Abstract
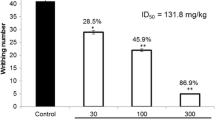
The plant species of genus Nepeta are used to treat various human diseases and for ornamental purposes as well. Nepethalate B (1) was isolated as a result of phytochemical investigations of Nepeta clarkei and was subjected in the present study for investigation of analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and central nervous system (CNS) depressant activities. The percentage inhibition in phase I of the acetic acid induced writhing test of compound 1 (dose of 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg of body weight) was 53.3, 58.0 and 86.7 % respectively. These results were found significantly higher (P < 0.01) as compared to the negative control. Moreover, the percentage inhibitions of three phases for 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg were higher than the values obtained for Aspirin (positive control). In formalin test, the percentage pain inhibition between 0 and 5 min (early phase) was 68.0, 25.5, and 75.5 % for 0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg intra-peritoneal doses of compound 1 respectively. In case of late phase (20–30 min) it was 63.0, 66.7 and 48.1 %, respectively. In comparison to aspirin, overall percentage inhibition of compound 1 was significantly higher in early and late phases. Interestingly, at all doses compound 1 showed more potent anti-inflammatory effects in terms of intensity and duration as compared to aspirin. The gross behavioral study of nepethalate B (1) was also carried out and the results revealed that it exhibited CNS depression in the mice and showed a prominent decrease in locomotor activity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Mehjabeen, M. Zia-Ul-Haq, and N. Jahan. 2011. Determination of LD50 and ED50 by dose response relationship and assessment of toxicological and non toxicological behaviour of Ipomoea hederacea. Journal of Pharmacy Research 4: 1176–1178.
Alcaraz, M.J., and M.J. Jimenez. 1989. Anti-inflammatory compounds from Sideritis javalambrensis n-hexane extract. Journal of Natural Products 52: 1088–1091.
Chen, Y.F., H.Y. Tsai, and T.S. Wu. 1995. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity from roots of Angelica pubescens. Planta Medica 61: 2–8.
Cigremis, Y., Z. Ulukanly, A. Ilcim, and M. Akgoz. 2010. In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial assays of acetone extracts from Nepeta meyeri Bentham. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 14: 661–668.
Coderre, T.J., and R. Melzack. 1992. The contribution of excitatory amino acids to central sensitisation and persistent nociception after formalin-induced tissue injury. Journal of Neuroscience 12: 3665–3670.
Coderre, T.J., A.L. Vacarino, and R. Melzack. 1990. Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection. Brain Research 535: 155–158.
Collier, H.O.J., L.C. Dinneen, C.A. Johnson, and C. Schneider. 1968. The abdominal constriction response and its suppression of analgesic drugs in mouse. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy 32: 295–310.
de Miranda, F.G.G., J.C. Vilar, I.A.N. Alves, C.S.C. de Holanda, and A.R. Antoniolli. 2001. Antinociceptive and antiedematogenic properties and acute toxicity of Tabebuia avellanedae Lor. ex Griseb. inner bark aqueous extract. BMC Pharmacology 1: 6.
Dubuisson, D., and S.G. Dennis. 1977. The formalin test: A quantitative study of the anal-gesic effect of morphine, mepetidin and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 4: 161–174.
Husnkaar, S., and K. Hole. 1987. The formalin test in mice: Dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain 30: 103–114.
Hunskar, S., O.B. Fasmer, and K. Hole. 1985. Formalin test in mice: A useful technique for evaluating mild analgesics. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 14: 69–76.
Hussain, J., F.U. Khan, I.U. Khan, R. Ullah, Z. Muhammad, N. Khan, S.T. Hussain, M. Ullah, H. Rahim, and A.U. Khan. 2010. Antifungal and immunomodulatory potential of Nepeta clarkei. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences 7: 689–692.
Hussain, J., N. Rehman, H. Hussain, L. Ali, and A. Al-Harassi. 2011. Two new phthalate derivatives from Nepeta clarkei. Nepethalates A and B: Two new phthalate derivatives from Nepeta clarkei. Helvetica Chimica Acta 94: 2106–2110.
Irwin, S. 1964. Drug screening and evaluation of new compounds in animals, 36–54. Chicago: Year Book Medical.
Jimeno, J., G. Faircloth, J.M.F. Sousa-Faro, P. Scheuer, and K. Rinehart. 2004. New marine derived anticancer therapeutics: A journey from the sea to clinical trials. Marine Drugs 2: 14–29.
Jimoha, A.O., A. Chika, M.T. Umara, I. Adebisic, and N. Abdullahid. 2011. Analgesic effects and anti-inflammatory properties of the crude methanolic extract of Schwenckia americana. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137: 543–546.
Khairnar, P.P., J.C. Pawar, and S.R. Chaudhary. 2010. Central nervous system activity of different extracts of Leucas logifolia Benth. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 3: 48–52.
Koster, R., M. Anderson, and E.J. De Beer. 1959. Acetic acid for analgesic screening. Federation Proceedings 18: 412.
Murray, R.D.H., F. Porreca, and A. Cowan. 1988. Methodological refinements in the mouse paw formalin test. New animal models of tonic pain. Journal of Pharmacological Methods 20: 175–186.
Neto, A.G., J.M. Costa, C.C. Belati, A.H. Vinholis, L.S. Possebom, A.A. Da Silva Filho, W.R. Cunha, J.C. Carvalho, J.K. Bastos, and M.L. e Silva. 2005. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of a crude root extract of Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng) Pedersen. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 96: 87–91.
Tjolsen, A., O.G. Berge, S. Hunskaar, J.H. Rosland, and K. Hole. 1992. The formalin test: An evaluation of the method. Pain 51: 5–17.
Verma, A., G.K. Jana, S. Sen, R. Chakraborty, S. Sachan, and A. Mishra. 2010. Pharmacological evaluation of Saraca indica leaves for central nervous system depressant activity in mice. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 2: 338–343.
Winter, E.A., E.A. Risley, and G.V. Nuss. 1962. Carrageenin-induced oedema in hind paw of rats as an assay for anti-inflammatory drug. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 111: 544–547.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Government of Pakistan, for providing financial support for the current study under the National Research Program for Universities (NRPU).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, J., Rehman, N.U., Al-Harrasi, A. et al. In vivo evaluation of analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and neuropharmacological activities of the chemical constituent from Nepeta clarkei . Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 1188–1194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0484-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0484-4