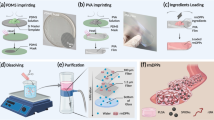
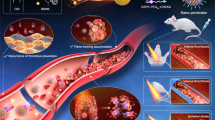
Abstract
Systemic thrombolysis with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) remains the only proven treatment that is effective in improving the clinical outcome of patients with acute ischemic stroke. However, thrombolytic therapy has some major limitations such as hemorrhage, neurotoxicity, and the short time window for the treatment. In this study, we designed iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanorods loaded with 6% tPA, which could be released within ~30 min. The Fe3O4 nanorods could be targeted to blood clots under magnetic guidance. In addition, the release of tPA could be significantly increased using an external rotating magnetic field, which subsequently resulted in a great improvement in the thrombolytic efficiency. Systematic and quantitative studies revealed the fundamental physical processes involved in the enhanced thrombolysis, while the in vitro thrombolysis assay showed that the proposed strategy could improve thrombolysis and recanalization rates and reduce the risk of tPA-mediated hemorrhage in vivo. Such a strategy will be very useful for the treatment of ischemic stroke and other deadly thrombotic diseases such as myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism in clinical settings.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jørgensen, H. S.; Nakayama, H.; Raaschou, H. O.; Olsen, T. S. Stroke. Neurologic and functional recovery the Copenhagen Stroke Study. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 10, 887–906.
Furie, B.; Furie, B. C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949.
Brott, T.; Bogousslavsky, J. Treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 710–722.
Adams, H. P., Jr.; del Zoppo, G.; Alberts, M. J.; Bhatt, D. L.; Brass, L.; Furlan, A.; Grubb, R. L.; Higashida, R. T.; Jauch, E. C.; Kidwell, C. et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007, 38, 1655–1711.
Clark, W. M.; Wissman, S.; Albers, G. W.; Jhamandas, J. H.; Madden, K. P.; Hamilton, S. Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (alteplase) for ischemic stroke 3 to 5 hours after symptom onset. The ATLANTIS study: A randomized controlled trial. Alteplase thrombolysis for acute noninterventional therapy in ischemic stroke. JAMA 1999, 282, 2019–2026.
Ogawa, A.; Mori, E.; Minematsu, K.; Taki, W.; Takahashi, A.; Nemoto, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Sasaki, M.; Inoue, T. Randomized trial of intraarterial infusion of urokinase within 6 hours of middle cerebral artery stroke: The middle cerebral artery embolism local fibrinolytic intervention trial (MELT) Japan. Stroke 2007, 38, 2633–2639.
Hua, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, P.; He, Y.; Tan, K. B.; Chen, Q. H.; Gao, Y. J.; Gao, Y. H. In vivo thrombolysis with targeted microbubbles loading tissue plasminogen activator in a rabbit femoral artery thrombus model. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2014, 38, 57–64.
Petit, B.; Yan, F.; Tranquart, F.; Allémann, E. Microbubbles and ultrasound-mediated thrombolysis: A review of recent in vitro studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2012, 22, 381–392.
Korin, N.; Kanapathipillai, M.; Matthews, B. D.; Crescente, M.; Brill, A.; Mammoto, T.; Ghosh, K.; Jurek, S.; Bencherif, S. A.; Bhatta, D. et al. Shear-activated nanotherapeutics for drug targeting to obstructed blood vessels. Science 2012, 337, 738–742.
McCarthy, J. R.; Weissleder, R. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1241–1251.
Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L. V.; Muller, R. N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110.
Voros, E.; Cho, M. J.; Ramirez, M.; Palange, A. L.; De Rosa, E.; Key, J.; Garami, Z.; Lumsden, A. B.; Decuzzi, P. TPA immobilization on iron oxide nanocubes and localized magnetic hyperthermia accelerate blood clot lysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1709–1718.
Cheng, R.; Huang, W. J.; Huang, L. J.; Yang, B.; Mao, L. D.; Jin, K. L.; ZhuGe, Q. C.; Zhao, Y. P. Acceleration of tissue plasminogen activator-mediated thrombolysis by magnetically powered nanomotors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7746–7754.
Chen, J. P.; Yang, P. C.; Ma, Y. H.; Tu, S. J.; Lu, Y. J. Targeted delivery of tissue plasminogen activator by binding to silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5137–5149.
Xie, Y. M.; Kaminski, M. D.; Torno, M. D.; Finck, M. R.; Liu, X. Q.; Rosengart, A. J. Physicochemical characteristics of magnetic microspheres containing tissue plasminogen activator. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 376–378.
Kempe, H.; Kempe, M. The use of magnetite nanoparticles for implant-assisted magnetic drug targeting in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9499–9510.
Zhao, Y. P.; Ye, D. X.; Wang, G. C.; Lu, T. M. Novel nanocolumn and nano-flower arrays by glancing angle deposition. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 351–354.
Cornell, R. M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses; VCH: Weinheim, New York, 1996.
Adams, H. P.; del Zoppo, G.; Alberts, M. J.; Bhatt, D. L.; Brass, L.; Furlan, A.; Grubb, R. L.; Higashida, R. T.; Jauch, E. C.; Kidwell, C. et al. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke. Stroke 2007, 38, 1655–1711.
Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K. R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T. et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329.
Armstrong, P. W.; Collen, D. Fibrinolysis for acute myocardial infarction: Current status and new horizons for pharmacological reperfusion, Part 2. Circulation 2001, 103, 2987–2992.
Chandler, W. L.; Alessi, M. C.; Aillaud, M. F.; Henderson, P.; Vague, P.; Juhan-Vague, I. Clearance of tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) and TPA/plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) complex: Relationship to elevated TPA antigen in patients with high PAI-1 activity levels. Circulation 1997, 96, 761–768.
Cameron, H. A.; McEwen, B. S.; Gould, E. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by excitatory input and NMDA receptor activation in the dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 4687–4692.
Chen, J. P.; Yang, P. C.; Ma, Y. H.; Wu, T. Characterization of chitosan magnetic nanoparticles for in situ delivery of tissue plasminogen activator. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 84, 364–372.
Diamond, S. L. Engineering design of optimal strategies for blood clot dissolution. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 1, 427–462.
Diamond, S. L.; Anand, S. Inner clot diffusion and permeation during fibrinolysis. Biophys. J. 1993, 65, 2622–2643.
Pleydell, C. P.; David, T.; Smye, S. W.; Berridge, D. C. A mathematical model of post-canalization thrombolysis. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 209–224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Huang, W., Huang, S. et al. Magnetically active Fe3O4 nanorods loaded with tissue plasminogen activator for enhanced thrombolysis. Nano Res. 9, 2652–2661 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1152-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1152-4