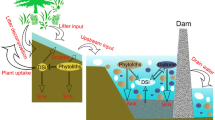
Abstract
Data on dissolved (DSi) and particulate (PSi) silica concentrations, along with DSi and DIN (dissolved inorganic nitrogen) stoichiometry in surface waters were reviewed for the Po river watershed. DSi in the cascade river and lake ecosystems followed clear upstream-downstream gradients. The DSi (77–178 kt Si y − 1) and PSi (879–1,486 kt Si y − 1) loadings from the Po river to the Adriatic Sea display strong inter-annual variability, related with the river discharge. In the lowland river reaches, the DSi to DIN ratio highlighted frequent potential Si limitation, especially in summer during diatom blooms.
Since the Po river watershed is heavily inhabited and exploited with agriculture (~43 % of the total surface) and livestock husbandry (~3.4 × 106 cattle heads), agriculture likely interferes with the natural silicon cycle. We present a preliminary assessment of the biogenic silica (BSi) which was fixed in and harvested with the main crop biomass. In the period 2000–2010, the total BSi in crops was 270–386 kt Si y − 1. Three main cereals (maize, wheat, rice) accounted for 70 % BSi, of which 89 % was accumulated in straw. The quantity of BSi that was annually accumulated in the cereal biomass increased 2–4 folds from 1950 to 2010. We estimated that a great part of the BSi accumulated in straw and fodder was processed by the cattle stock and returned to soil as manure. A large part of the cropland is exposed to erosion and PSi can be exported to canals and rivers at particularly high rates during flash flood events. Recent transformations of either agricultural practices or crop typology probably perturb the Si cycling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lake and river ecosystems, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Humborg C, Ittekkot V, Cociasu A, von Bodungen B (1997) Effect of Danube river dam on black sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure. Nature 386:385–388
Ittekot V, Humborg C, Schäfer P (2000) Hydrological alterations and marine biogeochemistry: a silicate issue? BioScience 50:776–782
Dürr HH, Meybeck M, Hartman J, Laruelle GG, Roubeix V (2011) Global spatial distribution of natural riverine silica inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeosciences 8:597–620
Conley DJ (2002) Terrestrial ecosystems and the global biogeochemical silica cycle. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 16:681–688
Street-Perrot FA, Baker PA (2008) Biogenic silica: a neglected component of the coupled global continental biogeochemical cycles of carbon and silicon. Earth Surf Process Landforms 33:1436–1457
Struyf E, Conley DJ (2012) Emerging understanding of ecosystem silica filters. Biogeochemistry 107:9–18
Struyf E, Smis A, Van Damme S, Meire P, Conley DJ (2009) The global biogeochemical silicon cycle. Silicon 1:207–213
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier J-D (2011) Benefits of plant silicon for crops: a review. Agron Sust Developm. doi:10.1007/S13593-011-0039-8
Cornelis J-T, Ranger J, Iserentant A, Delvaux B (2010) Tree species impact the terrestrial cycle of silicon through various uptakes. Biogeochemistry 97:231–245
Vandevenne F, Struyf E, Clymans W, Meire P (2012) Agricultural silica harvest: have humans created a new loop in the global silica cycle? Front Ecol Environ 10:243–248
Clymans W, Struyf E, Govers G, Vandevenne F, Conley DJ (2011) Anthropogenic impact on amorphous silica pools in temperate soils. Biogeosciences 8:2281–2293
Guntzer F, Keller C, Poulton PR, McGrath SP, Meunier J-D (2012) Long-term removal of wheat straw decreases soil amorphous silica at Broadbalk, Rothamsted. Plant Soil 352:173–184
Struyf E, Conley DJ (2009) Silica: an essential nutrient in wetland biogeochemistry. Front Ecol Environ 7:88–94
Schoelinck J, Bal K, Backx H, Okruszko T, Meire P, Srtuyf E (2010) Silica uptake in aquatic and wetland macrophytes: a strategic choice between silica, lignin and cellulose? New Phytologist 186:385–391
Howarth R, Chan F, Conley DJ, Garnier J, Doney SC, Marino R, Billen G (2011) Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 9:18–26.
Vancappellen P (2003) Biomineralization and global biogeochemical cycles. Rev Mineral Geochem 54:357–381
Zanchettin D, Traverso P, Tomasino M (2008) Po river discharge: a preliminary analysis of a 200 year time series. Clim Change 89:411–433
Viaroli P, Puma F, Ferrari I (2010) The ecological status of the Po river and its watershed: a synthesis. Biol Amb 24:7–19 (in Italian)
Vollenweider RA, Marchetti R, Viviani R (eds) (1992) Marine coastal eutrophication. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bartoli M, Racchetti E, Delconte CA, Sacchi E, Soana E, Laini A, Longhi D, Viaroli P (2012) Nitrogen balance and fate in a heavily impacted watershed (Oglio River, Northern Italy): inquest of the missing sources and sinks. Biogeosciences 9:361–373
IRSA-CNR (1991) The water quality of the Po river in the ’90s. In: Proceedings of the conference IRSA-ACOSEA, Ferrara (Italy), 18–20 April 1991. Water Research Institute, National Research Council, Rome (in Italian)
Justic D, Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Dortch Q (1995) Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 40:339–356
Viaroli P, Ferrari I, Mangia A, Rossi V, Menozzi P (1992) Sensitivity to acidification of Northern Apennine lakes (Italy) in relation to watershed characteristics and wet deposition. In: Mosello R, Whatne BM, Giussani G (eds) Limnology on groups of remote mountain lakes: ongoing and planned activities. Documenta Ist ital Idrobiol, vol 32, pp 93–105
Viaroli P, Ferrari I, Paris G, Rossetti G, Menozzi P (1994) Limnological research on Northern Apennine lakes (Italy) in relation to eutrophication and acidification risk. Hydrobiologia 274:155–162
Antonietti R, Ferrari I, Rossetti G, Tarozzi L, Viaroli P (1988) Zooplankton structure in an oligotrophic mountain lake in Northern Italy. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 23:545–552
Rossetti G (1994) Ecological research on the plankton of a high-altitude lake (Lago Scuro Parmense, Northern Apennines). PhD thesis, University of Parma (in Italian)
Mosello R, Boggero A, Carmine M, Marchetto A, Sassi A, Tartari G (1993) Hydrochemical studies of alpine lakes in the Ossola and Sesia valleys (Pennine and Lepontine Alps). Documenta Ist ital Idrobiol 46:1–436 (in Italian)
Salmaso N (2011) Interactions between nutrient availability and climatic fluctuations as determinants of the long-term phytoplankton community changes in Lake Garda, Northern Italy. Hydrobiologia 660:59–68
Garibaldi L, Anzani A, Marieni A, Leoni B, Mosello R (2003) Studies on the phytoplankton of the deep subalpine Lake Iseo. J Limnol 62:177–189
Giussani B, Dossi C, Monticelli D, Pozzi A, Recchia S (2006) A chemometric approach to the investigation of major and minor ion chemistry in Lake Como (Lombardia, Northern Italy). Ann Chim-Rome 96:1–8
CNR-ISE (2011) Research on the evolution of Lake Maggiore. Limnological aspects. Program 2008–2012. Campaign 2010. International Commission for the Protection of the Italian-Swiss Waters (in Italian)
Soana E, Racchetti E, Laini A, Bartoli M, Viaroli P (2011) Soil budget, net export, and potential sinks of nitrogen in the lower Oglio River watershed (Northern Italy). CLEAN Soil Air Water 39:956–965
Viaroli P, Rossetti G, Bertolini S, Pieri V, Venturelli G, Bernini F, Mozzanica E, Pedrelli C (2004) Environmental quality and conservation issues of lowland springs in the Piacenza and Parma provinces (Italy). Studi Trent Sci Nat Acta Biol 80:181–182 (in Italian)
Laini A (2012) Nitrate recycling and green house gas emission from lowland springs. PhD thesis, University of Parma (in Italian)
Naldi M, Pierobon E, Tornatore F, Viaroli P (2010) Relationships between flood events and formation and variability of nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Po river. Biol Amb 24:59–69 (in Italian)
Colombo G, Camerota C, Bisceglia R, Zaccaria V, Gaiani V, Carrieri A (1991) Spatial and temporal variations of physical and chemical characteristics and phytoplankton biomass in the Sacca di Goro lagoon. In: Bencivelli S, Castaldi N (eds) Integrated study of the Sacca di Goro ecology. Franco Angeli, Milano (in Italian)
Colombo G, Bisceglia R, Zaccaria V, Gaiani V (1994) Spatial and temporal variations of physical and chemical characteristics and phytoplankton biomass in the Sacca di Goro lagoon. In: Bencivelli S, Castaldi N, Finessi D (eds) Sacca di Goro: an integrated ecological study. Franco Angeli, Milano (in Italian)
American Public Health Association (1975) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 14th edn. Am Public Health Assoc Inc., New York
ARPA-SIM. http://www.arpa.emr.it/cms3/documenti/_cerca_doc/meteo/annali_idro/. Last accessed 21 September 2012
ISTAT, http://www.census.istat.it/index_agricoltura.htm and http://agri.istat.it/. Last accessed 21 September 2012
Roy J, Saugier B, Mooney HA (2001) Terrestrial global productivity. Academic Press, San Diego
Hodson MJ, White PJ, Mead A, Broadley MR (2005) Phylogenetic variations in the silicon composition of plants. Ann Bot 96:1027–1046
Antogiovanni M, Sargentini C (1991) Variability in chemical composition of straws. Opt Médit 16:49–53
Rodgers-Gray BS, Shaw MW (2004) Effects of straw and silicon soil amendments on some foliar and stem base diseases in pot grown winter wheat. Plant Physiol 53:733–740
Viaroli P, Fumagalli I (1991) Regeneration of dissolved reactive silica during decomposition of recalcitrant plant tissues in temporary shallow-water environments. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 24:2717–2721
Husnain, Wakatsuki T, Setyorini D, Hermansah, Sato K, Masunaga T (2008) Silica availability in soils and river water in two watersheds on Java Island, Indonesia. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 54:916–927
Wickramasinghe DB, Rowell DL (2006) The release of silicon from amorphous silica and rice straw in Sri Lankan soils. Biol Fertil Soils 42:231–240
Epstein E (1994) The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11–17
Centro Ricerche Produzioni Animali (2001) Zootechnical sewage and manure. User’s manual. Informatore Agrario, p 317 (in Italian)
Racchetti E, Bartoli M, Soana E, Longhi E, Christian RR, Pinardi M, Viaroli P (2011) Influence of hydrological connectivity of riverine wetlands on nitrogen removal via denitrification. Biogeochemistry 103:335–354
Racchetti E, Bartoli M, Ribaudo C, Longhi D, Brito LEQ, Naldi M, Iacumin P, Viaroli P (2010) Short term changes in pore water chemistry in river sediments during the early colonization by Vallisneria spiralis. Hydrobiologia 652:127–137
Rossetti G, Ferrari I, Viaroli P (2009) Role of abiotic and biotic factors in structuring the metazoan plankton community in a lowland river. Riv Res Appl 25:814–835
Tavernini S, Pierobon E, Viaroli P (2011) Physical factors and dissolved reactive silica affect phytoplankton community structure and dynamics in a lowland eutrophic river (Po river, Italy). Hydrobiologia 669:213–225
Sigmon DE, Cahoon LB (1997) Comparative effects of benthic microalgae and phytoplankton on dissolved silica fluxes. Aquat Microb Ecol 13:275–284
Pinardi M, Bartoli M, Longhi D, Mazzocchi U, Laini A, Ribaudo C, Viaroli P (2009) Benthic metabolism and denitrification in a river reach: a comparison between vegetated and bare sediments. J Limnol 68:133–145
Gommes R, Muntau H (1981) Chemical composition of aquatic plants in the Lake Maggiore. Mem ist Ital Idrobiol 38:237–307 (in French)
Viaroli P, Azzoni R, Bartoli M, Giordani G, Naldi M, Nizzoli D (2010) Primary productivity, biogeochemical buffers and factors controlling trophic status and ecosystem processes in Mediterranean coastal lagoons: a synthesis. Adv Oceanogr Limnol 1:271–293
Nizzoli D, Bartoli M, Cooper M, Welsh DT, Underwood GJC, Viaroli P (2007) Implications for oxygen, nutrient fluxes and denitrification rates during the early stage of sediment colonisation by the polychaete Nereis spp. in four estuaries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 75:125–134
Bartoli M, Nizzoli D, Viaroli P, Turolla E, Castaldelli G, Fano AE, Rossi R (2001) Impact of Tapes philippinarum farming on nutrient dynamics and benthic respiration in the Sacca di Goro. Hydrobiologia 455:203–212
Choudhury TMA, Kennedy IR (2005) Nitrogen fertilizer losses from rice soils and control of environmental pollution problems. Commun Soil Sci Plan 36:1625–1639
Guntzer F, Keller C, Meunier J-D (2012) Benefits of plant silicon for crops: a review. Agronomy Sust Developm 32:201–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viaroli, P., Nizzoli, D., Pinardi, M. et al. Factors Affecting Dissolved Silica Concentrations, and DSi and DIN Stoichiometry in a Human Impacted Watershed (Po River, Italy). Silicon 5, 101–114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9137-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-012-9137-8