled by mould thickness.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sagar SM, Pujara CM (1992) Radical treatment of angiosarcoma of the scalp using megavoltage electron beam therapy. Br J Radiol 65(773):421–424
Able CM, Mills MD, McNeese MD, Hogstrom KR (1991) Evaluation of a total scalp electron irradiation technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21(4):1063–1072
McKenzie MR, Freeman CR, Pla M, Guerra J, Souhami L, Pla C, Podgorsak EB (1993) Clinical experience with electron pseudoarc therapy. Br J Radiol 66(783):234–240
Tung SS, Shiu AS, Starkschall G, Morrison WH, Hogstrom KR (1993) Dosimetric evaluation of total scalp irradiation using a lateral electron–photon technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 27(1):153–160
Kinard JD, Zwicker RD, Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Kaufman N, Pieters R (1996) Short communication: total craniofacial photon shell technique for radiotherapy of extensive angiosarcomas of the head. Br J Radiol 69(820):351–355
Nag S, Cano ER, Demanes DJ, Puthawala AA, Vikram B, American Brachytherapy Society (2001) The American Brachytherapy Society recommendations for high-dose-rate brachytherapy for head-and-neck carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50(5):1190–1198
Svoboda V, Kovarik J, Morris F (1995) High dose-rate microselectron molds in the treatment of skin tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31(4):967–972
Chaudhuri A, De-Groot C, Seel M, Jolly M, Cameron T (2011) Treatment of regional cutaneous nodular metastases from melanoma using high-dose rate mould brachytherapy. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 55(2):206–212
Narayanan S, Patil K, Mandavkar M, Despande D, Srivastava S, Dinshaw K (2004) High dose rate brachytherapy of rare sites using surface mould. J Med Phys 29(1):26–29
Guix B, Finestres F, Tello J, Palma C, Martinez A, Guix J, Guix R (2000) Treatment of skin carcinomas of the face by high-dose-rate brachytherapy and custom-made surface moulds. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(1):95–102
Somanchi BV, Stanton A, Webb M, Loncaster J, Allan E, Muir LT (2008) Hand function after high dose rate brachytherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin of the hand. Clin Oncol 20(9):691–697
Harms W, Krempien R, Hensley FW, Berns C, Wannenmacher M, Fritz P (2001) Results of chest wall reirradiation using pulsed-dose-rate (PDR) brachytherapy molds for breast cancer local recurrences. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49(1):205–210
Fritz P, Hensley FW, Berns C, Schraube P, Wannenmacher M (1996) First experiences with superfractionated skin irradiations using large after loading moulds. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36(1):147–157
Duggan L, Butson M, Howlett S, Denham J, Kron T (2000) Verification of the dose distribution for 192Ir mould treatments using radiochromic film and LiFMg, Cu, P TLDs. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 23(1):15–20
Dempsey JF, Low DA, Mutic S, Markman J, Kirov AS, Nussbaum GH, Williamson JF (2000) Validation of a precision radiochromic film dosimetry system for quantitative two-dimensional imaging of acute exposure dose distributions. Med Phys 27(10):2462–2475
Chiu-Tsao S-T, Shah N, Wang L, Chadha M, Harrison L (2006) Dose perturbation in the presence of vaginal cylinder with Ir-192 HDR source: a radiochromic film dosimetry study. Brachytherapy 5(2):97
Sureka CS, Sunny CS, Subbaiah KV, Aruna P, Ganesan S (2007) Dose distribution for endovascular brachytherapy using Ir-192 sources: comparison of Monte Carlo calculations with radiochromic film measurements. Phys Med Biol 52(2):525–537
Bonnet J, Blouet A, David I, Marre D, Delannes M (2008) Quality control in pulsed dose rate brachytherapy with Ir-192 afterloading system: the use of radiochromic films. Brachytherapy 7(2):174
Hanley J, Napoli J, Chiu-Tsao S-T, Godfrey L (2008) Measurement of skin dose for MammoSite® patients using Gafchromic® EBT film. Brachytherapy 7(2):143
Kuo H-CG, Yaparpalvi R, Mah D, Mutyala S (2009) Clinical experience with GAF chromic film for dose measurement in high-dose-rate brachytherapy surface applicator (Leipzig) treatments: phantom and patient results. Brachytherapy 8(2):153
Hira M, Podgorsak MB, Jaggernauth W, Malhotra HK (2010) Measurement of dose perturbation around shielded ovoids in high-dose-rate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 10(3):232–241
Aldelaijan S, Mohammed H, Tomic N, Liang LH, DeBlois F, Sarfehnia A, Abdel-Rahman W, Seuntjens J, Devic S (2011) Radiochromic film dosimetry of HDR (192)Ir source radiation fields. Med Phys 38(11):6074–6083
Uniyal SC, Naithani UC, Sharma SD, Srivastava AK (2012) Radiochromic film dosimetry of rectal inhomogeneity and applicator attenuation in high dose rate brachytherapy of uterine cervix. J Appl Clin Med Phys 13(1):3654
Palmer A, Nisbet A, Bradley D (2013) Verification of high dose rate brachytherapy dose distributions with EBT3 Gafchromic film quality control techniques. Phys Med Biol 58(3):497–511
Odgers D, Haque M (2013) Near-catheter dosimetry of a HDR brachytherapy source using Gafchromic film. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 36(2):159–166
Perez-Calatayud J, Ballester F, Das RK, DeWard LA, Ibbott GS, Meigooni AS, Ouhib Z, Rivard MJ, Sloboda RS, Wiliamson JF (2012) Dose calculation for photon-emitting brachytherapy sources with average energy higher than 50 keV: report of the AAPM and ESTRO. Med Phys 39(5):2904–2929
Sutherland JG, Rogers DW (2010) Monte Carlo calculated absorbed-dose energy dependence of EBT and EBT2 film. Med Phys 37(3):1110–1116
Hartmann B, Martisikova M, Jakel O (2010) Technical note: homogeneity of Gafchromic® EBT2 film. Med Phys 37(4):1753–1756
Richley L, John AC, Coomber H, Fletcher S (2010) Evaluation and optimization of the new EBT2 radiochromic film dosimetry system for patient dose verification in radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol 55(9):2601–2617
Kairn T, Aland T, Kenny J (2010) Local heterogeneities in early batches of EBT2 film: a suggested solution. Phys Med Biol 55(15):L37–L42
Butson M, Cheung T, Yu P, Alnawaf H (2009) Dose and absorption spectra response of EBT2 Gafchromic film to high energy X-rays. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 32(4):196–202
Devic S, Aldelaijan S, Mohammed H, Tomic N, Liang LH, DeBlois F, Seuntjens J (2010) Absorption spectra time evolution of EBT-2 model Gafchromic film. Med Phys 37(5):2207–2214
Ferreira BC, Lopes MC, Capela M (2009) Evaluation of an Epson flatbed scanner to read Gafchromic EBT films for radiation dosimetry. Phys Med Biol 54(4):1073–1085
Desroches J, Bouchard H, Lacroix F (2010) Technical note: potential errors in optical density measurements due to scanning side in EBT and EBT2 Gafchromic film dosimetry. Med Phys 37(4):1565–1570
Nath R, Anderson LL, Luxton G, Weaver KA, Williamson JF, Meigooni AS (1995) Dosimetry of interstitial brachytherapy sources: recommendations of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 43. Med Phys 22(2):209–234
Baltas D, Sakelliou L, Zamboglou N (2007) The physics of modern brachytherapy for oncology. Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton
Perez-Calatayud J, Granero D, Ballester F (2004) Phantom size in brachytherapy source dosimetric studies. Med Phys 31(7):2075–2081
Hill R, Holloway L, Baldock C (2005) A dosimetric evaluation of water equivalent phantoms for kilovoltage X-ray beams. Phys Med Biol 50(21):N331–N344
Hill R, Kuncic Z, Baldock C (2010) The water equivalence of solid phantoms for low energy photon beams. Med Phys 37(8):4355–4363
International Organization for Standardization (1995) Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement, 2nd edn. ISO, Geneva
Johns HE, Cunningham JR (1983) The physics of radiology, 4th edn. Charles C Thomas, Springfield
Meredith WJ (1967) Radium dosage, the Manchester system. E. and S. Livingston, Edinburgh
Grenaro D, Perez-Calatayud J, Vijande J, Ballester F, Rivard M (2014) Limitations of the TG-43 formalism for skin high-dose-rate brachytherapy dose calculations. Med Phys 41(8):021703
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank May Whitaker and Nick Menzies for their assistance with manuscript editing and Dane Pope for producing the calibration phantom schematic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobolewski, M., Haque, M. Optimising treatment distance and treatment area for HDR surface mould brachytherapy. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 37, 681–689 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-014-0305-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-014-0305-6