Abstract
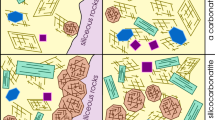
The Zhenyuan (镇沅) gold orefield is located in the Ailaoshan (哀牢山) gold belt, Sanjiang (三江) metallogenic region, China. The fluid inclusions (FIs) in mineralized quartz samples, collected from four deposits, i.e., Laowangzhai (老王寨), Donggualin (冬瓜林), Kudumu (库独木), and Daqiaoqing (搭桥箐), in the orefield, were studied to reveal ore-forming process. Only aqueous-type and H2O-NaCl-type FIs were observed in the samples. Two generations of FIs are identified due to the spatial occurrences of FIs in host minerals. The early generation is located in the internal zone of quartz crystal, and it has higher homogenization temperatures varying from 180 to 255 °C and salinities ranging from 8.7% to 11%; the late generation, often with beating bubbles under room temperature, is developed in the quartz margin, its homogenization temperatures is lower within 95 to 160 °C. After elimination of the late generation of FIs, early generation FIs compositions were tested. Gaseous phases in the FIs were H2O and CO2, with low contents of N2, CH4, and C2H6, and the liquids mainly contains Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, and SO4 2−. The reappraisal of the previously published hydrogen and oxygen isotope results suggested that the early generation of ore-forming fluid was mainly primary magma hydrothermal, while the late generation fluid contains large amounts of meteoric water. Thus, the result showed that Zhenyuan gold orefield may differ from typical orogenic deposits, which contains abundant CO2-dominated FIs. The two generations FIs developed as quartz grew displaying a continuous evolution of the ore-forming fluids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bi, X. W., Hu, R. Z., He, M. Y., 1997. Characteristics of Ore-Forming Fluid of Three Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan Gold Mineralization Belt. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 17(4): 435–441 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Bian, Q. T., She, H. Q., 1998. Preliminary Study on the Relationship between the Crust-Mantle Structure and the Formation of Laowangzhai Superlarge Gold Deposit. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 41(6): 561–569
Bodnar, R. J., 1993. Revised Equation and Stable for Determining the Freezing Point Depression of H2O-NaCl Solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57: 683–684
Burnard, P. G., Hu, R. Z., Turner, G., et al., 1999. Mantle Crustal and Atmospheric Noble Gases in Ailaoshan Gold Deposits, Yunnan Province, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(10): 1595–1604
Deng, J., Liu, W., Sun, Z. S., et al., 2003. Evidence of Mantle-Rooted Fluids and Multi-Level Circulation Ore-Forming Dynamics: A Case Study from the Xiadian Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(Suppl.): 123–134
Deng, J., Wang, Q. F., Sun, Z. S., 2002. Origin of Gold-Bearing Fluid and Its Initiative Localization Mechanism in Xiadian Gold Deposit, Shandong Province. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 21(3): 282–288
Deng, J., Yang, L. Q., Ge, L. S., et al., 2010a. Character and Post-Ore Changes, Modifications and Preservation of Cenozoic Alkali-Rich Porphyry Gold Metallogenic System in Western Yunnan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1633–1645 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Deng, J., Hou, Z. Q., Mo, X. X., et al., 2010b. Superimposed Orogenesis and Metallogenesis in Sanjiang Tethys. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 37–42 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Deng, J., Yang, L. Q., Wang, C. M., 2011. Research Advances of Superimposed Orogenesis and Metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2501–2509 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Field, C. W., Fifarek, R. H., 1985. Light Stable-Isotopes Systematics in the Epithermal Environment. Reviews in Economic Geology, 2: 99–128
Goldfarb, R. J., Ayuso, R., Miller, M. L., et al., 2004. The Late Cretaceous Donlin Greek Gold Deposit, Southwestern Alaska: Controls on Epizonal Ore Formation. Economic Geology, 99: 643–671
Guo, C. Y., Gao, B. F., Liu, X. F., et al., 2009. Characteristics and Their Geological Significance of Rare Earth Elements in Chang’an Gold Deposit, Yunnan Province. Gold, 30(1): 7–11 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Hou, Z. Q., Khin, Z., Pan, G. T., et al., 2007. Sanjiang Tethyan Metallogenesis in S.W. China: Tectonic Setting, Metallogenic Epochs and Deposit Types. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1–4): 48–87
Hu, R. Z., Bi, X. W., He, M. Y., et al., 1998. Mineralizer Constraintion Gold Mineralization of Ailaoshan Gold Belt. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 41(Suppl.): 74–82
Hu, Y. Z., Tang, S. C., Wang, H. P., et al., 1995. Geology of Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. 154–219 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Huang, Z. L., Liu, C. Q., Yang, H. L., et al., 2002. The Geochemistry of Lamprophyres in the Laowangzhai Gold Deposits, Yunnan Province, China: Implications for Its Characteristics of Source Region. Geochemical Journal, 36: 91–112
Huang, Z. L., Wang, L. K., 1997. The Petrochemistry of Lamprophyres in Laowangzhai Gold Orefeild, Yunnan. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, 17(4): 324–332 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, D. M., Cao, Z. M., Qin, G. J., et al., 1998. Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan Ophiolitic Mélange Zone. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. 1–17 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Li, Y., Jin, S. C., Yu, G. J., 1998. Isotope Geochemistry and Genesis of Mojiang Gold Deposit, Yunnan. Geology Geochemistry, 26(4): 15–20 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Sun, X. M., Zhang, Y., Xiong, D. X., et al., 2009. Crust and Mantle Contributions to Gold-Froming Process at the Daping Deposit, Ailaoshan Gold Belt, Yunnan, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 36: 235–249
Xiong, D. X., Sun, X. M., Shi, G. Y., 2007. Geochemistry and Metallogenic Model of Ailaoshan Cenozoic Organic Gold Belt in Yunnan Province, China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. 80–98 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, L. Q., Deng, J., Zhao, K., et al., 2011. Tectono-Thermochronology and Gold Mineralization Events of Orogenic Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan Orogenic Belt, Southwest China: Geochronological Constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2519–2532 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, X. H., 2005. A Study on the Genesis of Laowangzhai Gold Deposit of Structural Altered Rock Type in Zhenyuan County. Yunnan Geology, 24(4): 371–378 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Ying, H. L., Liu, B. G., 2000. The Trace Element and Isotope Composition and Their Restriction in the Origin Mineralization Matter of Laowangzhai Gold Ore Deposit, Yunnan. Gold Science and Technology, 8(2): 15–20 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, J. W., Wu, J., Li, C. S., et al., 2010. Geological Features and Genesis of Laowangzhai Gold Deposit in Zhenyuan County, Yunnan. Gold, 31(6): 19–23 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, J., Deng, J., Li, S. H., et al., 2010. Petrological Characteristics of Magmatites and Their Relationship with Gold Mineralization in the Chang’an Gold Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1740–1750 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, L. G., Chen, Z. S., Liu, J. X., et al., 1995. Two Stages of Water-Rock Isotope Interaction Theory and the Prospecting Usage. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. 4–10 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, Z. L., Zhang, S. F., Yuan, H. H., et al., 1987. An Isotope Geology and Origin Study of the Jinchang Gold Deposit, Mojiang, Yunnan. Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 14(4): 29–41 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu, H. P., Wang, L. J., Liu, J. M., 2003. Determination of Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer for Gaseous Composition of Fluid Inclusion from Different Mineralization Stages. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(2): 314–318 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Key Basic Research Development Program (Nos. 2009CB421006, 2009CB421008), the Century Training Program Foundation for the Talents of Humanities and Social Science by the State Education Commission (No. NCET-09-0710), and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities of China (No. B07011).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Wang, Q., Sun, X. et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluid in the Zhenyuan gold orefield, Yunnan Province, China. J. Earth Sci. 24, 203–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-013-0323-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-013-0323-4