Abstract
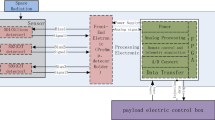
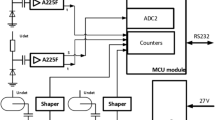
HiDOSE (Heavy ion DOSimetry Experiment) and nDOSE (neutron DOSimetry Experiment) experiments conducted as a part of BIOKIS (Biokon in Space) payload were designed to measure the dose equivalent due to charged particles and to neutron field, on the entire energy range, during STS-134 mission. Given the complexity of the radiation field in space environment, dose measurements should be considered an asset of any space mission, and for this reason HiDOSE and nDOSE experiments represent an important contribution to the radiation environment assessment during this mission, a short duration flight. The results of these experiments, obtained using Thermo Luminescence Dosimeters (TLDs) to evaluate the charged particles dosimetry and neutron bubbles dosimeters and stack bismuth track dosimeters for neutron dosimetry, indicate that the dose equivalent rate due to space radiation exposure during the STS-134 mission is in accordance with the results obtained from long duration flights.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpen, E. L., Powers-Risius, S. B., Curtis, S. B., Deguzman, R.: Tumorigenic potential of high-Z, high-LET charged-particle radiations. Radiat. Res. 136, 382–391 (1993)
Badhwar, G. D., Atwell, W., Reitz, G., Beaujean, R., Heinrich, W.: Radiation measurements on the Mir Orbital Station. Radiat. Meas. 35(5), 393–422 (2002)
Berger, T., Hajek, M., Summerer, L., Fugger, M., Vana, N.: The efficiency of various thermoluminescence dosemeter types to heavy ions. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 120, 365–368 (2006)
Bilski, P.: Dosimetry of densely ionizing radiation with three LiF phosphors for space applications. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 120, 397–400 (2006)
Cross, W. G., Tommasino, L.: Dosimetry of high energy neutrons and protons by Bi-209 fissions. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 70, 419–424 (1997)
Cucinotta, F. A., Durante, M.: Cancer risk from exposure to galactic cosmic rays: implications for space exploration by human beings. Lancet Oncol. 7, 431–435 (2006)
Damasso, M., Dachev, Ts., Giardi, M.T., Falzetta, G., Rea, G., Zanini, A.: Experimental data and GEANT4 Monte Carlo predictions of the radiation environment on board Foton-M3 satellite. In: Proceedings of Workshop Fundamental Space Research, 23?28 September, Sunny Beach, Bulgaria, pp. 159–162 (2008)
Durante, M., Bruno, C.: Impact of rocket propulsion technology on the radiation risk in missions to Mars. Eur. Phys. J. D 60, 215–218 (2010)
European Space Agency: HUMEX: Study on the Survivability and Adaptation of Humans to Long-Duration Exploratory Missions. Report N. ESA-ESTEC SP-1264. ESA Publications Division, The Netherlands (2003)
International Commission on Radiological Protection: Conversion coefficients for use in radiological protection against external radiation. Ann. ICRP 26 (3–4). Pergamon Press; ICRP Publication 74, Oxford (1996)
Koshiishi, H., Matsumoto, H., Chishiki, A., Goka, T., Omodaka, T.: Evaluation of the neutron radiation environment inside the International Space Station based on the Bonner Ball Neutron Detector experiment. Radiat. Meas. 42(9), 1510–1520 (2007)
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Radiation Protection Guidance for Activities in Low-Earth Orbit. Report No 132 (2000)
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements: Operational Radiation Safety Program for Astronauts in Low-Earth Orbit: A Basic Framework. Report No 142 (2002)
Pugliese, M., Bengin, V., Casolino, M., Roca, V., Zanini, A., Durante, M.: Tests of shielding effectiveness of Kevlar and Nextel onboard the International Space Station and the Foton-M3 capsule. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 49, 359–363 (2010a)
Pugliese, M., Roca, V., Durante, M.: The use of TL dosimeters in HZE radiation fields. In: Proceedings of 3rd European IRPA Congress, 14–18 June, Helsinki, Finland P04–18 (2010b)
Vana, N., Schoner, W., Fugger, M., Akatov, Yu.: DOSIMIR-Radiation Measurements inside the Soviet Space Station MIR - First Results. ESA-ISY-2 193 (1992)
Vukich, M., Ganga, P.L., Cavalieri, D., Rizzetto, L., Rivero, D., Pollastri, S., Mugnai, S., Mancuso, S., Pastorelli, S., Lambreva, M., Antonacci, A., Margonelli, A., Bertalan, I., Johanningmeier, U., Giardi, M.T., Rea, G., Pugliese, M., Quarto, M., Roca, V., Zanini, A., Borla, O., Rebecchi, L., Altiero, T., Guidetti, R., Cesari, M., Marchioro, T., Bertolani, R., Pace, E., De Sio, A., Casarosa, M., Tozzetti, L., Branciamore, S., Gallori, E., Scarigella, M., Bruzzi, M., Bucciolini, M., Talamonti, C., Donati, A., Zolesi, V.: BIOKIS: a model payload for multidisciplinary experiments in microgravity. Microgravity. Sci. Technol. 24, 397–409 (2012)
Zanini, A., Storini, M., Saavedra, O.: Cosmic rays at High Mountain Observatories. Adv. Space Res. 44(10), 1160–1165 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pugliese, M., Loffredo, F., Quarto, M. et al. Results of nDOSE and HiDOSE Experiments for Dosimetric Evaluation During STS-134 Mission. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 25, 353–358 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-014-9363-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-014-9363-3