Abstract
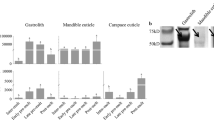
Fish scales are a potential source of collagen for fabricating scaffolds for cells during tissue engineering because fish collagen has a low risk of zoonosis. Since the assembly of collagen fibrils has a significant impact on the functionality of the scaffold, the ability to replicate the fibril assembly of human tissues is critical. To determine the mechanism of fish collagen fibril assembly, we first identified non-collagenous proteins (NCPs), the potential regulators of fibril assembly in vivo, and then used tandem mass spectrometry to analyze the NCPs contained in the basal plates of goldfish Carassius auratus scales, a collagenous plate which is characterized by a plywood-like assembly of collagen fibrils similar to that found in the cornea. We identified a 19-kDa acidic protein as dermatopontin, the NCP which is a possible regulator of fibril assembly in the mammalian cornea. We cloned a goldfish dermatopontin cDNA of 1,074 bp containing an open reading frame encoding 196 amino acids. Reverse transcription-PCR revealed that dermatopontin mRNA was expressed in a wide range of tissues, including scale, skin, fin, eye, and skeletal muscle. In situ hybridization revealed that dermatopontin mRNA was expressed primarily in the basal plate-producing hyposquamal scleroblasts of the scales, suggesting that the dermatopontin is linked to the collagen fibril assembly of the basal plate.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takagi Y, Ura K (2007) Teleost fish scales: a unique biological model for the fabrication of materials for corneal strama regeneration. J Nanosci Nanotech 7:757–762
Schnaper HW, Kleinman HK (1993) Regulation of cell function by extracellular matrix. Pediatr Nephrol 7:96–104
Streuli C (1999) Extracellular matrix remodelling and cellular differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:634–640
Kresse H, Schönherr E (2001) Proteoglycans of the extracellular matrix and growth control. J Cell Physiol 189:266–274
Marastoni S, Ligresti G, Lorenzon E, Colombati A, Mongiat M (2008) Extracellular matrix: a matter of life and death. Connect Tissue Res 49:203–206
Parenteau-Bareil R, Gauvin R, Berthod F (2010) Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 3:1863–1887
Yamada S, Yamamoto K, Ikeda T, Yanagiguchi K, Hayashi Y (2014) Potency of fish collagen as a scaffold for regenerative medicine. BioMed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2014/302932
Parfitt GJ, Pinali C, Young RD, Quantock AJ, Knupp C (2010) Three-dimensional reconstruction of collagen-proteglycan interactions in the mouse corneal stroma by electron tomography. J Struct Biol 170:392–397
Cooper LJ, Bentley AJ, Nieduszynski IA, Talabani S, Thomson A, Utani A, Shinkai H, Fullwood NJ, Beown GM (2006) The role of dermatopontin in the stromal organization of the cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 47:3303–3310
Perkins DN, Pappin DJ, Creasy DM, Cottrell JS (1999) Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 20:3551–3567
Ohira Y, Shimizu M, Ura K, Takagi Y (2007) Scale regeneration and calcification in the goldfish Carassius auratus: quantitative and morphological process. Fish Sci 73:46–54
Morse A (1945) Formic acid-sodium citrate decalcification and butyl alcohol dehydration of teeth and bones for sectioning in paraffin. J Dental Res 24:143–153
MacBeath JRE, Shackleton DR, Hulmes DJS (1993) Tyrosine-rich acidic matrix protein (TRAMP) accelerates collagen fibril formation in vitro. J Biol Chem 268:19826–19832
Takeda U, Utani A, Wu J, Adachi E, Koseki H, Taniguchi M, Matsumoto T, Ohashi T, Sato M, Shinkai H (2002) Targeted disruption of dermatopontin causes abnormal collagen fibrillogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 119:678–683
Tan Y, Iimura K, Sato T, Ura K, Takagi Y (2013) Spatiotemporal expression of the dermatopontin gene in zebrafish Danio rerio. Gene 516:277–284
Okamoto O, Fujiwara S (2006) Dermatopontin, a novel player in the biology of the extracellular matrix. Connect Tissue Res 47:177–189
Takeuchi T (2010) Structual comparison of dermatopontin amino acid sequences. Biologia 65:874–879
Cronshaw AD, Macbeath JRE, Shackleton DR, Collins JF, Fothergill-Gilmore LA, Hulmes DJS (1993) TRAMP (Tyrosine Rich Acidic Matrix Protein), a protein that co-purifies with lysil oxidase from porcine skin: identification of TRAMP as the dermatan sulphate proteoglycan-associated 22 K extracellular matrix protein. Matrix 13:255–256
Neame PJ, Choi HU, Rosenberg LC (1989) The isolation and primary structure of a 22-kDa extracellular matrix protein from bovine skin. J Biol Chem 264:5474–5479
Forbes EG, Cronshaw AD, MacBeath JRE, Hulmes DJS (1994) Tyrosine-rich acidic matrix protein (TRAMP) is a tyrosine-sulphated and widely distributed protein of the extracellular matrix. FEBS Lett 351:433–436
Superti-Furga A, Rocchi M, Schäfer BW, Gitzelmann R (1993) Complementary DNA sequence and chromosomal mapping of a human proteoglycan-binding cell-adhesion protein (dermatopontin). Genomics 17:463–467
Beanes SR, Danng C, Soo C, Ting K (2003) Skin repair and scar formation: the central role for TGF-β. Exp Rev Mol Med 5:1–11
Okamoto O, Hozumi K, Katagiri F, Takahashi N, Sumiyoshi H, Matsuo N, Yoshioka H, Nomizu M, Fujiwara S (2010) Dermatopontin promotes epidermal keratinocyte adhesion via α3β1 integrin and a proteoglycan receptor. Biochemistry 49:145–155
Kagan MH, Li W (2003) Lysyl oxidase: properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J Cell Biochem 88:660–672
Trackman CP (2005) Diverse biological functions of extracellular collagen processing enzymes. J Cell Biochem 96:927–937
Schaefer L, Iozzo R (2008) Biological functions of the small leucine-rich proteoglycans: from genetics to signal transduction. J Biol Chem 283:21305–21309
Corsi A, Xu T, Chen X-D, Boyde A, Liang J, Mankani M, Sommer B, Iozzo RV, Eichstetter I, Gheron Robey P, Bianco P, Young MF (2002) Phenotypic effects of biglycan deficiency are linked to collagen fibril abnormalities, are synergized by decorin deficiency, and mimic Ehlers–Danlos-like changes in bone and other connective tissues. J Bone Miner Res 17:1180–1189
Zhang G, Chen S, Goldoni S, Calder B, Simpson H, Owens R, McQuillan D, Young M, Iozzo R, Birk D (2009) Genetic evidence for the coordinated regulation of collagen fibrillogenesis in the cornea by decorin and biglycan. J Biol Chem 284:8888–8897
Jiang X, Ye M, JIang X, Liu G, Feng S, Cui L, Zou H (2007) Method development of efficient protein extraction in bone tissue for proteome analysis. J Proteome Res 6:2287–2294
Brittijn SA, Brittijn A, Duivesteijn SJ, Belmamoune M, Bertens LFM, Bitter W, De Bruijin J, Champagne DL, Cuppen E, Flik G, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Janssen RAJ, De Jjong IML, De Kloet ER, Kros A, Meijer AH, Mets JR, Van Der Sar AM, Schaafl MJM, Schlute-Merker S, Spainkll HP, Tak PP, Vereek FJ, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Vonk FJ, Witte F, Yuan H, Richardson M (2009) Zebrafish development and regeneration: new tools for biomedical research. Int J Dev Biol 53:835–850
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants in Aid from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (Nos. 18380109, 21380116, 24380101). Authors thank technical assistance by Ms. Michitatsu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komatsu, N., Ogawa, N., Iimura, K. et al. Identification, cDNA cloning, and expression analysis of dermatopontin in the goldfish Carassius auratus . Fish Sci 80, 1249–1256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0814-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-014-0814-y