Abstract
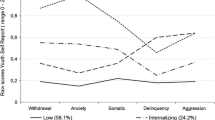
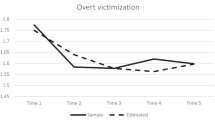
The current study explored the concurrent and longitudinal association between internalizing behaviors, externalizing behaviors, and peer victimization among children with and without ADHD. Eighty children (42 ADHD, 38 non-ADHD) ages 8–12 participated in the present study conducted over a 6-month period. During the baseline session, parents completed a structured diagnostic interview and the Vanderbilt ADHD Parent Rating Scale to determine whether their child met criteria for ADHD, and the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) to assess their child’s internalizing and externalizing behaviors; children completed the Perception of Peer Support Scale (PPSS) to assess experiences of peer victimization. At the 6-month follow-up session, parents completed the CBCL and children completed the PPSS. Concurrently, internalizing behaviors were associated with peer victimization among children with and without ADHD; ADHD moderated this relation, such that internalizing behaviors were more strongly related to peer victimization among children with ADHD. Longitudinally, internalizing behaviors at baseline predicted peer victimization at 6-month follow-up; however, further analyses demonstrated there was a covarying change in internalizing behaviors and peer victimization. These findings suggest internalizing behaviors are related to peer victimization concurrently, and over time, and are associated with increased risk for peer victimization in the presence of ADHD. Additionally, internalizing behaviors and peer victimization appear to share a dynamic relationship; that is, decreases in internalizing behaviors predict similar decreases in peer victimization. No significant relations were observed between externalizing behaviors and peer victimization. Implications and limitations are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach TM, Rescorla L (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Burlington, University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry
Alloy LB, Abramson LY (1988) Depressive realism: four theoretical perspectives. In: Alloy LB (ed) Cognitive processes in depression. Guilford Press, New York, pp 223–265
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Association Publishing, Washington, DC
August GJ, Realmuto GM, MacDonald AW III, Nugent SM, Crosby R (1996) Prevalence of ADHD and comorbid disorders among elementary school children screened for disruptive behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 24(5):571–595
Barkley RA (ed) (2014) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a handbook for diagnosis and treatment. Guilford Publications, New York
Betts LR, Houston JE, Steer OL (2015) Development of the multidimensional peer victimization scale–revised (MPVS-R) and the multidimensional peer bullying scale (MPVS-RB). J Genet Psychol 176(2):93–109
Biederman J, Faraone SV, Chen WJ (1993) Social adjustment inventory for children and adolescents: concurrent validity in ADHD children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 32(5):1059–1064
Boivin M, Hymel S, Bukowski WM (1995) The roles of social withdrawal, peer rejection, and victimization by peers in predicting loneliness and depressed mood in childhood. Dev Psychopathol 7(04):765–785
Bollmer JM, Milich R, Harris MJ, Maras MA (2005) A friend in need the role of friendship quality as a protective factor in peer victimization and bullying. J Interpers Violence 20(6):701–712
Bond L, Carlin JB, Thomas L, Rubin K, Patton G (2001) Does bullying cause emotional problems? A prospective study of young teenagers. BMJ 323(7311):480–484
Cantwell DP (1996) Attention deficit disorder: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 35(8):978–987
Card NA, Hodges EV (2008) Peer victimization among schoolchildren: correlations, causes, consequences, and considerations in assessment and intervention. School Psychol Q 23(4):451
Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Newman DL, Silva PA (1996) Behavioral observations at age 3 years predict adult psychiatric disorders: longitudinal evidence from a birth cohort. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53(11):1033–1039
Cotter RB, Burke JD, Stouthamer-Loeber M, Loeber R (2005) Contacting participants for follow-up: how much effort is required to retain participants in longitudinal studies? Eval Progr Plan 28(1):15–21
Craig W, Harel-Fisch Y, Fogel-Grinvald H, Dostaler S, Hetland J, Simons-Morton B, Molcho M, Gaspar de Mato M, Overpeck M, Due P, Pickett W (2009) A cross-national profile of bullying and victimization among adolescents in 40 countries. Int Journal Public Health 54:216–224
Crick NR, Bigbee MA (1998) Relational and overt forms of peer victimization: a multiinformant approach. J Consult Clin Psychol 66(2):337
Crick NR, Grotpeter JK (1995) Relational aggression, gender, and social-psychological adjustment. Child Dev 66:710–722
Crick NR, Grotpeter JK (1996) Children’s treatment by peers: victims of relational and overt aggression. Dev Psychopathol 8(02):367–380
Crick NR, Nelson DA (2002) Relational and physical victimization within friendships: nobody told me there’d be friends like these. J Abnorm Child Psychol 30(6):599–607
Crick NR, Casas JF, Nelson DA (2002) Toward a more comprehensive understanding of peer maltreatment: studies of relational victimization. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 11(3):98–101
Edelbrock C, Costello AJ, Kessler MD (1984) Empirical corroboration of attention deficit disorder. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 23(3):285–290
Eiraldi RB, Power TJ, Nezu CM (1997) Patterns of comorbidity associated with subtypes of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder among 6- to 12-year-old children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(4):503–514
Fekkes M, Pijpers FI, Fredriks AM, Vogels T, Verloove-Vanhorick SP (2006) Do bullied children get ill, or do ill children get bullied? A prospective cohort study on the relationship between bullying and health-related symptoms. Pediatrics 117(5):1568–1574
Fischer EH, Dornelas EA, Goethe JW (2001) Characteristics of people lost to attrition in psychiatric follow-up studies. J Nerv Ment Dis 189(1):49–55
Fogleman ND, Walerius DM, Rosen PJ, Leaberry KD (2016) Peer victimization linked to negative affect in children with and without ADHD. J Appl Dev Psychol 46:1–10
Gladstone GL, Parker GB, Malhi GS (2006) Do bullied children become anxious and depressed adults?: A cross-sectional investigation of the correlates of bullying and anxious depression. J Nerv Ment Dis 194(3):201–208
Green SM, Navratil JL, Loeber R, Lahey BB (1994) Potential dropouts in a longitudinal study: prevalence, stability, and associated characteristics. J Child Fam Stud 3(1):69–87
Hanish LD, Guerra NG (2002) A longitudinal analysis of patterns of adjustment following peer victimization. Dev Psychopathol 14(01):69–89
Hawker DS, Boulton MJ (2000) Twenty years’ research on peer victimization and psychosocial maladjustment: a meta-analytic review of cross-sectional studies. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 41(4):441–455
Hay DF, Payne A, Chadwick A (2004) Peer relations in childhood. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45(1):84–108
Hodges EV, Perry DG (1999) Personal and interpersonal antecedents and consequences of victimization by peers. J Pers Soc Psychol 76(4):677
Hodges EV, Boivin M, Vitaro F, Bukowski WM (1999) The power of friendship: protection against an escalating cycle of peer victimization. Dev Psychol 35(1):94
Hoza B, Pelham WE, Milich R, Pillow D, McBride K (1993) The self-perceptions and attributions of attention deficit hyperactivity disordered and nonreferred boys. J Abnorm Child Psychol 21(3):271–286
Hoza B, Gerdes AC, Hinshaw SP, Arnold LE, Pelham WE Jr, Molina BS, Abikoff HB, Epstein JN, Greenhill LL, Hechtman L, Odbert C, Swanson JM, Wigal T (2004) Self-perceptions of competence in children with ADHD and comparison children. J Consult Clin Psychol 72(3):382–391
Hoza B, Mrug S, Gerdes AC, Hinshaw SP, Bukowski WM, Gold JA, Kraemer HC, Pelham WE Jr, Wigal T, Arnold LE (2005) What aspects of peer relationships are impaired in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? J Consult Clin Psychol 73(3):411–423
Hubbard JA, Coie JD (1994) Emotional correlates of social competence in children’s peer relationships. Merrill-Palmer Q 1982:1–20
Humphrey JL, Storch EA, Geffken GR (2007) Peer victimization in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Child Health Care 11(3):248–260
Juvonen J, Graham S, Schuster MA (2003) Bullying among young adolescents: the strong, the weak, and the troubled. Pediatrics 112(6):1231–1237
Kaltiala-Heino R, Rimpelä M, Marttunen M, Rimpelä A, Rantanen P (1999) Bullying, depression, and suicidal ideation in Finnish adolescents: school survey. BMJ 319(7206):348–351
Kendall PC (1993) Cognitive-behavioral therapies with youth: guiding theory, current status, and emerging developments. J Consult Clin Psychol 61(2):235
Kochenderfer-Ladd B, Ladd GW (2001) Variations in peer victimization: relations to children’s maladjustment. In: Juvonen J, Graham S (eds) Peer harassment in school: the plight of the vulnerable and victimized. Guilford Press, New York, pp 25–48
Kochenderfer-Ladd B, Skinner K (2002) Children’s coping strategies: moderators of the effects of peer victimization? Dev Psychol 38(2):267
Koot HM, Verhulst FC (1992) Prediction of children’s referral to mental health and special education services from earlier adjustment. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 33(4):717–729
Kumpulainen Kirsti, Räsänen Eila, Henttonen Irmeli, Almqvist Fredrik, Kresanov Kaija, Linna Sirkka-Liisa, Moilanen Irma, Piha Jorma, Puura Kaija, Tamminen Tuula (1998) Bullying and psychiatric symptoms among elementary school-age children. Child Abuse Negl 22(7):705–717
Ladd GW, Kochenderfer-Ladd B (2002) Identifying victims of peer aggression from early to middle childhood: analysis of cross-prevalence of victimization and characteristics of identified victims. Psychol Assess 14(1):74–96
Ladd GW, Kochenderfer BJ, Coleman CC (1996) Friendship quality as a predictor of young children’s early school adjustment. Child Dev 67(3):1103–1118
Mitsis EM, McKay KE, Schulz KP, Newcorn JH, Halperin JM (2000) Parent–teacher concordance for DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a clinic-referred sample. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(3):308–313
MTA Cooperative Group (2004) National Institute of Mental Health Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD follow-up: 24-month outcomes of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 113(4):754–761
Ollendick TH, King NJ (1994) Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of internalizing problems in children: the role of longitudinal data. J Consult Clin Psychol 62(5):918
Olweus D (1993) Victimization by peers: antecedents and long-term outcomes. Soc Withdrawal Inhib Shyness Child 315:341
Olweus D (1994) Bullying at school: basic facts and effects of a school based intervention program. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 35(7):1171–1190
Pelham WE Jr, Fabiano GA (2008) Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 37(1):184–214
Perry DC, Williard JC, Perry LC (1990) Peers’ perceptions of the consequences that victimized children provide aggressors. Child Dev 61(5):1310–1325
Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA (2007) The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry 164(6):942–948
Reijntjes A, Kamphuis JH, Prinzie P, Telch MJ (2010) Peer victimization and internalizing problems in children: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Child Abuse Negl 34(4):244–252
Reijntjes A, Kamphuis JH, Prinzie P, Boelen PA, Van der Schoot M, Telch MJ (2011) Prospective linkages between peer victimization and externalizing problems in children: a meta-analysis. Aggress Behav 37(3):215–222
Reinherz HZ, Giaconia RM, Hauf AMC, Wasserman MS, Silverman AB (1999) Major depression in the transition to adulthood: risks and impairments. J Abnorm Psychol 108(3):500
Rosen PJ, Factor PI (2015) Emotional impulsivity and emotional and behavioral difficulties among children with ADHD an ecological momentary assessment study. J Atten Disord 19(9):779–793
Rosen PJ, Milich R, Harris MJ (2009) Why’s everybody always picking on me? Social cognition, emotion regulation, and chronic peer victimization in children. In: Harris MJ (ed) Bullying rejection & peer victimization. Springer, New York, pp 79–100
Rosen PJ, Milich R, Harris MJ (2012) Dysregulated negative emotional reactivity as a predictor of chronic peer victimization in childhood. Aggress Behav 38(5):414–427
Rosen PJ, Walerius DM, Fogleman ND, Factor PI (2015) The association of emotional lability and emotional and behavioral difficulties among children with and without ADHD. ADHD Atten Deficit Hyperactivity Disord 7(4):281–294
Scholte RH, Engels RC, Overbeek G, De Kemp RA, Haselager GJ (2007) Stability in bullying and victimization and its association with social adjustment in childhood and adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol 35(2):217–228
Shaffer D, Fisher P, Lucas CP, Dulcan MK, Schwab-Stone ME (2000) NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children Version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(1):28–38
Shaw P, Stringaris A, Nigg J, Leibenluft E (2014) Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 171(3):276–293
Stadler C, Feifel J, Rohrmann S, Vermeiren R, Poustka F (2010) Peer-victimization and mental health problems in adolescents: are parental and school support protective? Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 41(4):371–386
Storch EA, Ledley DR (2005) Peer victimization and psychosocial adjustment in children: current knowledge and future directions. Clin Pediatr 44(1):29–38
Storch EA, Masia-Warner C, Crisp H, Klein RG (2005) Peer victimization and social anxiety in adolescence: a prospective study. Aggress Behav 31(5):437–452
Sullivan TN, Farrell AD, Kliewer W (2006) Peer victimization in early adolescence: association between physical and relational victimization and drug use, aggression, and delinquent behaviors among urban middle school students. Dev Psychopathol 18(01):119–137
Troop-Gordon W (2017) Peer victimization in adolescence: the nature, progression, and consequences of being bullied within a developmental context. J Adolesc 55:116–128
Turner HA, Finkelhor D, Hamby SL, Shattuck A, Ormrod RK (2011) Specifying type and location of peer victimization in a national sample of children and youth. J Youth Adolesc 40(8):1052–1067
Twenge JM, Nolen-Hoeksema S (2002) Age, gender, race, socioeconomic status, and birth cohort difference on the children’s depression inventory: a meta-analysis. J Abnorm Psychol 111(4):578
Unnever JD, Cornell DG (2003) Bullying, self-control, and ADHD. J Interpers Violence 18(2):129–147
United States Census Bureau (2010) State and county QuickFacts (Data derived from population estimates, American Community Survey, Census of Population and Housing, County Business Patterns, Economic Census, Survey of Business Owners, Building Permits, Consoliated Federal Funds Report, Census of Governments). http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/21/2148006.html
Waxmonsky JG, Wymbs FA, Pariseau ME, Belin PJ, Waschbusch DA, Babocsai L, Fabiano GA, Akinnusi OO, Haak JL, Pelham WE (2012) A novel group therapy for children with ADHD and severe mood dysregulation. J Attent Disord 17(6):527–541
Wiener J, Mak M (2009) Peer victimization in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychol Schools 46(2):116–131
Wolraich ML, Lambert W, Doffing MA, Bickman L, Simmons T, Worley K (2003) Psychometric properties of the Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic parent rating scale in a referred population. J Pediatr Psychol 28(8):559–568
Wolraich ML, Lambert EW, Bickman L, Simmons T, Doffing MA, Worley KA (2004) Assessing the impact of parent and teacher agreement on diagnosing attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Dev Behav Pediatr 25(1):41–47
Ybarra ML, Mitchell KJ, Wolak J, Finkelhor D (2006) Examining characteristics and associated distress related to Internet harassment: findings from the Second Youth Internet Safety Survey. Pediatrics 118(4):e1169–e1177
Zeman J, Shipman K, Suveg C (2002) Anger and sadness regulation: predictions to internalizing and externalizing symptoms in children. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 31(3):393–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogleman, N.D., Leaberry, K.D., Rosen, P.J. et al. Relation between internalizing behaviors, externalizing behaviors, and peer victimization among children with and without ADHD. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord 10, 209–222 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-018-0248-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-018-0248-y