Abstract
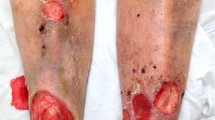
Diabetes mellitus may lead to amputation in 3 % of population. Risk for amputation is 15 folds in diabetics compared with nondiabetics. The aim of the study is to compare the outcome of dressing a diabetic foot ulcer with epidermal growth factor with that of conventional dressing with normal saline. The patients with diabetic foot were divided into study and control groups of 20 each. In the study group, epidermal growth factor (EGF) gel was used as dressing; in control group, dressing was done with normal saline. Treatment was given for 8 weeks or until ulcer healed, whichever occurred first. Evaluation of healing response was recorded on 1, 3, 5, and 8 weeks. After the first week of dressing 90 % of the study group and 30 % of the control group patients showed decrease in wound soakage, size, and increase in proliferation of healthy granulation tissue. After the eighth week of dressing in the study group, 80 % of the patients showed complete response to EGF application. Whereas in control group only 35 % of the patients showed complete response. Duration of hospital stay in the study group was lower as compared with the control group. EGF dressing causes early healing up to first 5 weeks as compared with conventional dressing. The results in healing were not significantly different in two study groups after 8-week duration. Hospital stay was lower in the study group as compared with the control group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henemyre-Harris CL, Adkins AL, Chuang AH, Graham JS (2008) Addition of epidermal growth factor improves the rate of sulfur mustard wound healing in an in vitro model. 8:e16
Bennett NT, Schultz GS (1993) Growth factors and wound healing: biochemical properties of growth factors and their receptors. Am J Surg 165:728–737
Reiber GE, Lipsky BA, Gibbons GW (1998) The burden of diabetic foot ulcers. Am J Surg 176(2):55–195
Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM (1990) Pathways to diabetic limb amputation: basis of prevention. Diabetes Care 13:513–521
Ellenberg M (1968) Diabetic neuropathic ulcer. J Mt Sinai Herp 35:585–594
McEnery KW, Gilula LA, Hardy DC, Staple TW (1993). Imaging of diabetic foot. In: Levin ME, O'Neal LW, Bowker JH (eds) The diabetic foot, 5th edn. St. Louis, MO, Mosby Year, 341–364
Clouse ME, Gramm HF, Legg M, Flood J (1974) Diabetic osteoarthropathy. clinical and roentgenographic observations in 90 cases. Am J Rad 121:34
Tsang MW, Wong WK, Hung CS et al (2003) Human epidermal growth factor enhances healing for diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 23:1856–1861
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Work was done in Department of Surgery, IGMC Shimla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singla, S., Singla, S., Kumar, A. et al. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor in Healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Indian J Surg 74, 451–455 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0447-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-012-0447-2