Abstract
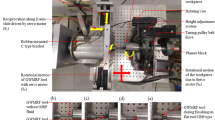
This work presents the characteristics of advanced abrasion based hybrid machining process consisting of electrochemical dissolution and magnetic abrasive machining process. The cylindrical electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining (C-EMAM) setup was developed and mounted as an attachment on lathe for high efficiency machining of cylindrical jobs. Experiments were conducted to explore the performance of the process on AISI-304 stainless steel tubes using unbonded magnetic abrasives. The effect of various process parameters viz. rotational speed of the workpiece, current to the electromagnet, electrolytic current and frequency of vibration on material removal and surface roughness were investigated. The electrochemical process has major contribution in material removal, whereas magnetic abrasive machining helps in reduction in surface roughness. This process has higher machining efficiency particularly at high value of electrolytic current and high rotational speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C-EMAM:
-
Cylindrical electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining
- MAM:
-
Magnetic abrasive machining
- MAP:
-
Magnetic abrasive particle
- MAF:
-
Magnetic abrasive finishing
- UMAs:
-
Unbonded magnetic abrasives
- FP:
-
Ferromagnetic particle
- ECD:
-
Electrochemical dissolution
- HRC:
-
Rockwell hardness
- MR:
-
Material removal
- Ra:
-
Arithmetic mean surface roughness
References
Shinmura, T., Takazawa, K., Hatano, E., and Aizawa, T., “Study on Magnetic Abrasive Process-Finishing Characteristics,” Bull. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 347–348, 1984.
Shinmura, T., Takazawa, K., Hatano, E., and Aizawa, T., “Study on Magnetic Abrasive Process-Process Principle and Finishing Possibility,” Bull. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 54–55, 1985.
Shinmura, T., Takazawa, K., and Hatano, E., “Study on Magnetic Abrasive Finishing-Effect of Machining Fluid on Finishing Characteristics,” Bull. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 20, No. 1, pp. 52–54, 1986.
Shinmura, T., Takazawa, K., and Hatano, E., “Study on Magnetic Abrasive Finishing-Effect of various types of Magnetic Abrasives on Finishing Characteristics,” Bull. Jpn. Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 139–141, 1987.
Chang, G. W., Cheng, T. J., and Hsu, R. T., “Study on cylindrical Magnetic Abrasive Finishing using Unbonded Magnetic Abrasives,” Int. J. of Mach. Tools and Manuf., Vol. 42, pp. 575–583, 2002.
Im, I. T., Mun, S. D., and Oh, S. M., “Micro machining of a STS 304 bar by magnetic abrasive finishing,” J. of Mech. Sci. and Technol., Vol. 23, pp. 1982–1988, 2009.
Tsai, L., Wang, A. C., Chou, S. H., and Zhong, C. J., “Investigating of Flexible Self-Sharpening and Optimal Parameters in Magnetic Finishing with Gel Abrasive,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 5, pp. 655–661, 2012.
Sidpara, A. and Jain, V. K., “Experimental Investigations into Surface Roughness and Yield Stress in Magnetorheological Fluid Based Nano-finishing Process,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 6, pp. 855–860, 2012.
Fang, J. C., Jin, Z. J., Xu, W. J., and Shi, Y. Y., “Magnetic Electrochemical Finishing Machining,” J. of Mater. Process. Technol., Vol. 129, pp. 283–287, 2002.
Yan, B. H., Chang, G. W., Cheng, T. J., and Hsu, R. T., “Electrolytic Magnetic Abrasive Finishing,” Int. J. of Mach. Tools and Manuf., Vol. 43, pp. 1355–1366, 2003.
EI-Taweel, T. A., “Modelling and analysis of hybrid electrochemical turning-magnetic abrasive finishing of 6061 Al/Al2O3 composite,” Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., Vol. 37, pp. 705–714, 2008.
Seo, M. and Chiba, M., “Nano-mechano-electrochemistry of passive metal surfaces,” Electrochimica Acta., Vol. 47, pp. 319–325, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Judal, K.B., Yadava, V. Electrochemical magnetic abrasive machining of AISI304 stainless steel tubes. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 14, 37–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0006-1