Abstract
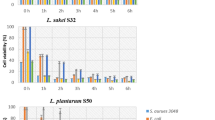
Two traditional sausage products (“salsiccia” and “salame”) processed from the raw meat of the Black Sicilian swine “Suino Nero dei Nebrodi” were microbiologically investigated during the manufacturing and ripening stages. Both products were dominated by lactic acid bacteria (LAB), especially rod-shaped types. The concentration of enterococci was consistent in salame. Coagulase-negative cocci increased slower than LAB. Yeasts showed an increasing trend during the ripening of both products. Enterobacteriaceae were counted at a constant level of about 105 CFU/g in both products, while pseudomonads diminished during ripening. Coagulase-positive staphylococci, Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. were not detected at the end of the ripening process. Characterisation of LAB at the strain and species level revealed that Lactococcus lactis was found only in the meat mixture, while Lactobacillus sakei and various enterococci persisted during the monitoring period. Some LAB strains isolated from sausages were also identified on the surface of the factory equipment. Two strains (Lactobacillus sakei SS106A and Enterococcus faecalis SS91) were characterised by their anti-Listeria properties due to bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance production. A multiple strain starter composed of Lactobacillus sakei and enterococci has been proposed to maintain the typical characteristics of the two fermented meat products microbiologically investigated in this study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosiadis J, Soultos N, Abrahim A, Bloukas JG (2003) Physicochemical, microbiological and sensory attributes for the characterization of Greek traditional sausages. Meat Sci 66:279–287
Aquilanti L, Santarelli S, Silvestri G, Osimani A, Petruzzelli A, Clementi F (2007) The microbial eology of a typical Italian salami during its natural fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 120:136–145
Aymerich T, Martín B, Garriga M, Hugas M (2003) Microbial quality and direct PCR identification of lactic acid bacteria and nonpathogenic staphylococci from artisanal low-acid sausages. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4583–4594
Barbut S (2006) Fermentation and chemical acidification of salami-type products—effect on yield, texture and microstructure. J Muscle Food 17:34–42
Baruzzi F, Matarante A, Caputo L, Morea M (2006) Molecular and physiological characterization of natural microbial communities isolated from a traditional Southern Italian processed sausage. Meat Sci 72:261–269
Benito M, Serradilla MJ, Ruiz-Moyano S, Martín A, Pérez-Nevado F, Córdoba G (2008) Rapid differentiation of lactic acid bacteria from autochthonous fermentation of Iberian dry-fermented sausages. Meat Sci 80:656–661
Bonomo MG, Ricciardi A, Salzano G (2011) Influence of autochthonous starter cultures on microbial dynamics and chimica-physical features of traditional fermented susages of Basilicata region. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:137–146
Borch E, Kant-Muermans ML, Blixt Y (1996) Bacterial spoilage of meat and cured meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 33:103–120
Cenci-Goga BT, Ranucci D, Miraglia D, Ciuffi A (2008) Use of a starter cultures of dairy origin in the production of Salame nostrano, an Italian dry-cured sausage. Meat Sci 78:381–390
Chaillou S, Daty M, Baraige F, Dudez AM, Anglade P, Jones R, Alpert CA, Champomier-Verges MC, Zagorec M (2009) Intraspecies genomic diversity and natural population structure of the meat-borne lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus sakei. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:970–980
Chevallier I, Ammor S, Laguet A, Labayle S, Castanet V, Dufour E, Talon R (2006) Microbial ecology of a small-scale facility producing traditional dry sausage. Food Contr 17:446–453
Cocolin L, Rantsiou K, Iacumin L, Urso R, Cantoni C, Comi G (2004) Study of the ecology of fresh sausages and characterization of populations of lactic acid bacteria by molecular methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1883–1894
Comi G, Urso R, Iacumin L, Rantsiou K, Cattaneo P, Cantoni C, Cocolin L (2005) Characterisation of naturally fermented sausages produced in the North East of Italy. Meat Sci 69:381–392
Coppola R, Iorizzo M, Saotta R, Sorrentino E, Grazia L (1997) Characterization of micrococci and staphylococci isolated from soppressata molisana, a Southern Italy fermented sausage. Food Microbiol 14:47–53
Coppola S, Mauriello G, Aponte M, Moschetti G, Villani F (2000) Microbial succession during repening of Naples-type salami, a southern Italian fermented sausage. Meat Sci 56:321–329
Corsetti A, Settanni L, Braga TM, De Fatima Silva Lopes M, Suzzi G (2008) An investigation on the bacteriocinogenic potential of lactic acid bacteria associated with wheat (Triticum durum) kernels and non-conventional flours. LWT—Food. Part Sci Technol 41:1173–1182
Danilović B, Joković N, Petrović L, Veljović K, Tolinački M, Savić D (2011) The characterisation of lactic acid bacteria during the fermentation of an artisan Serbian sausage (Petrovská Klobása). Meat Sci 88:668–674
Di Cagno R, Lopez CC, Tofalo R, Gallo G, De Angelis M, Paparella A, Hammes W, Gobbetti M (2008) Comparison of the compositional, microbiological, biochemical and volatile profile characteristics of three Italian PDO fermented sausages. Meat Sci 79:224–235
Drosinos EH, Mataragas M, Xiraphi N, Moschonas G, Gaitis F, Metaxopoulos J (2005) Characterization of the microbial flora from a traditional Greek fermented sausage. Meat Sci 69:307–317
Drosinos E, Paramithiotis S, Kolovos G, Tsikouras I, Metaxopoulos I (2007) Phenotypic and technological diversity of lactic acid bacteria and staphylococci isolated from traditionally fermented sausages in Southern Greece. Food Microbiol 24:260–270
Fontana C, Cocconcelli PS, Vignolo G (2005) Monitoring the bacterial population dynamics during fermentation of artisanal Argentinean sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 103:131–142
Franciosi E, Settanni L, Cavazza A, Poznanski E (2009) Presence of enterococci in raw cow’s milk and “Puzzone di Moena” cheese. J Food Process Preserv 33:204–217
Gálvez A, Giménez-Gallego G, Maqueda M, Valdivia E (1989) Purification and amino acid composition of peptide antibiotic AS-48 produced by Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecalis subsp. liquefaciens S-48. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33:437–441
Gardini F, Suzzi G, Lombardi A, Galgano F, Crudele MA, Andrighetto C, Schirone M, Tofalo R (2001) A survey of yeasts in traditional sausages of southern Italy. FEMS Yeast Res 1:161–167
Giraffa G (2002) Enterococci from foods. FEMS Microbiol Rev 744:1–9
Gordon CL, Amad MH (1991) Thermal susceptibility of Streptococcus faecium strains isolated from frankfurters. Can J Microbiol 37:609–612
Hammes WP, Hertel C (1998) New developments in meat starter cultures. Meat Sci 49:125–138
Hammes WP, Knauf HJ (1994) Starters in processing of meat products. Meat Sci 36:155–168
Hartnett DJ, Vaughan A, Van Sinderen D (2002) Antimicrobial producine lactic acid bacteria isolated from raw barley and sorghum. J Inst Brew 108:169–177
Hierro E, De La Hoz L, Ordonez JA (1997) Contribution of microbial and meat endogenous enzymes to the lipolysis of dry fermented sausages. J Agric Food Chem 45:2989–2995
Holck AL, Axelsson L, Birkeland S, Aukrust T, Blom H (1992) Purification and amino acid sequecence of sakicin A, a bacteriocin produced from Lactobacillus sakei Lb 706. J Gen Microbiol 138:2715–2720
Holley RA (2000) Brochotrix. In: Robinson RK, Batt CA, Patel PD (eds) Encyclopedia of food microbiology. Academic Press, London
Hugas M, Garriga M, Aymerich MT (2003) Functionalty of enterococci in meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 88:223–233
Iacumin L, Comi G, Cantoni C, Cocolin L (2006) Ecology and dynamics of coagulase-negative cocci isolated from naturally fermented Italian sausages. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:480–486
Jack RW, Tagg JR, Ray B (1995) Bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59:171–200
Kaban G, Kaya M (2009) Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus xylosus on the quality characteristics of dry fermented sausage “Sucuk”. J Food Sci 74:58–63
Lücke FK (1998) Fermented sausages. In: Wood BJB (ed) Microbiology of fermented foods Blackie. Academic and Professional, London
Lücke FK (2000) Utilization of microbes to process and preserve meat. Meat Sci 56:105–115
Mauriello G, Casaburi A, Blaiotta G, Villani F (2004) Isolation and technological properties of coagulase negative staphylococci from fermented sausages of southern Italy. Meat Sci 67:149–158
Metaxopoulos J, Samelis J, Papadelli M (2001) Technological and microbiological evaluation of traditional processes as modified for the industrial manufacturing of dry fermented sausage in Greece. Ital J Food Sci 1:3–18
Mortvedt CI, Nissen-Meyer J, Sletten K, Nes IF (1991) Purification and amino acid sequence of lactocin S, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus sakei L45. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1829–1834
Nilsen T, Nes IF, Holo H (2003) Enterolysin A, a cell wall-degrading bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecalis LMG 2333. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2975–2984
Papa F, Grazia L (1990) Produzione ed utilizzazione di colture starter fresche nell’industria dei salumi (in Italian) . Industrie Alimentari 29:537–540, (in Italian)
Papamanoli E, Tzanetakis N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E, Kotzekidou P (2003) Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Greek dry-fermented sausage in respect of their technological and probiotic properties. Meat Sci 65:859–867
Parente E, Cogan TM (2004) Starter cultures: general aspects. In: Fox PF, McSweeney PLH, Cogan TM Guinee TP (eds) Cheese: chemistry, physics and microbiology, vol. 1: general aspects, 3rd edn. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 123–147
Parente E, Grieco S, Crudele MA (2001) Phenoptypic diversity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented sausages produced in Basilicata (southern Italy). J Appl Microbiol 90:943–952
Rantsiou K, Cocolin L (2006) New developments in the study of the microbiota of naturally fermented sausages as determined by molecular methods: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 108:255–267
Rantsiou K, Urso R, Iacumin L, Cantoni C, Cattaneo P, Comi G, Cocolin L (2005) Culture dependent and independent methods to investigate the microbial ecology of Italian fermented sausages. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1977–1986
Rebecchi A, Crivori S, Sarra PG, Cocconcelli PS (1998) Physiological and molecular techniques for the study of bacterial community development in sausage fermentation. J Appl Microbiol 84:1043–1049
Samelis J, Metaxopoulos J, Vlassi M, Pappa A (1998) Stability and safety of traditional Greek salami—a microbiological ecology study. Int J Food Microbiol 44:69–82
Sawitzki MC, Fiorentini ÂM, Cunha Junior A, Bertol TM, Sant’anna ES (2008) Lactobacillus plantarum AJ2 isolated from naturally fermented sausage and its effects on the technological properties of Milano-type salami. Ciênc Tecnol Aliment 28:709–717
Schillinger U, Lücke FK (1989) Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus sake isolated from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1901–1906
Settanni L, Massitti O, Van Sinderen D, Corsetti A (2005) In situ activity of a bacteriocin-producing Lactococcus lactis strain. Influence on the interactions between lactic acid bacteria during sourdough fermentation. J Appl Microbiol 99:670–681
Settanni L, Tanguler H, Moschetti G, Reale S, Gargano V, Erten H (2011) Evolution of fermenting microbiota in tarhana produced under controlled technological conditions. Food Microbiol 28:1367–1373
Stenlid J, Karlsson JO, Hogberg N (1994) Intra-specific genetic variation in Heterobasidium annosum revealed by amplification of minisatellite DNA. Mycol Res 98:57–63
Svec P, Vancanneyt M, Koort J, Naser SM, Hoste B, Vihavainen E, Vandamme P, Swings J, Björkroth J (2005) Enterococcus devriesei sp. nov., associated with animal sources. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2479–2484
Tagg JR, Dajani AS, Wannamaker LW (1976) Bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 40:722–756
Teuber M, Perreten V, Wirsching F (1996) Antibiotikumresistente Bakterien: eine neue dimension in der Lebensmittelmikrobiologie. Lebensmittel-Technologie 29:182–199
Tichaczek PS, Nissen-Meyer J, Nes IF, Vogel RF, Hammes WP (1992) Characterization of the bacteriocins curvacin A from Lactobacillus curvatus LTH1174 and sakacin P from L. sakei LTH673. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:460–468
Työppönen S, Petäjä E, Mattila-Sandholm T (2003) Bioprotectives and probiotics for dry sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 83:233–244
Urso R, Comi G, Cocolin L (2006) Ecology of lactic acid bacteria in Italian fermented sausages: isolation, identification and molecular characterization. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:671–680
Van Den Braak N, Power E, Anthony R, Endtz H, Verbrugh HA, Van Belkum A (2000) Random amplification of polymorphic DNA versus pulsed field gel electrophoresis of SmaI DNA macrorestriction fragments for typing strains of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:45–52
Weisburg W, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Zambonelli C, Papa F, Romano P, Suzzi G, Grazia L (eds) (1992) Microbiologia dei salumi. Edagricole, Bologna
Zapparoli G, Torriani S, Dellaglio F (1998) Differentiation of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis strains by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 166:324–332
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the student Antonio Vieni (University of Palermo) for his help with microbiological analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francesca, N., Sannino, C., Moschetti, G. et al. Microbial characterisation of fermented meat products from the Sicilian swine breed “Suino Nero Dei Nebrodi”. Ann Microbiol 63, 53–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0444-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0444-5