Abstract
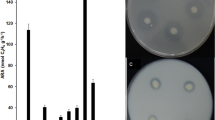
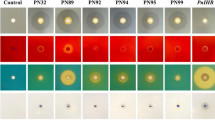
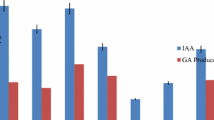
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of selected herbicides (quizalafop-p-ethyl, clodinafop, metribuzin and glyphosate) at one, two and three times the recommended field rates on the plant-growth-promoting (PGP) traits of Pseudomonas putida strain PS9 isolated from the mustard rhizosphere. P. putida strain PS9 was selected for its high herbicide-tolerance and its production of substantial amounts of indole acetic acid, siderophores (salicylic acid and 2,3 dihydroxy benzoic acid) and exo-polysaccharides. It also exhibits HCN and ammonia releasing ability. A progressive, herbicide-concentration-dependent, decline in PGP properties (except exo-polysaccharide production) of P. putida strain PS9 was observed when the strain was grown in the presence of increasing concentrations of each herbicide. Generally, among the selected herbicides, the maximum toxicity to PGP traits of P. putida strain PS9 was shown by quizalafop-p-ethyl at three times the recommended dose. This study concludes that herbicides should be screened before field application for their degree of toxicity to PGP traits of beneficial microorganisms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahemad M, Khan MS (2011) Pesticide interactions with soil microflora: importance in bioremediation. In: Ahmad I, Ahmad F, Pichtel J (eds) Microbes and microbial technology: agricultural and environmental applications. Springer, New York, pp 393–413
Ahemad M, Khan MS (2010) Ameliorative effects of Mesorhizobium sp. MRC4 on chickpea yield and yield components under different doses of herbicide stress. Pestic Biochem Physiol 98:183–190
Ahemad M, Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2009) Remediation of herbicides contaminated soil using microbes. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Musarrat J (eds) Microbes in sustainable agriculture. Nova, New York, pp 261–284
Alexander DB, Zuberer DA (1991) Use of chrome azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 12:39–45
Bakker AW, Schipper B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Bano N, Musarrat J (2003) Isolation and characterization of phorate degrading soil bacteria of environmental and agronomic significance. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:349–353
Barea JM, Azcoόn R, Azcόn-Aguilar C (2004) Mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. In: Varma A, Abbott L, Werner D, Hampp R (eds) Plant surface microbiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 351–371
Bellinaso ML, Greer CW, Peralba MC, Henriques JA, Gaylarde CC (2003) Biodegradation of the herbicide trifluralin by bacteria isolated from soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:191–194
Boldt TS, Jacobsen CS (1998) Different toxic effects of the sulphonylurea herbicides metsulfuron methyl, chlorsulfuron and thifensulfuron methyl on fluorescent pseudomonads isolated from an agricultural soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 161:29–35
Brick JM, Bostock RM, Silversone SE (1991) Rapid in situ assay for indole acetic acid production by bacteria immobilized on nitrocellulose membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:535–538
Buscot F (2005) What are soils? In: Buscot F, Varma S (eds) Microorganisms in soils: roles in genesis and functions. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–18
Cazorla FM, Romero D, Pérez-García A, Lugtenberg BJJ, de Vicente A, Bloemberg G (2007) Isolation and characterization of antagonistic Bacillus subtilis strains from the avocado rhizoplane displaying biocontrol activity. J Appl Microbiol 103:1950–1959
Chen Z, Ma S, Liu LL (2008) Studies on phosphorus solubilizing activity of a strain of phosphobacteria isolated from chestnut type soil in China. Bioresour Technol 99:6702–6707
Chitra RS, Sumitra VC, Yash DS (2002) Effect of different nitrogen sources and plant growth regulators on glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthase activities of radish cotyledons. Bulg J Plant Physiol 28:46–56
Das AC, Debnath A, Mukherjee D (2003) Effect of the herbicides oxadiazon and oxyfluorfen on phosphates solubilizing microorganisms and their persistence in rice fields. Chemosphere 53:217–221
Devi KK, Seth N, Kothamasi S, Kothamasi D (2007) Hydrogen cyanide-producing rhizobacteria kill subterranean termite Odontotermes obesus rambur by cyanide poisoning under in vitro conditions. Curr Microbiol 54:74–78
Dye DW (1962) The inadequacy of the usual determinative tests for the identification of xanthomonas spp. N Z J Sci 5:393–416
Gordon S, Weber RP (1951) The colorimetric estimation of IAA. Plant Physiol 26:192–195
Herman PL, Behrens M, Chakraborty S, Crastil BM, Barycki J, Weeks DP (2005) A three component dicamba O-demethylase from Pseudomonas maltiphilia strain DI-6: gene isolation, characterization and heterologous expression. J Biol Chem 280:24759–24767
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Willams ST (1994) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Jackson ML (1967) Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi
Johnsen K, Jacobsen CS, Torsvik V, Sorensen J (2001) Pesticide effects on bacterial diversity in agricultural soils-a review. Biol Fertil Soils 33:443–453
Kang BG, Kim WT, Yun HS, Chang SC (2010) Use of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria to control stress responses of plant roots. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:179–183. doi:10.1007/s11816-010-0136-1
Kapoor K, Arora L (1996) Observations on growth responses of cyanobacteria under the influence of herbicides. Pollut Res 15:343–351
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahemad M, Oves M, Wani PA (2010) Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing fungi-current perspective. Arch Agron Soil Sci 56:73–98
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA, Ahemad M, Oves M (2009) Functional diversity among plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Musarrat J (eds) Microbial strategies for crop improvement. Springer, Berlin, pp 105–132
King JE (1932) The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J 26:292–297
Kloepper JW, Zablotowick RM, Tipping EM, Lifshitz R (1991) Plant growth promotion mediated by bacterial rhizosphere colonizers. In: Keister DL, Cregan PB (eds) The rhizosphere and plant growth. Kluwer, Netherlands, pp 315–326
Kumar N, Anubhuti BJI, Amb MK (2010) Chronic toxicity of the triazole fungicide tebuconazole on a heterocystous, nitrogen-fixing rice paddy field cyanobacterium, Westiellopsis prolifica Janet. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:1134–1139
Kumar S, Mukerji KG, Lal R (1996) Molecular aspects of pesticide degradation by microorganisms. Crit Rev Microbiol 22:1–26
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Improvement of plant growth and nickel uptake by nickel resistant-plant-growth promoting bacteria. J Hazard Mater 166:1154–1161
Masson-Boivin C, Giraud E, Perret X, Batut J (2009) Establishing nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with legumes: how many rhizobium recipes? Trends Microbiol 17:458–466
Miethke M, Marahiel MA (2007) Siderophore-based iron acquisition and pathogen control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:413–451
Mody BR, Bindra MO, Modi VV (1989) Extracellular polysaccharides of cowpea rhizobia: compositional and functional studies. Arch Microbiol 1:2–5
Ortiz-Hernández ML, Sánchez-Salinas E (2010) Biodegradation of the organophosphate pesticide tetrachlorvinphos by bacteria isolated from agricultural soils in México. Rev Int Contam Ambient 26:27–38
Oves M, Zaidi A, Khan MS, Ahemad M (2009) Variation in plant growth promoting activities of phosphate-solubilizing microbes and factors affecting their colonization and solubilizing efficiency in different agro-ecosystems. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A (eds) Phosphate solubilizing microbes for crop improvement. Nova, New York, pp 247–263
Pham CH, Min J, Gu MB (2004) Pesticide induced toxicity and stress response in bacterial cells. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 72:380–386
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Microbiology 17:362–370
Reeves MW, Pine L, Neilands JB, Balows A (1983) Absence of siderophore activity in Legionella species grown in iron-deficient media. J Bacteriol 154:324–329
Rodrigues EP, Rodrigues LS, de Oliveira ALM, Baldani VLD, Teixeira KRS, Urquiaga S, Reis VM (2008) Azospirillum amazonense inoculation: effects on growth, yield and N2 fixation of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 302:249–261
Sándor Z, Kátai J, Tállai M, Varga A, Balogh E (2007) The effect of herbicides applied in maize on the dynamics of some soil microbial groups and soil enzyme activity. Cereal Res Commun 35:1025–1028
Saravanakumar D, Vijayakumar C, Kumar N, Samiyappan R (2007) PGPR-induced defense responses in the tea plant against blister blight disease. Crop Prot 26:556–565
Tank N, Saraf M (2003) Phosphate solubilization, exopolysaccharide production and indole acetic acid secretion by rhizobacteria isolated from Trigonella foenum-graecum. Indian J Microbiol 43:37–40
Tank N, Saraf M (2010) Salinity-resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria ameliorates sodium chloride stress on tomato plants. J Plant Interact 5:51–58
Tian F, Ding Y, Zhu H, Yao L, Du B (2009) Genetic diversity of siderophore-producing bacteria of tobacco rhizosphere. Braz J Microbiol 40:276–284
Vasileva V, Ilieva A (2007) Effect of presowing treatment of seeds with insecticides on nodulating ability, nitrate reductase activity and plastid pigments content of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.). Agron Res 5:87–92
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Chromium-reducing and plant growth-promoting Mesorhizobium improves chickpea growth in chromium-amended soil. Biotechnol Lett 30:159–163
Zaidi A, Khan MS, Ahemad M, Oves M (2009) Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 56:263–284
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Dr. Nakhat Ara Naqvi, Parijat Agrochemicals, New Delhi, India, for providing technical grade herbicides and the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahemad, M., Khan, M.S. Evaluation of plant-growth-promoting activities of rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida under herbicide stress. Ann Microbiol 62, 1531–1540 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0407-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0407-2