Abstract
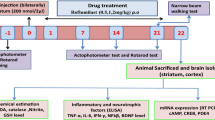
Huntington’s disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant progressive neurodegenerative disorder which affects medium spiny GABAergic neurons mainly in the striatum. Oxidative damage, neuro-inflammation, apoptosis, protein aggregation, and signaling of neurotrophic factors are some of the common cellular pathways involved in HD. Quinolinic acid (QA) causes excitotoxicity by stimulating N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors via calcium overload leading to neurodegeneration. Neuroprotective potential of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) agonists and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors have been well documented in experimental models of neurodegenerative disorders; however, their exact mechanisms are not clear. Therefore, present study has been designed to explore possible neuroprotective mechanism of valproic acid (VPA) and its interaction with rosiglitazone against QA induced HD-like symptoms in rats. Single bilateral intrastriatal QA (200 nmol/2 μl saline) administration significantly caused motor incoordination, memory impairment, oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction (complex I, II, II and IV), cellular alterations [tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), caspase-3, brain derived neurotrophic factor, acetylcholinesterase], and striatal neurodegeneration as compared to sham group. Treatment with rosiglitazone (5, 10 mg/kg) and VPA (100, 200 mg/kg) for 21 days significantly attenuated these behavioral, biochemical, and cellular alterations as compared to control (QA 200 nmol) group. However, VPA (100 mg/kg) treatment in combination with rosiglitazone (5 mg/kg) for 21 days synergized their neuroprotective effect, which was significant as compared to their effects per se in QA-treated animals. The present study provides an evidence of possible interplay of PPARγ agonists and HDAC inhibitors as a novel therapeutic strategy in the management of HD.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baitharu I, Jain V, Deep SN, Hota KB, Hota SK, Prasad D, Ilavazhagan G (2013) Withania somnifera root extract ameliorates hypobaric hypoxia induced memory impairment in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 145(2):431–441
Baquet ZC, Gorski JA, Jones KR (2004) Early striatal dendrite deficits followed by neuron loss with advanced age in the absence of anterograde cortical brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci 24(17):4250–4258
Berman SB, Hastings TG (1999) Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 73(3):1127–1137
Bernardo A, Minghetti L (2008) Regulation of glial cell functions by PPAR-gamma natural and synthetic agonists. PPAR Res 2008:864140
Block F, Kunkel M, Schwarz M (1993) Quinolinic acid lesion of the striatum induces impairment in spatial learning and motor performance in rats. Neurosci Lett 149(2):126–128
Carta AR, Pisanu A, Carboni E (2011) Do PPAR-gamma agonists have a future in Parkinson’s disease therapy? Parkinsons Dis 2011:689181
Chen PS, Wang CC, Bortner CD, Peng GS, Wu X, Pang H, Lu RB, Gean PW, Chuang DM, Hong JS (2007) Valproic acid and other histone deacetylase inhibitors induce microglial apoptosis and attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 149(1):203–212
Chiang MC, Chern Y, Huang RN (2012) PPARgamma rescue of the mitochondrial dysfunction in Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 45(1):322–328
Choi DW (1992) Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol 23(9):1261–1276
Cristiano L, Bernardo A, Ceru MP (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and peroxisomes in rat cortical and cerebellar astrocytes. J Neurocytol 30(8):671–683
Curtis CL, Ross GJ III, Hyde EA, Szymanski RE, Hull JS, Dunbar GL (1992) Intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid cause spatial learning deficits in rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:1602
Dash PK, Orsi SA, Zhang M, Grill RJ, Pati S, Zhao J, Moore AN (2010) Valproate administered after traumatic brain injury provides neuroprotection and improves cognitive function in rats. PLoS ONE 5(6):e11383
Ding G, Fu M, Qin Q, Lewis W, Kim HW, Fukai T, Bacanamwo M, Chen YE, Schneider MD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM, Yang Q (2007) Cardiac peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is essential in protecting cardiomyocytes from oxidative damage. Cardiovasc Res 76(2):269–279
Drew PD, Xu J, Storer PD, Chavis JA, Racke MK (2006) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist regulation of glial activation: relevance to CNS inflammatory disorders. Neurochem Int 49(2):183–189
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Escribano L, Simon AM, Perez-Mediavilla A, Salazar-Colocho P, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2009) Rosiglitazone reverses memory decline and hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor down-regulation in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379(2):406–410
Escribano L, Simon AM, Gimeno E, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, de Maturana RL, Garcia-Osta A, Ricobaraza A, Perez-Mediavilla A, Del Rio J, Frechilla D (2010) Rosiglitazone rescues memory impairment in Alzheimer’s transgenic mice: mechanisms involving a reduced amyloid and tau pathology. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(7):1593–1604
Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Cipolloni PB, Storey E, Beal MF (1993) Excitotoxin lesions in primates as a model for Huntington’s disease: histopathologic and neurochemical characterization. Exp Neurol 119(1):46–71
Ferrante RJ, Kubilus JK, Lee J, Ryu H, Beesen A, Zucker B, Smith K, Kowall NW, Ratan RR, Luthi-Carter R, Hersch SM (2003) Histone deacetylase inhibition by sodium butyrate chemotherapy ameliorates the neurodegenerative phenotype in Huntington’s disease mice. J Neurosci Methods 23(28):9418–9427
Ferrer I, Goutan E, Marin C, Rey MJ, Ribalta T (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington disease. Brain Res 866(1–2):257–261
Furtado JC, Mazurek MF (1996) Behavioral characterization of quinolinate-induced lesions of the medial striatum: relevance for Huntington’s disease. Exp Neurol 138(1):158–168
Ganzella M, Jardim FM, Boeck CR, Vendite D (2006) Time course of oxidative events in the hippocampus following intracerebroventricular infusion of quinolinic acid in mice. Neurosci Res 55(4):397–402
Gardian G, Vecsei L (2004) Huntington’s disease: pathomechanism and therapeutic perspectives. J Neural Transm 111(10–11):1485–1494
Gaur V, Kumar A (2011) Neuroprotective potentials of candesartan, atorvastatin and their combination against stroke induced motor dysfunction. Inflammopharmacology 19(4):205–214
Gauthier LR, Charrin BC, Borrell-Pages M, Dompierre JP, Rangone H, Cordelieres FP, De Mey J, MacDonald ME, Lessmann V, Humbert S, Saudou F (2004) Huntingtin controls neurotrophic support and survival of neurons by enhancing BDNF vesicular transport along microtubules. Cell 118(1):127–138
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177(2):751–766
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126(1):131–138
Hashimoto R, Hough C, Nakazawa T, Yamamoto T, Chuang DM (2002) Lithium protection against glutamate excitotoxicity in rat cerebral cortical neurons: involvement of NMDA receptor inhibition possibly by decreasing NR2B tyrosine phosphorylation. J Neurochem 80(4):589–597
Heneka MT, Landreth GE, Hull M (2007) Drug insight: effects mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in CNS disorders. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3(9):496–504
Hwang J, Kleinhenz DJ, Lassegue B, Griendling KK, Dikalov S, Hart CM (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands regulate endothelial membrane superoxide production. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288(4):C899–C905
Jeong MR, Hashimoto R, Senatorov VV, Fujimaki K, Ren M, Lee MS, Chuang DM (2003) Valproic acid, a mood stabilizer and anticonvulsant, protects rat cerebral cortical neurons from spontaneous cell death: a role of histone deacetylase inhibition. FEBS Lett 542(1–3):74–78
Jiang M, Peng Q, Liu X, Jin J, Hou Z, Zhang J, Mori S, Ross CA, Ye K, Duan W (2013) Small-molecule TrkB receptor agonists improve motor function and extend survival in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22(12):2462–2470
Jin J, Albertz J, Guo Z, Peng Q, Rudow G, Troncoso JC, Ross CA, Duan W (2013) Neuroprotective effects of PPAR-γ agonist rosiglitazone in N171-82Q mouse model of Huntington’s disease. J Neurochem 125(3):410–419
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A, Nehru B (2009) Effect of caffeic acid and rofecoxib and their combination against intrastriatal quinolinic acid induced oxidative damage, mitochondrial and histological alterations in rats. Inflammopharmacology 17(4):211–219
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A (2010a) Pioglitazone ameliorates behavioral, biochemical and cellular alterations in quinolinic acid induced neurotoxicity: possible role of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) in Huntington’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96(2):115–124
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A, Nehru B (2010b) Protective effect of montelukast against quinolinic acid/malonic acid induced neurotoxicity: possible behavioral, biochemical, mitochondrial and tumor necrosis factor-α level alterations in rats. Neuroscience 171(1):284–299
Kalonia H, Kumar P, Kumar A (2011) Attenuation of proinflammatory cytokines and apoptotic process by verapamil and diltiazem against quinolinic acid induced Huntington like alterations in rats. Brain Res 1372:115–126
Kalonia H, Mishra J, Kumar A (2012) Targeting neuro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress by minocycline attenuates quinolinic-acid-induced Huntington’s disease-like symptoms in rats. Neurotox Res 22(4):310–320
Kiaei M, Kipiani K, Chen J, Calingasan NY, Beal MF (2005) Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor-gamma agonist extends survival in transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 191(2):331–336
Kim J-H, Kim S, Yoon I-S, Lee J-H, Jang B-J, Jeong SM, Lee J-H, Lee B-H, Han J-S, Oh S, Kim H-C, Park TK, Rhim H, Nah S-Y (2005) Protective effects of ginseng saponins on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal degeneration in rats. Neuropharmacology 48(5):743–756
Kim HJ, Rowe M, Ren M, Hong JS, Chen PS, Chuang DM (2007) Histone deacetylase inhibitors exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a rat permanent ischemic model of stroke: multiple mechanisms of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321(3):892–901
King TE (1967) Preparation of succinate dehydrogenase and reconstitution of succinate oxidase. In: Estabrook RW, Pullman ME (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 10. Academic Press, New York, pp 322–331
King TE, Howard RL (1967) Preparations and properties of soluble NADH dehydrogenases from cardiac muscle. In: Estabrook RW, Pullman ME (eds) Methods in enzymololgy, vol 10. Academic Press, New York, pp 275–294
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Archiv Biochem Biophy 186(1):189–195
Kukreja RC, Kontos HA, Hess ML, Ellis EF (1986) PGH synthase and lipoxygenase generate superoxide in the presence of NADH or NADPH. Circ Res 59(6):612–619
Kumar A, Prakash A, Pahwa D, Mishra J (2012a) Montelukast potentiates the protective effect of rofecoxib against kainic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103(1):43–52
Kumar A, Sharma N, Gupta A, Kalonia H, Mishra J (2012b) Neuroprotective potential of atorvastatin and simvastatin (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induced Parkinson-like symptoms. Brain Res 1471:13–22
Kumar A, Sharma N, Mishra J, Kalonia H (2013) Synergistical neuroprotection of rofecoxib and statins against malonic acid induced Huntington’s disease like symptoms and related cognitive dysfunction in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 709(1–3):1–12
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2001) Neuropsychological effects of epilepsy and antiepileptic drugs. Lancet 357(9251):216–222
Lampen A, Carlberg C, Nau H (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta is a specific sensor for teratogenic valproic acid derivatives. Eur J Pharmacol 431(1):25–33
Langley B, Gensert JM, Beal MF, Ratan RR (2005) Remodeling chromatin and stress resistance in the central nervous system: histone deacetylase inhibitors as novel and broadly effective neuroprotective agents. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4(1):41–50
Lee EY, Lee JE, Park JH, Shin IC, Koh HC (2012) Rosiglitazone, a PPAR-gamma agonist, protects against striatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by 6-OHDA lesions in the substantia nigra of rats. Toxicol Lett 213(3):332–344
Liu Y, Peterson DA, Kimura H, Schubert D (1997) Mechanism of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction. J Neurochem 69(2):581–593
Luck H (1965) Catalase. In: Hans UB (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 885–894
Mark RJ, Ashford JW, Goodman Y, Mattson MP (1995) Anticonvulsants attenuate amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity, Ca2+ deregulation, and cytoskeletal pathology. Neurobiol Aging 16:187–198
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2008) Glial reactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23(4):474–483
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11(1):47–60
Park SW, Yi JH, Miranpuri G, Satriotomo I, Bowen K, Resnick DK, Vemuganti R (2007) Thiazolidinedione class of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists prevents neuronal damage, motor dysfunction, myelin loss, neuropathic pain, and inflammation after spinal cord injury in adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1002–1012
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Pedersen WA, McMillan PJ, Kulstad JJ, Leverenz JB, Craft S, Haynatzki GR (2006) Rosiglitazone attenuates learning and memory deficits in Tg2576 Alzheimer mice. Exp Neurol 199:265–273
Pemberton LA, Kerr SJ, Smythe G, Brew BJ (1997) Quinolinic acid production by macrophages stimulated with IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and IFN-alpha. J Interf Cytokine Res 17:589–595
Peng GS, Li G, Tzeng NS, Chen PS, Chuang DM, Hsu YD, Yang S, Hong JS (2005) Valproate pretreatment protects dopaminergic neurons from LPS-induced neurotoxicity in rat primary midbrain cultures: role of microglia. Brain Res 134(1):162–169
Perez-De La Cruz V, Carrillo-Mora P, Santamaria A (2012) Quinolinic acid, an endogenous molecule combining excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and other toxic mechanisms. Int J Tryptophan Res 5:1–8
Phiel CJ, Zhang F, Huang EY, Guenther MG, Lazar MA, Klein PS (2001) Histone deacetylase is a direct target of valproic acid, a potent anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, and teratogen. J Biol Chem 276:36734–36741
Poeggeler B, Rassoulpour A, Wu HQ, Guidetti P, Roberts RC, Schwarcz R (2007) Dopamine receptor activation reveals a novel, kynurenate-sensitive component of striatal N-methyl-d-aspartate neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 148:188–197
Ponchaut S, Draye JP, Veitch K, Van Hoof F (1991) Influence of chronic administration of valproate on ultrastructure and enzyme content of peroxisomes in rat liver and kidney. Oxidation of valproate by liver peroxisomes. Biochem Pharmacol 41:1419–1428
Quintanilla RA, Jin YN, Fuenzalida K, Bronfman M, Johnson GV (2008) Rosiglitazone treatment prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in mutant huntingtin-expressing cells: possible role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) in the pathogenesis of Huntington disease. J Biol Chem 283:25628–25637
Reiner A, Wang HB, Del Mar N, Sakata K, Yoo W, Deng YP (2012) BDNF may play a differential role in the protective effect of the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 on striatal projection neurons in R6/2 Huntington’s disease mice. Brain Res 1473:161–172
Rossato JI, Zeni G, Mello CF, Rubin MA, Rocha JB (2002) Ebselen blocks the quinolinic acid-induced production of thiobarbituric acid reactive species but does not prevent the behavioral alterations produced by intra-striatal quinolinic acid administration in the rat. Neurosci Lett 318:137–140
Sadri-Vakili G, Cha JH (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a novel therapeutic approach to Huntington’s disease (complex mechanism of neuronal death). Curr Alzheimer Res 3(4):403–408
Samadi P, Boutet A, Rymar VV, Rawal K, Maheux J, Kvann JC, Tomaszewski M, Beaubien F, Cloutier JF, Levesque D, Sadikot AF (2013) Relationship between BDNF expression in major striatal afferents, striatum morphology and motor behavior in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Genes Brain Behav 12(1):108–124
Sanberg PR, Calderon SF, Giordano M, Tew JM, Norman AB (1989) The quinolinic acid model of Huntington’s disease: locomotor abnormalities. Exp Neurol 105(1):45–53
Santamaria A, Rios C (1993) MK-801, an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, blocks quinolinic acid-induced lipid peroxidation in rat corpus striatum. Neurosci Lett 159(1–2):51–54
Schwarcz R, Whetsell WO Jr, Mangano RM (1983) Quinolinic acid: an endogenous metabolite that produces axon-sparing lesions in rat brain. Science 219(4582):316–318
Schwarcz R, Guidetti P, Sathyasaikumar KV, Muchowski PJ (2010) Of mice, rats and men: revisiting the quinolinic acid hypothesis of Huntington’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 90(2):230–245
Shear DA, Dong J, Gundy CD, Haik-Creguer KL, Dunbar GL (1998) Comparison of intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid and 3-nitropropionic acid for use in animal models of Huntington’s disease. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 22(7):1217–1240
Shehadeh J, Fernandes HB, Mullins MMZ, Graham RK, Leavitt BR, Hayden MR, Raymond LA (2006) Striatal neuronal apoptosis is preferentially enhanced by NMDA receptor activation in YAC transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol Dis 21(2):392–403
Simonian NA, Getz RL, Leveque JC, Konradi C, Coyle JT (1996) Kainic acid induces apoptosis in neurons. Neuroscience 75:1047–1055
Sottocasa GL, Kuylenstierna B, Ernster L, Bergstrand A (1967) An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol 32:415–438
Sudha S, Lakshmana MK, Pradhan N (1995) Chronic phenytoin induced impairment of learning and memory with associated changes in brain acetylcholine esterase activity and monoamine levels. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52(1):119–124
Tuzcu M, Baydas G (2006) Effect of melatonin and vitamin E on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 537(1–3):106–110
Valvassori SS, Rezin GT, Ferreira CL, Moretti M, Goncalves CL, Cardoso MR, Streck EL, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J (2010) Effects of mood stabilizers on mitochondrial respiratory chain activity in brain of rats treated with d-amphetamine. J Psychiatr Res 44(14):903–909
Van den Branden C, Roels F (1985) Peroxisomal beta-oxidation and sodium valproate. Biochem Pharmacol 34(12):2147–2149
Verma R, Mishra V, Gupta K, Sasmal D, Raghubir R (2011) Neuroprotection by rosiglitazone in transient focal cerebral ischemia might not be mediated by glutamate transporter-1. J Neurosci Res 89:1849–1858
Wang L, Ashley-Koch A, Steffens DC, Krishnan KR, Taylor WD (2012) Impact of BDNF Val66Met and 5-HTTLPR polymorphism variants on neural substrates related to sadness and executive function. Genes Brain Behav 11(3):352–359
Wills ED (1966) Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J 99(3):667–676
Yang Y, Qin X, Liu S, Li J, Zhu X, Gao T, Wang X (2011) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ is inhibited by histone deacetylase 4 in cortical neurons under oxidative stress. J Neurochem 118(3):429–439
Zadori D, Geisz A, Vamos E, Vecsei L, Klivenyi P (2009) Valproate ameliorates the survival and the motor performance in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94(1):148–153
Zahler WL, Cleland WW (1968) A specific and sensitive assay for disulfides. J Biol Chem 243(4):716–719
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E (2007) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 81(5–6):294–330
Acknowledgments
The Major Research Project sanctioned to Professor Anil Kumar by University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi is gratefully acknowledged. Mr. Jitendriya Mishra is the project fellow in this project.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing financial interests to declare. There is no conflict of interest between any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, J., Chaudhary, T. & Kumar, A. Rosiglitazone Synergizes the Neuroprotective Effects of Valproic Acid Against Quinolinic Acid-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Targeting PPARγ and HDAC Pathways. Neurotox Res 26, 130–151 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9458-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9458-z