Abstract
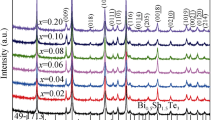
The Bi0.5Na0.02Sb1.48−x In x Te3 alloys (x = 0.02–0.20) were synthesized by vacuum melting and hot pressing methods at 753 K, 60 MPa for 30 min. Effects of Na and In dual partial substitutions for Sb on the thermoelectric properties were investigated from 300 to 500 K. Substituting Sb with Na and In can enhance the Seebeck coefficient effectively near room temperature. The electrical resistivity of the Na and In dual-doping samples is higher within the whole test temperature range. The Bi0.5Na0.02Sb1.48−x In x Te3 samples (x = 0.02, 0.06) play a great role in optimizing the thermal conductivity. As for the Bi0.5 Na0.02Sb1.46In0.02Te3 alloy, the minimum value of thermal conductivity reaches 0.53 W·m−1·K−1 at 320 K. The thermoelectric performance of the Na and In dual-doped samples is greatly improved, and a figure of merit ZT of 1.26 is achieved at 300 K for the Bi0.5Na0.02Sb1.42In0.06Te3, representing 26 % enhancement with respect to ZT = 1.0 of the undoped sample.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tritt TM. Holey and unholey semiconductors. Science. 1999;283(5403):804.
DiSalvo FJ. Thermoelectric cooling and power generation. Science. 1999;285(5428):703.
Bell LE. Cooling, heating, generating power, and recovering waste heat with thermoelectric systems. Science. 2008;321(5895):1457.
Dresselhaus MS, Chen G, Tang MY, Yang RG, Lee H, Wang DZ. New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials. Adv Mater. 2007;19(8):1043.
Poudel B, Hao Q. High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science. 2008;320(5876):634.
Cao YQ, Zhao XB, Zhu TJ, Zhang XB, Tu JP. Syntheses and thermoelectric properties of Bi2Te3/Sb2Te3 bulk nanocomposites with laminated nanostructure. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92(1):143106.
Li YL, Jiang J, Xu GJ, Li W, Zhou LM, Li Y, Cui P. Synthesis of micro/nanostructured p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 and its thermoelectric properties. J Alloys Compd. 2009;480(2):954.
Xie WJ, Tang XF, Yan YG, Zhang QJ, Tritt TM. Unique nanostructures and enhanced thermoelectric performance of melt-spun BiSbTe alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;94(2):102111.
Kim DH, Kim C, Heo SH, Kim HY. Influence of powder morphology on thermoelectric anisotropy of spark-plasma-sintered Bi–Te-based thermoelectric materials. Acta Mater. 2011;59(1):405.
Delaizir G, Bernard-Granger G, Monnier J, Grodzki R, Kim-Hak O, Szkutnik P, Soulier M, Saunier S, Goeuriot D, Rouleau O, Simon J, Godart C, Navone C. A comparative study of spark plasma sintering (SPS), hot isostatic pressing (HIP) and microwaves sintering techniques on p-type Bi2Te3 thermoelectric properties. Mater Res Bull. 2012;47(8):1954.
Liu CJ, Lai HC, Liu YL, Liu LR. High thermoelectric figure-of-merit in p-type nanostructured (Bi, Sb)2Te3 fabricated via hydrothermal synthesis and evacuated-and-encapsulated sintering. J Mater Chem. 2012;22(11):4825.
Yu FR, Xu B, Zhang JJ, Yu DL, He JL, Liu ZY. Structural and thermoelectric characterizations of high pressure sintered nanocrystalline Bi2Te3 bulks. Mater Res Bull. 2012;47(6):1432.
André C, Vasilevskiy D, Turenne S, Masut RA. Increase in the density of states in n-type extruded (Bi(1−x)Sb x )2(Te(1−y)Se y )3 thermoelectric alloys. J Phys D. 2011;44(23):235401.
Ajay SN, Zhao YY, Yu LG, Aik Michael KK, Dresselhaus MS, Xiong QH. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of solution grown Bi2Te3−x Se x nanoplatelet composites. Nano Lett. 2012;12(3):1203.
Kim MY, Yeo YH, Park DH, Oh TS. Thermoelectric characteristics of the (Bi, Sb)2(Te, Se)3 nanocomposites processed with nanoparticle dispersion. Ceramics Int. 2012;38(S1):S529.
Zhu YG, Shen HL, Chen HL. Effects of nano-TiO2 dispersion on thermoelectric properties of Co4Sb11.7Te0.3 composites. Rare Met. 2012;31(1):43.
Gothard N, Ji X, He J, Tritt TM. Thermoelectric and transport properties of n-type Bi2Te3 nanocomposites. J Appl Phys. 2008;103(5):054314.
Chen C, Zhang BP, Liu DW, Ge ZH. Thermoelectric properties of Cu y Bi x Sb2−x−y Te3 alloys fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Intermetallics. 2012;25(6):131.
Ceyda Yelgel Ö, Srivastava GP. Thermoelectric properties of n-type Bi2(Te0.85Se0.15)3 single crystals doped with CuBr and SbI3. Phys Rev B. 2012;85(12):125207.
Soliman LI, Nassary MM, Shaban HT, Salwa AS. Influence of Se on the electron mobility in thermal evaporated Bi2(Te1−x Se x )3 thin films. Vacuum. 2010;85(3):358.
Cui JL, Xue HF, Xiu WJ, Mao LD, Ying PZ, Jiang L. Crystal structure analysis and thermoelectric properties of p-type pseudo-binary (Al2Te3) x –(Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3)1−x alloys prepared by spark plasma sintering. J Alloys Compd. 2008;460(1–2):426.
Du BL, Li H, Tang XF. Enhanced thermoelectric performance in Na-doped p-type nonstoichiometric AgSbTe2 compound. J Alloys Compd. 2011;509(5):2039.
Chung DY, Lordanidis L, Choi KS, Kanatzidis MG. Complex chalcogenides as thermoelectric materials: a solid state chemistry approach. Bull Korean Chem. 1998;19(12):1283.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51161009) and the Research Project of Jiangxi Provincial Education Department (No. GJJ13722 and GJJ11615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, XK., Hu, KG., Ma, DH. et al. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Bi0.5Na0.02Sb1.48−x In x Te3 alloys fabricated by vacuum melting and hot pressing. Rare Met. 34, 770–775 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0124-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0124-z