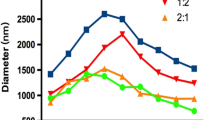
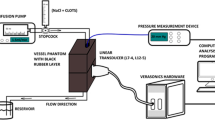
Abstract
The increasingly high incidence of ischemic stroke caused by thrombosis of the arterial vessels is one of the major factors that threaten people’s health and lives in the world. The present treatments for thrombosis are unsatisfactory yet. We developed the microbubbles loading tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and their in vitro thrombolysis efficacy under ultrasound exposure has been proved previously. We tried to investigate their thrombolysis effect in vivo in this present study. Thrombus model was made by clamping bilateral femoral arteries in 70 arteries of 40 rabbits. The targeted tPA-loaded microbubbles were made by lyophilization, taking arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-serine peptide as the targeting ligand. Its thrombolysis efficacy, calculated as count rate and efficiency rate of recanalization, was evaluated by Pearson’s χ2 and One-way ANOVA, respectively. The count rate of recanalization of the targeted tPA-loaded microbubbles under ultrasound exposure (70 %) was similar to that of the combination of tPA, microbubbles and ultrasound exposure (80 %) (P = 0.61), while its tPA dosage (0.06 mg/kg) was much less than that of latter (0.9 mg/kg). Its efficiency rate of recanalization was the highest among all groups (53.22 ± 40.39 %) (P < 0.01). Ultrasound-induced targeted tPA-loaded microbubbles release is a promising thrombolytic method with satisfactory thrombolytic efficacy, lowered tPA dose and potentially decreased hemorrhagic risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caplan LR (2006) Stroke thrombolysis. Circulation 114:187–190
Wardlaw JM, Koumellis P, Liu M (2013) Thrombolysis (different doses, routes of administration and agents) for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD000514. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000514.pub3
Pan SM, Liu JF, Liu M, Shen S, Li HJ, Dai LH, Chen XJ (2012) Efficacy and safety of a modified intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator regimen in Chinese patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis
Crumrine RC, Marder VJ, Taylor GM, Lamanna JC, Tsipis CP, Scuderi P, Petteway SR Jr, Arora V (2011) Intra-arterial administration of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) causes more intracranial bleeding than does intravenous rt-PA in a transient rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Exp Transl Stroke Med 3:10
Hajar K, Kerr DM, Lees KR (2011) Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. J Vasc Surg 54:901–907
Kramer C, Aguilar MI, Hoffman-Snyder C, Wellik KE, Wingerchuk DM, Demaerschalk BM (2011) Safety and efficacy of ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis in the treatment of acute middle cerebral artery infarction: a critically appraised topic. Neurologist 17:346–351
Cherniavsky EA, Strakha IS, Adzerikho IE, Shkumatov VM (2011) Effects of low frequency ultrasound on some properties of fibrinogen and its plasminolysis. BMC Biochem 12:60
Xie F, Slikkerveer J, Gao S, Lof J, Kamp O, Unger E, Radio S, Matsunaga T, Porter TR (2011) Coronary and microvascular thrombolysis with guided diagnostic ultrasound and microbubbles in acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24:1400–1408
Everbach EC, Francis CW (2000) Cavitational mechanisms in ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis at 1 MHz. Ultrasound Med Biol 26:1153–1160
Datta S, Coussios CC, McAdory LE et al (2006) Correlation of cavitation with ultrasound enhancement of thrombolysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 32:1257–1267
Prokop AF, Soltani A, Roy RA (2007) Cavitational mechanisms in ultrasound-accelerated fibrinolysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 33:924–933
Datta S, Coussios C, Ammi AY et al (2008) Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis using Definity® as a cavitation nucleation agent. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:1421–1433
Hitchcock K, Ivancevich N, Haworth K et al (2011) Ultrasound-enhanced rt-PA thrombolysis in an ex vivo porcine carotid artery model. Ultrasound Med Biol 37:1240–1251
Sutton JT, Haworth KJ, Pyne-Geithman G et al (2013) Ultrasound-mediated drug delivery for cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10:573–592
Escoffre JM, Piron J, Novell A, Bouakaz A (2011) Doxorubicin delivery into tumor cells with ultrasound and microbubbles. Mol Pharm 8:799–806
Cool SK, Geers B, Lentacker I, De Smedt SC, Sanders NN (2013) Enhancing nucleic acid delivery with ultrasound and microbubbles. Methods Mol Biol 948:195–204
Borden MA, Streeter JE, Sirsi SR, Dayton PA (2013) In vivo demonstration of cancer molecular imaging with ultrasound radiation force and buried-ligand microbubbles. Mol Imaging 12:1–8
Novell A, Escoffre J-M, Bouakaz A (2013) Ultrasound contrast imaging in cancer—technical aspects and prospects. Curr Mol Imaging 2:77–88
Laing ST, Moody MR, Kim H, Smulevitz B, Huang SL, Holland CK, McPherson DD, Klegerman ME (2012) Thrombolytic efficacy of tissue plasminogen activator-loaded echogenic liposomes in a rabbit thrombus model. Thromb Res 30:629–635
Laing ST, Moody M, Smulevitz B, Kim H, Kee P, Huang S, Holland CK, McPherson DD (2011) Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolytic effect of tissue plasminogen activator-loaded echogenic liposomes in an in vivo rabbit aorta thrombus model–brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1357–1359
Hua X, Liu P, Gao YH, Zhou LN, Liu Z, Li X, Zhou SW, Gao YJ (2010) Construction of thrombus-targeted microbubbles carrying tissue plasminogen activator and their in vitro thrombolysis efficacy: a primary research. J Thromb Thrombolysis 30:29–35
Liu P, Wang X, Zhou S, Hua X, Liu Z, Gao Y (2011) Effects of a novel ultrasound contrast agent with long persistence on right ventricular pressure: comparison with SonoVue. Ultrasonics 51:210–214
Tola M, Yurdakul M, Ozbulbul NI (2012) B-flow imaging for the measurement of residual lumen diameter of renal artery stenosis. J Clin Ultrasound 40:85–90
Dupont WD, Plummer WD (1998) Power and sample size calculations for studies involving linear regression. Control Clin Trials 19:589–601
Powers CM (2011) Use of alteplase beyond 3 hours of ischemic stroke onset. Adv Emerg Nurs J 33:65–70
Graham GD (2003) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke in clinical practice: a meta-analysis of safety data. Stroke 34:2847–2850
Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, Del Zoppo GJ (2009) Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CD000213
Yepes M, Roussel BD, Ali C, Vivien D (2009) Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the ischemic brain: more than a thrombolytic. Trends Neurosci 32:48–55
Kempe M, Kempe H, Snowball I, Wallén R, Arza CR, Götberg M, Olsson T (2010) The use of magnetite nanoparticles for implant-assisted magnetic drug targeting in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials 31:9499–9510
Kim JY, Kim JK, Park JS, Byun Y, Kim CK (2009) The use of PEGylated liposomes to prolong circulation lifetimes of tissue plasminogen activator. Biomaterials 30:5751–5756
Wang SS, Chou NK, Chung TW (2009) The t-PA-encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles shelled with CS or CS-GRGD alter both permeation through and dissolving patterns of blood clots compared with t-PA solution: an in vitro thrombolysis study. J Biomed Mater Res A 91:753–761
Chen JP, Yang PC, Ma YH, Tu SJ, Lu YJ (2012) Targeted delivery of tissue plasminogen activator by binding to silica-coated magnetic nanoparticle. Int J Nanomedicine 7:5137–5149
Klibanov AL, Shevchenko TI, Raju BI, Seip R, Chin CT (2010) Ultrasound-triggered release of materials entrapped in microbubble-liposome constructs: a tool for targeted drug delivery. J Control Release 148:13–17
Liao AH, Li YK, Lee WJ, Wu MF, Liu HL, Kuo ML (2012) Estimating the delivery efficiency of drug-loaded microbubbles in cancer cells with ultrasound and bioluminescence imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol 38:1938–1948
Feril LB Jr, Tachibana K (2012) Use of ultrasound in drug delivery systems: emphasis on experimental methodology and mechanisms. Int J Hyperth 28:282–289
Tinkov S, Bekeredjian R, Winter G, Coester C (2009) Microbubbles as ultrasound triggered drug carriers. J Pharm Sci 98:1935–1961
Amaral-Silva A, Piñeiro S, Molina CA (2011) Sonothrombolysis for the treatment of acute stroke: current concepts and future directions. Expert Rev Neurother 11:265–273
Leeman JE, Kim JS, Yu FT, Chen X, Kim K, Wang J, Chen X, Villanueva FS, Pacella JJ (2012) Effect of acoustic conditions on microbubble-mediated microvascular sonothrombolysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 38:1589–1598
Ren ST, Lon LH, Wang M, Li YP, Qin H, Zhang H, Jing BB, Li YX, Zang WJ, Wang B, Shen XL (2012) Thrombolytic effects of combined therapy with targeted microbubbles and ultrasound in a 6 h cerebral thrombosis rabbit model. J Thromb Thrombolysis 33:74–81
Hagisawa K, Nishioka T, Suzuki R, Maruyama K, Takase B, Ishihara M, Kurita A, Yoshimoto N, Nishida Y, Iida K, Luo H, Siegel RJ (2013) Thrombus-targeted perfluorocarbon-containing liposomal bubbles for enhancement of ultrasonic thrombolysis: in vitro and in vivo study. J Thromb Haemost 11:1565–1573
See Sutton JT, Ivancevich NM, Perrin SR, Vela DC, Holland CK (2013) Clot retraction affects the extent of ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis in an ex vivo porcine thrombosis model. Ultrasound Med Biol 39:813–824
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. Zhaoyang Zhong for professional pathological examination and Prof. Zheng Liu and Prof. Rui Li for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant numbers 30500478, 30801060].
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, X., Zhou, L., Liu, P. et al. In vivo thrombolysis with targeted microbubbles loading tissue plasminogen activator in a rabbit femoral artery thrombus model. J Thromb Thrombolysis 38, 57–64 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1071-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-014-1071-8