Abstract
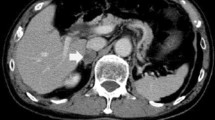
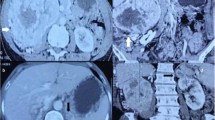
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most lethal urological cancer. It is estimated that one thirds of the patients with localized cancer will develop distant metastasis after radical treatment. Adrenal metastasis of RCC are relatively rare and can be either synchronous or metachronous; ipsilateral, contralateral or bilateral; solitary or part of a massive metastatic spread. Contralateral adrenal metastasis are uncommon. It is well-known that some patients with isolated metastasis may benefit from surgical treatment. However, the optimal diagnosis and treatment of the contralateral adrenal metastasis from RCC has not yet been well defined. Since it was first described, laparoscopic adrenalectomy has become the gold standard for the surgical treatment of most adrenal conditions. The benefits of a minimally invasive approach to adrenal resection such as decreased hospital stay, shorter recovery time, and improved patient satisfaction are widely accepted. We report our experience with laparoscopic management of contralateral, metachronous adrenal metastases from RCC. Patients undergoing radical/partial nephrectomy for RCC were prospectively followed and evaluated regularly for general health status, local recurrence of tumor, and distant metastases. Patients identified to have had adrenal lesion/mass during the follow-up period were evaluated in detail both with imaging as well as endocrinal evaluation for assessment of functional status of these lesions. All these patients underwent laparoscopic adrenalectomy under general anesthesia. During the study period Jan 2006–Dec 2015, 8 patients (7 male and 1 female) with a mean age of 57.8 years underwent laparoscopic adrenalectomy. The mean operating time was 111.2 ± 32.5 min, blood loss was 45 ± 8.6 cm3 and postoperative stay was 37.5 ± 9.3 h. None of the patients had any major complications both early and delayed. The overall survival was 44.62 months. Metachronous, solitary, and contralateral adrenal metastasis from RCC is an extremely rare clinical complication that can occur very late after the radical/partial nephrectomy. Increased use of imaging modalities has led to more efficient and early detection of these lesions. Aggressive surgery remains the treatment of choice in these cases. Laparoscopic adrenalectomy remains a good, safe option with minimal morbidity and short hospital stay.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lau WK, Zincke H, Blute ML et al (2003) Contralateral adrenal metastasis of renal cell carcinoma: treatment, outcome, and a review. BJU Int 91:775–779
Kessler OJ, Mukamel E, Servadio C et al (1998) Metachronous renal cell carcinoma metastasis to the contralateral adrenal gland. J Urol 51:539–543
Plawner J (1991) Results of surgical treatment of kidney cancer with solitary metastasis to contralateral adrenal. Urology 37:233–236
Yuvaraja BT, Mahantshetty U, Chamarajanagar RS, Raibhattanavar SG, Tongaonkar HB (2005) Management of renal cell carcinoma with solitary metastasis. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 3:48
Zakoji H, Miyamoto T, Inuzuka H, Sawada N, Takeda M (2014) Contralateral adrenal metastasis of renal cell carcinoma arising from a horseshoe kidney: an initial case report. Urology Case Reports 2:131–133
Nerli RB, Reddy MN, Guntaka A, Patil SM, Hiremath MB (2010) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for adrenal masses in children. J Paed Urol 4:6
Ravish IR, Nerli RB, Reddy MN, Suresh N, Thakkar R (2007) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for large pheochromocytoma. BJU Int 100:1126–1129
Antonelli A, Cozzoli A, Simeone C, Zani D, Zanotelli T, Portes IE, Cunico SC (2006) Surgical treatment of adrenal metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: a single-centre experience of 45 patients. BJU Int 97:505–508
Dieckmann KP, Wullbrand A, Kroizig G (1996) Contralateral adrenal metastasis in renal cell cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol 30:139–143
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM et al (2009) Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 27:5794–5799
Jason Abel E, Karam JA, Carrasco A, Matin SF (2011) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for metachronous metastases after ipsilateral nephrectomy for renal-cell carcinoma. J Endourol 25:1323–1327
Chkhotua A, Managadze L, Pertia A (2013) Surgical and oncological results of treatment of metastases of renal cell carcinoma to the contralateral adrenal gland. doi:10.5772/53745
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nerli, R.B., Patil, S.M., Pathade, A. et al. Metastases of Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Contralateral Adrenal Gland Managed by Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy. Indian J Surg Oncol 8, 326–330 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-017-0662-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-017-0662-1