Abstract
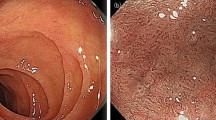
Collagenous colitis (CC) is one of the causes of undefined watery diarrhea, which is histologically accompanied by thickening of the subepithelial collagen layer. CC associated with lansoprazole normally occurs within several weeks after initial administration, but no case presenting after long-term administration of lansoprazole has yet been reported. A 77-year-old male with 6-year history of administration of lansoprazole complained of watery diarrhea and weight loss. Colonoscopy revealed disappearance of vascular networks and red spots in the sigmoid colon. Biopsy specimen showed erosion and collagen bands thickened, so the patient was diagnosed as CC. After lansoprazole discontinuation, the watery diarrhea disappeared and histological abnormalities improved.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindstrom CG. “Collagenous colitis” with watery diarrhea—a new entity? Pathol Eur. 1976;11:87–9.
Olesen M, Eriksson S, Bohr J, Jarnerot G, Tysk C. Microscopic colitis: a common diarrhoeal disease. An epidemiological study in Orebro, Sweden, 1993–1998. Gut. 2004;53:346–50.
Pardi DS, Loftus EV Jr, Smyrk TC, Kammer PP, Tremaine WJ, Schleck CD, et al. The epidemiology of microscopic colitis: a population based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gut. 2007;56:504–8.
Rubio-Tapia A, Martinez-Salgado J, Garcia-Leiva J, Martinez-Benitez B, Uribe M. Microscopic colitides: a single center experience in Mexico. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007;22:1031–6.
Warren BF, Edwards CM, Travis SP. ‘Microscopic colitis’: classification and terminology. Histopathology. 2002;40:374–6.
Riddell RH, Tanaka M, Mazzoleni G. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a possible cause of collagenous colitis: a case–control study. Gut. 1992;33:683–6.
Beaugerie L, Luboinski J, Brousse N, Cosnes J, Chatelet FP, Gendre JP, et al. Drug-induced lymphocytic colitis. Gut. 1994;35:426–8.
Wilcox GM, Mattia A. Collagenous colitis associated with lansoprazole. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;34:164–6.
Thomson RD, Lestina LS, Bensen SP, Toor A, Maheshwari Y, Ratccliffe NR. Lansoprazole-associated microscopic colitis: a case series. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:2908–13.
Rammer M, Kirchgatterer A, Hobling W, Knoflach P. Lansoprazole associated collagenous colitis: a case report. Z Gastroenterol. 2005;43:657–60.
Hilmer SN, Heap TR, Eckstein RP, Lauer CS, Shenfield GM. Microscopic colitis associated with exposure to lansoprazole. Med J Aust. 2006;184:185–6.
Wickbom A, Lindoqvist M, Bohr J, Ung KA, Bergman J, Eriksson S, et al. Colonic mucosal tears in collagenous colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:726–9.
Chande N, Driman D. Microscopic colitis associated with lansoprazole: report of two cases and a review of the literature. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:530–3.
Umeno J, Matsumoto T, Nakamura S, Jo Y, Yada S, Hirakawa K, et al. Linear mucosal defect may be characteristic of lansoprazole-associated collagenous colitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:1185–91.
Baert F, Wouters K, D’Haens G, Hoang P, Naegels S, D’Heygere F, et al. Lymphocytic colitis: a distinct clinical entity? A clinicopathological confrontation of lymphocytic and collagenous colitis. Gut. 1999;45:375–81.
Duncan HD, Talbot IC, Silk DB. Collagenous colitis and cimetidine. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997;9:819–20.
Mukherjee S. Diarrhea associated with lansoprazole. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18:602–3.
Mayhew BS, Jones DR, Hall SD. An in vitro model for predicting in vivo inhibition of cytochrome P4503A4 by metabolic intermediated complex formation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28:1031–7.
Pinto AG, Wang YH, Chalasani N, Skaar T, Kolwankar D, Gorski JC, et al. Inhibition of human intestinal wall metabolism by macrolide antibiotics: effect of clarithromycin on cytochrome P450 3A4/5 activity and expression. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;77:178–88.
Bohr J, Tysk C, Eriksson S, Abrahamsson H, Jarnerot G. Collagenous colitis: a retrospective study of clinical presentation and treatment in 163 patients. Gut. 1996;39:846–51.
Cruz-Correa M, Milligan F, Giardiello FM, Bayless TM, Torbenson M, Yardley JH, et al. Collagenous colitis with mucosal tears on endoscopic insufflation: a unique presentation. Gut. 2002;51:600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, K., Fujiya, M., Itabashi, K. et al. Collagenous colitis appeared after 6-year administration of lansoprazole. Clin J Gastroenterol 3, 18–21 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-009-0126-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-009-0126-4