Abstract
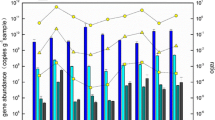
Spartina alterniflora, an aggressive invasive plant species at the estuarine wetlands of China’s coasts, has become a major threat to the natural ecosystems. To understand its potential influence on nitrification processes, the community structures and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) were investigated using 454-pyrosequencing and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) in S. alterniflora invading salt marsh sediments at the Yangtze River estuary in Chongming island, Shanghai, China. Copy numbers of archaeal and bacterial ammonia monooxygenase subunit A (amoA) genes did not show accordant shifts with S. alterniflora invasion in the two sampling sites. However, the copy numbers of archaeal amoA gene were higher in summer than in spring. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that more than 90% of the archaeal and 92% of the bacterial amoA gene sequences were closely related to marine group I.1a and the clusters 13 and 15 in Nitrosospira lineage, respectively. The effect of different seasons (spring and summer) was important for the abundance variation of AOA, while different stages of S. alterniflora invasion did not show significant effect for both AOA and AOB. Variation of AOA community was significantly related to total carbon (TC) and sulfate concentration (P < 0.05), whereas the AOB community was significantly related to sulfate concentration, total nitrogen (TN), TC and pH (P < 0.05). In conclusion, the abundance and diversity of ammonia oxidizing microbial communities were not strongly affected by S. alterniflora invasion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell, G.C.J., Revill, A.T., Smith, C., Bissett, A.P., Volkman, J.K., and Robert, S.S. 2009. Archaeal ammonia oxidizers and nirS-type denitrifiers dominate sediment nitrifying and denitrifying populations in a subtropical macrotidal estuary. ISME J. 4, 286–300.
Avrahami, S. and Conrad, R. 2003. Patterns of community change among ammonia oxidizers in meadow soils upon long-term incubation at different temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 6152–6164.
Bai, S., Li, J., He, Z., Van Nostrand, J.D., Tian, Y., Lin, G., Zhou, J., and Zheng, T. 2013. Geochip-based analysis of the functional gene diversity and metabolic potential of soil microbial communities of mangroves. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15, 1–14.
Bais, H.P., Weir, T.L., Perry, L.G., Gilroy, S., and Vivanco, J.M. 2006. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57, 233–266.
Beman, J.M. and Francis, C.A. 2006. Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahia del Tobari, Mexico. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 7767–7777.
Beman, J.M., Sachdeva, R., and Fuhrman, J.A. 2010. Population ecology of nitrifying archaea and bacteria in the southern california bight. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 1282–1292.
Bernhard, A.E. and Bollmann, A. 2010. Estuarine nitrifiers: new players, patterns and processes. Estuar. Coast Shelf. Sci. 88, 1–11.
Bernhard, A.E., Donn, T., Giblin, A.E., and Stahl, D.A. 2005. Loss of diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria correlates with increasing salinity in an estuary system. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1289–1297.
Bernhard, A.E., Landry, Z.C., Blevins, A., José, R., Giblin, A.E., and Stahl, D.A. 2010. Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient in relation to potential nitrification rates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 1285–1289.
Berry, D., Mahfoudh, K.B., Wagner, M., and Loy, A. 2011. Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 7846–7849.
Brochier-Armanet, C., Boussau, B., Gribaldo, S., and Forterre, P. 2008. Mesophilic crenarchaeota: Proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 245–252.
Caffrey, J.M., Bano, N., Kalanetra, K., and Hollibaugh, J.T. 2007. Ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea from estuaries with differing histories of hypoxia. ISME J. 1, 660–662.
Cheng, X., Peng, R., Chen, J., Luo, Y., Zhang, Q., An, S., Chen, J., and Li, B. 2007. CH4 and N2O emissions from Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis in experimental mesocosms. Chemosphere 68, 420–427.
Craft, C., Clough, J., Ehman, J., Joye, S., Park, R., Pennings, S., Guo, H., and Machmuller, M. 2008. Forecasting the effects of accelerated sealevel rise on tidal marsh ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 7, 73–78.
Damsté, J.S.S., Rijpstra, W.I.C., Hopmans, E.C., Jung, M.Y., Kim, J.G., Rhee, S.K., Stieglmeier, M., and Schleper, C. 2012. Intact polar and core glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether lipids of group I.1a and I.1b Thaumarchaeota in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 6866–6874.
Dang, H., Li, J., Chen, R., Wang, L., Guo, L., Zhang, Z., and Klotz, M.G. 2010. Diversity, abundance, and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing betaproteobacteria in response to environmental gradients and coastal eutrophication in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 4691–4702.
Fan, F., Yang, Q., Li, Z., Wei, D., Cui, X., and Liang, Y. 2011. Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizers on nitrification in a cold climate soil are linked to the bacterial ammonia oxidizer community. Microb. Ecol. 62, 982–990.
Fenchel, T. 2002. Microbial behavior in a heterogeneous world. Science 296, 1068–1071.
Francis, C.A., Roberts, K.J., Beman, J.M., Santoro, A.E., and Oakley, B.B. 2005. Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 14683–14688.
Haichar, F.Z., Marol, C., Berge, O., Rangel-Castro, J.I., Prosser, J.I., Balesdent, J., Heulin, T., and Achouak, W. 2008. Plant host habitat and root exudates shape soil bacterial community structure. ISME J. 2, 1221–1230.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 95–98.
Hansel, C.M., Fendorf, S., Jardine, P.M., and Francis, C.A. 2008. Changes in bacterial and archaeal community structure and functional diversity along a geochemically variable soil profile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 1620–1633.
Hatzenpichler, R., Lebedeva, E.V., Spieck, E., Stoecker, K., Richter, A., Daims, H., and Wagner, M. 2008. A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 2134–2139.
Hayashi, T., Kaneko, R., Tanahashi, M., and Naganuma, T. 2007. Molecular diversity of the genes encoding ammonia monooxygenase and particulate methane monooxygenase from deep-sea sediments. Res. J. Microbiol. 2, 530–537.
Hollibaugh, J.T., Gifford, S.M., Moran, M.A., Ross, M.J., Sharma, S., and Tolar, B.B. 2014. Seasonal variation in the metratranscriptomes of a Thaumarchaeota population from SE USA coastal waters. ISME J. 8, 685–698.
Hou, L.J., Liu, M., Jiang, H.Y., Xu, S.Y., Ou, D.N., Liu, Q.M., and Zhang, B.L. 2003. Ammonium adsorption by tidal flat surface sediments from the Yangtze estuary. Environ. Geol. 45, 72–78.
Hu, Z., Meng, H., Shi, J.H., Bu, N.S., Fang, C.M., and Quan, Z.X. 2014. Community size and composition of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifiers in an alluvial intertidal wetland ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 5, 371.
Ingalls, A.E., Shah, S.R., Hansman, R.L., Aluwihare, L.I., Santos, G.M., Druffel, E.R., and Pearson, A. 2006. Quantifying archaeal community autotrophy in the mesopelagic ocean using natural radiocarbon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 6442–6447.
Jia, Z. and Conrad, R. 2009. Bacteria rather than archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 1658–1671.
Jiang, L.F., Luo, Y.Q., Chen, J.K., and Li, B. 2009. Ecophysiological characteristics of invasive Spartina alterniflora and native species in salt marshes of Yangtze River estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 81, 74–82.
Kim, J., Jung, M., Lee, K., Kim, D., Ko, S., Lee, J., and Rhee, S. 2014. The archaea community associated with lava-formed Gotjawal forest soil in Jeju, Korea. J. Agr. Chem. Environ. 3, 96–102.
Kim, J., Jung, M., Lee, K., Kim, D., Ko, S., Lee, J., and Rhee, S. 2014. The Archaea community associated with lava-formed Gotjawal forest soil in Jeju, Korea. J. Agr. Chem. Environ. 3, 96-102.
Kim, J.G., Jung, M.Y., Park, S.J., Rijpstra, W.I.C., Sinninghe Damsté, J.S., Madsen, E.L., Min, D., Kim, J.S., Kim, G.J., and Rhee, S.K. 2012. Cultivation of a highly enriched ammonia-oxidizing archaeon of thaumarchaeotal group I.1b from an agricultural soil. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1528–1543.
Könneke, M., Bernhard, A.E., de la Torre, J.R., Walker, C.B., Waterbury, J.B., and Stahl, D.A. 2005. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437, 543–546.
Kowalchuk, G.A. and Stephen, J.R. 2001. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: A model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 485–529.
Lage, M.D., Reed, H.E., Weihe, C., Crain, C.M., and Martiny, J.B. 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment alter the composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in salt marsh sediments. ISME J. 4, 933–944.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., and Lopez, R. 2007. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948.
Leininger, S., Urich, T., SchloteS, M., Schwark, L., Qi, J., Nicol, G., Prosser, J., Schuster, S., and Schleper, C. 2006. Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442, 806–809.
Li, X.R., Xiao, Y.P., Ren, W.W., Liu, Z.F., Shi, J.H., and Quan, Z.X. 2012. Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in different types of soil in the Yangtze river estuary. J. Zhejiang. Univ. Sci. B. 13, 769–782.
Liao, C., Luo, Y., Jiang, L., Zhou, X., Wu, X., Fang, C., Chen, J., and Li, B. 2007. Invasion of Spartina alterniflora enhanced ecosystem carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Yangtze estuary, China. Ecosystems 10, 1351–1361.
Mincer, T.J., Church, M.J., Taylor, L.T., Preston, C., Karl, D.M., and DeLong, E.F. 2007. Quantitative distribution of presumptive archaeal and bacterial nitrifiers in monterey bay and the Monterey Bay and the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Environ. Microbiol. 9, 1162–1175.
Moin, N.S., Nelson, K.A., Bush, A., and Bernhard, A.E. 2009. Distribution and diversity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers in salt marsh sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 7461–7468.
Mosier, A.C. and Francis, C.A. 2008. Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ. Microbiol. 10, 3002–3016.
Nelson, K.A., Moin, N.S., and Bernhard, A.E. 2009. Archaeal diversity and the prevalence of Crenarchaeota in salt marsh sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 4211–4215.
Page, H.M., Lastra, M., Rodil, I.F., Briones, M.J.I., and Garrido, J. 2010. Effects of non-native Spartina patens on plant and sediment organic matter carbon incorporation into the local invertebrate community. Biol. Invasions 12, 3825–3838.
Parameswaran, P., Jalili, R., Tao, L., Shokralla, S., Gharizadeh, B., Ronaghi, M., and Fire, A.Z. 2007. A pyrosequencing-tailored nucleotide barcode design unveils opportunities for large-scale sample multiplexing. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, e130.
Park, B.J., Park, S.J., Yoon, D.N., Schouten, S., Sinninghe Damsté, J.S., and Rhee, S.K. 2010. Cultivation of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing archaea from marine sediments in coculture with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 7575–7587.
Pester, M., Schleper, C., and Wagner, M. 2011. The Thaumarchaeota: an emerging view of their phylogeny and ecophysiology. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 14, 300–306.
Purkhold, U., Pommerening-Röser, A., Juretschko, S., Schmid, M.C., Koops, H.P., and Wagner, M. 2000. Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: Implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 5368–5382.
Quan, W., Han, J., Shen, A., Ping, X., Qian, P., Li, C., Shi, L., and Chen, Y. 2007. Uptake and distribution of N, P and heavy metals in three dominant salt marsh macrophytes from Yangtze River estuary, China. Mar. Environ. Res. 64, 21–37.
R Development Core Team. 2004. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria (http://www.r-project.org).
Rotthauwe, J.H., Witzel, K.P., and Liesack, W. 1997. The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4704–4712.
Schloss, P.D., Westcott, S.L., Ryabin, T., Hall, J.R., Hartmann, M., Hollister, E.B., Lesniewski, R.A., Oakley, B.B., Parks, D.H., and Robinson, C.J. 2009. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 7537–7541.
Seyler, L.M., McGuinness, L.M., and Kerkhof, L.J. 2014. Crenarchaeal heterotrophy in salt marsh sediments. ISME J. 8, 1534–1543.
Szukics, U., Abell, G.C., Hödl, V., Mitter, B., Sessitsch, A., Hackl, E., and Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. 2010. Nitrifiers and denitrifiers respond rapidly to changed moisture and increasing temperature in a pristine forest soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 72, 395–406.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2011. Mega5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739.
Tourna, M., Freitag, T.E., Nicol, G.W., and Prosser, J.I. 2008. Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 10, 1357–1364.
Treusch, A.H., Leininger, S., Kletzin, A., Schuster, S.C., Klenk, H.P., and Schleper, C. 2005. Novel genes for nitrite reductase and amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic Crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1985–1995.
Turner, R.E. 1993. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus leaching rates from Spartina alterniflora salt marshes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 92, 135–140.
Venter, J.C., Remington, K., Heidelberg, J.F., Halpern, A.L., Rusch, D., Eisen, J.A., Wu, D., Paulsen, I., Nelson, K.E., and Nelson, W. 2004. Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304, 66–74.
Wang, Q., Quensen, J.F., Fish, J.A., Lee, T.K., Sun, Y., Tiedje, J.M., and Cole, J.R. 2013. Ecological patterns of nifH genes in four terrestrial climatic zones explored with targeted metagenomics using FrameBot, a new informatics tool. MBio 4, E00592–00513.
Wankel, S.D., Mosier, A.C., Hansel, C.M., Paytan, A., and Francis, C.A. 2011. Spatial variability in nitrification rates and ammonia-oxidizing microbial communities in the agriculturally impacted Elkhorn Slough estuary, California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 269–280.
Williams, S.L. and Grosholz, E.D. 2008. The invasive species challenge in estuarine and coastal environments: Marrying management and science. Estuar. Coast 31, 3–20.
Yao, H., Campbell, C.D., Chapman, S.J., Freitag, T.E., Nicol, G.W., and Singh, B.K. 2013. Multi-factorial drivers of ammonia oxidizer communities: evidence from a national soil survey. Environ. Microbiol. 15, 2545–2556.
Zeleke, J., Sheng, Q., Wang, J.G., Huang, M.Y., Xia, F., Wu, J.H., and Quan, Z.X. 2013. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the communities of methanogens and sulfate-reducing bacteria in estuarine marsh sediments. Front Microbiol. 4, 243.
Zhang, Q.F., Peng, J.J., Chen, Q., Li, X.F., Xu, C.Y., Yin, H.B., and Yu, S. 2011. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on abundance and composition of ammonia oxidizers in estuarine sediment. J. Soils Sediments. 11, 1020–1031.
Zhang, L.M., Wang, M., Prosser, J.I., Zheng, Y.M., and He, J.Z. 2009. Altitude ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils of Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 70, 208–217.
Zheng, Y., Hou, L., Liu, M., Lu, M., Zhao, H., Yin, G., and Zhou, J. 2012. Diversity, abundance, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 8351–8363.
Zheng, Y., Hou, L., Newell, S., Liu, M., Zhou, J., Zhao, H., You, L., and Cheng, X. 2014. Community dynamics and activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 408–419.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, F., Zeleke, J., Sheng, Q. et al. Communities of ammonia oxidizers at different stages of Spartina alterniflora invasion in salt marshes of Yangtze River estuary. J Microbiol. 53, 311–320 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-4660-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-4660-0