Abstract
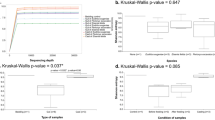
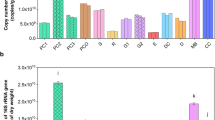
The gut microbiome of earthworms has a complex interdependence with the host. When the soil minerals pass through earthworm’s gut, they may affect the gut microbiota. To gain insight into the response of gut microbiota to the passed minerals, we fed earthworm (Eisenia fetida) on nutrient-poor soil and ore powder, and used high throughput sequencing to characterize the earthworm intestinal microbial community to find evidence for a core bacterial community of the E. fetida. The results showed that earthworms’ gut maintained a core microbiome that appeared in all samples. These core microbiota may play a significant role in a species’ environmental interactions. The composition of intestinal microbiomes varied with substrates. The earthworm guts from two nutrient-poor substrates had similar microbial communities and they were different from nutrient-rich substrate. Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes were more abundant in the gut of earthworms kept on a nutrient-poor substrate such as ore powder or mineral soil than in the gut of earthworms kept in organic-rich compost soil; some of these microorganisms may help earthworms survive in nutrient-poor substrates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aira M, Bybee S, Pérezlosada M, Domínguez J (2015) Feeding on microbiomes: effects of detritivory on the taxonomic and phylogenetic bacterial composition of animal manures. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:817–822
Aira M, Olcina J, Pérez-Losada M, Domínguez J (2016) Characterization of the bacterial communities of casts from Eisenia Andrei fed with different substrates. Appl Soil Ecol 98:103–111
Basker A, Kirkman JH, Macgregor AN (1994) Changes in potassium availability and other soil properties due to soil ingestion by earthworms. Biol Fertil Soils 17:154–158
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DA, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–59. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2276
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Byzov BA, Nechitaylo TY, Bumazhkin BK, Kurakov AV, Golyshin PN, Zvyagintsev DG (2009) Culturable microorganisms from the earthworm digestive tract. Microbiology 78:360–368
Byzov BA, Tikhonov VV, Nechitailo TY, Demin VV (2015) Taxonomic composition and physiological and biochemical properties of bacteria in the digestive tracts of earthworms. Eurasian Soil Science 48:268–275
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Carpenter D, Hodson ME, Eggleton P, Kirk C (2007) Earthworm induced mineral weathering: preliminary results. Eur J Soil Biol 43:S176–S183
Colman DR, Toolson EC, Takacs-Vesbach CD (2012) Do diet and taxonomy influence insect gut bacterial communities? Mol Ecol 21:5124–5137
Dillon RJ, Dillon VM (2004) The gut bacteria of insects: nonpathogenic interactions. Entomology 49:71–92
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Edwards CA (2004) The importance of earthworms as key representatives of the soil fauna. In: Edwards CA (ed) Earthworm ecology, second edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 3–11
Edwards CA, Fletcher KE (1988) Interactions between earthworms and microorganisms in organic-matter breakdown. Agric Ecosyst Environ 24:235–247. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(88)90069-2
Engel P, Moran NA (2013) The gut microbiota of insects - diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:699–735
Flint HJ, Scott KP, Louis P, Duncan SH (2012) The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:577–589
Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, Deming CB, Davis J, Young AC, Bouffard GG, Blakesley RW, Murray PR, Green ED (2009) Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science 324:1190–1192
Hug LA, Baker BJ, Anantharaman K, Brown CT, Probst AJ, Castelle CJ, Butterfield CN, Hernsdorf AW, Amano Y, Ise K (2016) A new view of the tree of life. Nat Microbiol 1:16048
Kersters K, De Vos P, Gillis M, Swings J, Vandamme P, Stackebrandt E (2006) Introduction to the Proteobacteria. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 3–37. doi:10.1007/0-387-30745-1_1
Kim HJ, Shin KH, Hur HG, Cha CJ (2004) Analysis of aerobic and Culturable bacterial community structures in earthworm (Eisenia fetida) intestine. J Appl Biol Chem 47:137–142
Knapp BA, Seeber J, Podmirseg SM, Meyer E, Insam H (2008) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis for analysing the gut microflora of Lumbricus rubellus Hoffmeister under different feeding conditions. Bull Entomol Res 98:271–279
Knapp BA, Podmirseg SM, Seeber J, Meyer E, Insam H (2009) Diet-related composition of the gut microbiota of Lumbricus rubellus as revealed by a molecular fingerprinting technique and cloning. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2299–2307
Kodama N, Kimura T, Yonemura S, Kaneda S, Ohashi M, Ikeno H (2014) Automated analysis of two-dimensional positions and body lengths of earthworms (Oligochaeta); MimizuTrack. PLoS One 9:e97986
Koubová A, Chroňáková A, Pižl V, Sánchez-Monedero MA, Elhottová D (2015) The effects of earthworms Eisenia spp. on microbial community are habitat dependent. Eur J Soil Biol 68:42–55
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R (2008) Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320:1647–1651
Liu D, Lian B, Wang B, Jiang G (2011) Degradation of potassium rock by earthworms and responses of bacterial communities in its gut and surrounding substrates after being fed with mineral. PLoS One 6:e28803
Liu DF, Lian B, Wang B (2016) Solubilization of potassium containing minerals by high temperature resistant Streptomyces sp.isolated from earthworm's gut. Acta Geochimica 35:262–270
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Ma L, Xie Y, Han Z, Giesy JP, Zhang X (2017) Responses of earthworms and microbial communities in their guts to Triclosan. Chemosphere 168:1194–1202. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.079
Magoč T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Maslowski KM, Mackay CR (2011) Diet, gut microbiota and immune responses. Nat Immunol 12:5–9
Needham SJ, Worden RH, McIlroy D (2004) Animal-sediment interactions: the effect of ingestion and excretion by worms on mineralogy. Biogeosciences 1:113–121
Pass DA (2015) The earthworm microbiome. Dissertation, Cardiff University
Plum NM, Filser J (2005) Floods and drought: response of earthworms and potworms (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae, Enchytraeidae) to hydrological extremes in wet grassland. Pedobiologia 49:443–453. doi:10.1016/j.pedobi.2005.05.004
Rudi K, Odegård K, Løkken TT, Wilson R (2009) A feeding induced switch from a variable to a homogenous state of the earthworm gut microbiota within a host population. PLoS One 4:e7528
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Singh A, Singh DP, Tiwari R, Kumar K, Singh RV, Singh S, Prasanna R, Saxena AK, Nain L (2015) Taxonomic and functional annotation of gut bacterial communities of Eisenia Foetida and Perionyx excavatus. Microbiol Res 175:48–56
Sruthy PB, Anjana JC, Rathinamala J, Jayashree S (2013) Screening of earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae) gut as a transient microbial habitat. Adv Zool Bot 1:53–56
Thakuria D, Schmidt O, Finan D, Egan D, Doohan FM (2009) Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: a natural selection process. ISME J 4:357–366 http://www.nature.com/ismej/journal/v4/n3/suppinfo/ismej2009124s1.html
Thakuria D, Schmidt O, Finan D, Egan D, Doohan FM (2010) Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: a natural selection process. ISME J 4:357–366
Zhang W, Chen D, Zhao C (2007) Functions of earthworm in ecosystem biodiversity. Science 15:142–153
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1204405 and 41373078) and Natural Science Foundation of Henan Educational Committee, China (14B180010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Lian, B., Wu, C. et al. A comparative study of gut microbiota profiles of earthworms fed in three different substrates. Symbiosis 74, 21–29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0491-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-017-0491-6