Abstract
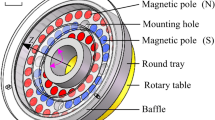
A magnetic abrasive finishing process is a method of non-traditional precision machining in which the finishing process is completed using magnetic force and magnetic abrasives. In this research, a STS 304 cylindrical workpiece was finished using a magnetic abrasive finishing process at 30,000 rpm, and the roughness, roundness, and changes in the micro-diameter were investigated. The study showed that it is possible to control the micro-diameter and weight of the STS 304 cylindrical workpiece by using a near linear approach. Surface roughness as fine as 0.06 µm (Ry) and roundness as fine as 0.12 µm (LZS) were achievable by using a diamond paste with 1 µm particles. Vibrational motion applied to the workpiece improved the surface roughness. The improvement of the surface roughness was achieved because the vibrational motion effectively removes unevenness in the rotational direction and the direction orthogonal to it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. K. Park and T. Shimura, A study of a new precision finishing process for inside surface of silicon nitride fine ceramic pipe by application of magnetic abrasive machining, Annals of the KSME, 25(1) (2001) 47–53.
V. S. Maiboroda, O. V. Stepanov, N. L. Taranenko and V. Y. Vermenko, Rheological characteristics of magnetic-abrasive powers in a magnetic field, Power Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 33(1–2) (1994) 57–60.
T. Shinmura, K. Takazawa, E. Hatano and M. Matsunaga, Study on magnetic-abrasive finishing (rounding condition and its confirmation by experiment), Annals of the CIRP, 39(1) (1990), 325–328.
C. T. Lin, L. D. Yang and H. M. Chow, Study of magnetic abrasive finishing in free-form surface operations using the Taguchi method, International journal of advanced manufacturing technology, 34 (1992) 122–130.
H. Yamaguchi and T. Shimura, Study of an internal magnetic abrasive finishing using a pole rotation system, Precision Engineering, 24(3) (2000) 237–244.
T. Shimura and H. Yamaguchi, Precision surface finishing of Si3N4 fine ceramic components by the application of magnetic abrasive machining process, Annals of the JSPE, 67(112) (2001) 1986–1990.
S. Yin and T. Shinmura, Study of vibration-assisted magnetic abrasive finishing process (effects of vibration on cylindrical finishing characteristics and its mechanism), Annals of the JSME, 67(661) (2002) 258–264.
M. Vahdati and A. Shokuhfar, A trend toward abrasive nano finishing of plane surfaces with magnetic field energy, Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik, 39(2) (2008) 167–170.
S. Jha, V. K. Jain and R. Komanduri, Effect of extrusion pressure and number of finishing cycles on surface roughness in magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process, The Internal Journal of Advanced The Manufacturing Technology, 33 (2007) 725–729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Ik-Tae Im received the B.S., M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea, in 1993, 1995 and 1999, respectively. He has been a visiting scientist at the Department of Materials Engineering, the University of Tokyo, Japan, where he studied on the film growth during the MOCVD process. His research interests include the numerical modeling on the transport phenomena in various materials processing. He is a professor at the Division of Mechanical Design Engineering at Chonbuk National University in Jeonju, Korea.
Sang Don Mun received the B.S. degree and M.S. in Precision Mechanical Engineering from Chonbuk National University, Korea, in 1991 and 1993, respectively. He then received the Ph.D. in Precision Mechanical Engineering at the same university in 1997. Dr. Mun is currently a Professor at the Division of Mechanical Design Engineering at Chonbuk National University in Jeonju, Korea. His research interests include magnetic abrasive finishing, tool wear, and micro machining.
Seong Mo Oh received his B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Wonkwang University, Korea, in 1992. He then received his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from Wonkwang in 1994 and 2000 respectively. Dr. Oh is currently a Lecturer at the Division of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering at Wonkwang University in Jeonbuk, Korea. Dr. Oh’s research interests include tribology, functional surfaces, and micromachining.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, IT., Mun, S.D. & Oh, S.M. Micro machining of an STS 304 bar by magnetic abrasive finishing. J Mech Sci Technol 23, 1982–1988 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0524-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0524-z