Abstract
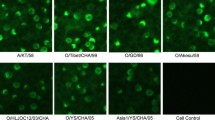
Monoclonal antibodies (McAbs) 1A9 and 9F12 against Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) serotype O were produced by fusing SP2/0 myeloma cells with splenocyte from the mouse immunized with O/China99. Both McAbs reacted with O/China99 but not with Asia 1, as determined by immunohistochemistry assay. The microneutralization titer of the McAbs 1A9 and 9F12 were 640 and 1 280, respectively. Both McAbs contain kappa light chains, but the McAbs 1A9 and 9F12 were IgG1 and IgM, respectively. In order to define the McAbs binding epitopes, the reactivity of these McAbs against VP1, P20 and P14 were examined using indirect ELISA, the result showed that both McAbs reacted with VP1 and P20. McAbs may be used for further studies of vaccine, diagnostic methods, prophylaxis, etiological and immunological researches on FMDV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng I C, Liang S M, Tu J, et al. 2006. Study on the porcinophilic foot-and-mouth disease virus I. production and characterization of monoclonal antibody against VP1. J Vet Med Sci, 68: 859–864.
Crowther J R, Faris S, Carpenter Q C, et al. 1993. Identification of a fifth neutralizable site on type O foot-and-mouth disease virus following characterization of single and quintuple monoclonal antibody escape mutants. J Gen Virol, 74: 1547–1553.
Domingo E, Escarmis C, Baranowski E, et al. 2003. Evolution of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res, 91(1): 47–63.
Harlow E, Lane D. 1988. Monoclonal antibodies. In: Antibodies a Laboratory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, p139–244.
Hong T H, Chen S T, Tang T K, et al. 1989. The production of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies in mice using novel immunization methods. J Immunol Methods, 120: 151–157.
Jackson T, Sharma A, Ghazaleh R A, et al. 1997. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-specific binding by foot-and-mouth disease viruses to the purified integrin alpha (v) beta3 in vitro. J Virol, 71: 8357–8361.
Knowles N J, Samuel A R. 2003. Molecular epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res, 91: 65–80.
Mateu M G, Andreu D, Domingo E. 1995. Antibodies raised in a natural host and monoclonal antibodies recognize similar antigenic features of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology, 210: 113–124.
Ming Y, Alfonso C, Rachel S B, et al. 2007. Production and characterization of two serotype independent monoclonal antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 115: 126–134.
OIE (World Organization for Animal Health), 2004. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. 5th ed, Paris. World Organization for Animal Health, p 111–128.
Reed L J, Muench H. 1938. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent end-points. Am J Hyg, 27: 493–497.
Tesar M, Berger H G, Marquardt O. 1989. Serological probes for some foot-and-mouth disease virus nonstructural proteins. Virus Genes, 3: 29–44.
Wang J H, Liang C M, Peng J M, et al. 2003. Induction of immunity in swine by purified recombinant VP1 of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vaccine, 21: 3721–3729.
McCullough K C, Butcher R. 1982. Monoclonal antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus 146S and 12S particles. Arch Virol, 74(1): 1–9.
Smitsaart E N, Saiz J C, Yedloutschnig R J, et al. 1990. Detectionof foot-and-mouth disease virus by competitive ELISA using a monoclonal antibody specific for the 12S protein subunit from six of the seven serotypes. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 26: 251–265.
Samir K R, Tamishraha B. 2008. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against FMD virus type Asia-1 and determination of antigenic variations in the field strains. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 122: 241–249.
Xie Q C, McCahon D, Crowther J R, et al. 1987. Neutralization of foot-and-mouth disease virus can be mediated through any of at least three separate antigenic sites. J Gen Virol, 68: 1637–1647.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation items: The national high technology research and development program of China 863 (2006AA10A 204); The national science and technology pillar program (2006BAD06A17).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S., Lin, T., Shao, Jj. et al. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against VP1 protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus O/China99. Virol. Sin. 24, 566–572 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-009-3061-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-009-3061-0