Abstract
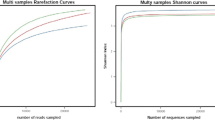
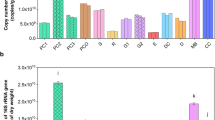
Earthworms and their casts have been widely used for organic waste degradation and plant growth promotion. The microbial communities that reside in the guts and casts of earthworms markedly influence both applications. In the present study, next-generation sequencing was applied to identify the microbial communities in the guts and casts of three epigeic earthworm species, Eudrilus eugeniae, Perionyx excavatus, and Eisenia fetida, reared under two different feeding conditions. A total of 580 genera belonging to 43 phyla were identified. By comparing bacterial diversity among samples divided into groups based on the earthworm species, sample types, and conditions, the beta diversity analysis supported the impact of the sample type and suggested that there was significant dissimilarity of the bacterial diversity between the gut and cast. Besides, bacterial Phylum compositions within the group were compared. The result showed that the top three high relative frequency phyla found in the casts were the same regardless of earthworm species, while those found in the gut depended on both the condition and earthworm species. Focusing on the cellulolytic and plant growth-promoting bacteria, certain cellulolytic bacteria, Paenibacillus, Comamonas, and Cytophaga, were found only in the cast. Citrobacter and Streptomyces aculeolatus were detected only in the guts of earthworms reared in the bedding containing vegetables and bedding alone, respectively. Besides, Actinomadura and Burkholderia were detected only in the gut of E. eugeniae and E. fetida, respectively. The results proved that the microbial composition was affected by sample type, condition, and earthworm species. In addition, the proportion of these beneficial bacteria was also influenced by these factors. Hence, the information from this study can be used as a guide for selecting earthworm species or their casts for more efficient organic waste decomposition and plant growth promotion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46
Bamidele JA, Idowu AB, Ademolu KO, Atayese AO (2014) Microbial diversity and digestive enzyme activities in the gut of earthworms found in sawmill industries in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Rev Biol Trop 62:1241–1249
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Knight R, Huttley GA, Caporaso JG (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0470-z
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857
Brito-Vega H, Espinosa-Victoria D (2009) Bacterial diversity in the digestive tract of earthworms (Oligochaeta). J Biol Sci 9:192–199
Byzov BA, Nechitaylo T, Bumazhkin BK, Kurakov AV, Golyshin PN, Zvyagintsev DG (2009) Culturable microorganisms from the earthworm digestive tract. Microbiology 78:360–368
Callahan B, McMurdie P, Rosen M et al (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583
Chauhan A, Kumar S, Singh AP, Gupta M (2010) Vermicomposting of vegetable wastes with cowdung using three earthworm species Eisenia foetida, Eudrilus eugeniae and Perionyx excavatus. Nat Sci 8:33–43
Domínguez J, Gómez-Brandón M (2012) Vermicomposting: composting with earthworms to recycle organic wastes In: Dr. Sunil Kumar (Ed) Management of Organic Waste, InTech, London, pp 2–20
Gómez-Brandón M, Lores M, Domĭnguez J (2012) Species-specific effects of epigeic earthworms on microbial community structure during first stages of decomposition of organic matter. PLoS ONE 7:e31895. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031895
Grdiša M, Grsic K, Grdisa M (2013) Earthworms — role in soil fertility to the use in medicine and as a food. Invertebr Surviv J 10:38–45
Huang K, Li F, Wei Y, Chen X, Fu X (2013) Changes of bacterial and fungal community compositions during vermicomposting of vegetable wastes by Eisenia fetida. Bioresour Technol 150:235–241
Katheem KS, Jessy RS, Ibrahim MH (2014) Earthworm’s gut as reactor in vermicomposting process: a mini review. Int J Sci Res Publ 4:1–6
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glöckner FO (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e1. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks808
Monroy F, Aira M, Domínguez J (2009) Reduction of total coliform numbers during vermicomposting is caused by short-term direct effects of earthworms on microorganisms and depend on the dose of application of pig slurry. Sci Total Environ 407:5411–5416
Morton JT, Sanders J, Quinn RA et al (2017) Balance trees reveal microbial niche differentiation. Msystems 2:e00162-e1116. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00162-16
Munnoli PM, Teixeira da Silva JA, Bhosle S (2010) Dynamics of the soil-earthworm-plant relationship: a review. Dyn Soil Dyn Plant 4:1–21
Natarajan N, Gajendran M (2014) Vermiconversion of paper mill sludge for recycling the nutrients using earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 8:6–11
Nechitaylo TY, Yakimov MM, Godinho M, Timmis KN, Belogolova E, Byzov BA, Kurakov AV, Jones DL, Golyshin PN (2010) Effect of the earthworms Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa on bacterial diversity in soil. Microb Ecol 59:574–587
Nozaki M, Miura C, Tozawa Y, Miura T (2009) The contribution of endogenous cellulase to the cellulose digestion in the gut of earthworm (Pheretima hilgendorfi: Megascolecidae). Soil Biol Biochem 41:762–769
Parthasarathi K, Jayanthi L, Soniya MA, Sekar J, Basha SA (2014) Efficiency of Perionyx excavatus (perrier) in litter (Anacardium occidium L.) decomposition and nutrient mineralization. Int J Mod Res Rev 2:453–458
Parthasarathi K, Ranganathan LS, Anandi V, Zeyer J (2007) Diversity of microflora in the gut and casts of tropical composting earthworms reared on different substrates. J Environ Biol 28:87–97
Pathma J, Sakthivel N (2012) Microbial diversity of vermicompost bacteria that exhibit useful agricultural traits and waste management potential. Springer plus 1:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-1-26
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2—approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 5:e9490. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009490
R Core Team (2020) A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available from: www.R-project.org
Shamseldin A (2013) The role of different genes involved in symbiotic nitrogen fixation — review. Global J Biotechnol Biochem 8:84–94
Sharma SB, Sayyed RZ, Trivedi MH, Gobi TA (2013) Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springer plus 2:587. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-587
Shweta M (2012) Cellulolysis: a transient property of earthworm or symbiotic/ingested microorganisms? Int J Sci Res Publ 2:1–8
Surat W, Mhuantong W, Sangsrakru D, Chareonviriyaphap T, Arunyawat U, Kubera A, Sittivicharpinyo T, Siripan O, Pootakham W (2016) Gut bacterial diversity in Plasmodium-infected and Plasmodium-uninfected Anopheles minimus. Chiang Mai J Sci 43:427–440
Vijayakumar B, Shanmugasundaram P, Menaga SV, Sujatha R, Anandhi VA (2009) Study on isolation and characterization of earthworm gut flora of Perionyx excavatus. Biomed Pharmacol J 2:403–406
Wang CM, Shyu CL, Ho SP, Chiou SH (2008) Characterization of a novel thermophilic, cellulose-degrading bacterium Paenibacillus sp. strain B39. Lett App Microbiol 47:46–53
Wu G, Lewis J, Hoffmann C, Chen Y-Y, Knight R, Bittinger K, Hwang J, Chen J, Berkowsky R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD (2010) Sampling and pyrosequencing methods for characterizing bacterial communities in the human gut using 16S sequence tags. BMC Microbiol 10:206. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-206
Yuvaraj A, Thangaraj R, Maheswaran R (2019) Decomposition of poultry litter through vermicomposting using earthworm Drawida sulcata and its effect on plant growth. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:7241–7254
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Assoc. Professor Somchai Chantsavang for providing all earthworm samples and suggesting how to rear and identify these earthworm species.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand (ว-ท(ด)112.58).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wonnapinij, P., Sriboonlert, A. & Surat, W. Exploration of microbial communities in the guts and casts of Eudrilus eugeniae, Perionyx excavatus, and Eisenia fetida. Folia Microbiol 67, 329–337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-022-00948-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-022-00948-7