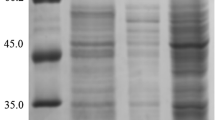
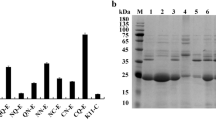
Abstract
The extracellular α-amylase from the hyperthermophilic archaeum Pyrococcus furiosus (PFA) is extremely thermostable and of an industrial importance and interest. PFA aggregates and accumulates as insoluble inclusion bodies when expressed as a heterologous protein at a high level in Escherichia coli. In the present study, we investigated the roles of chaperones from P. furiosus in the soluble expression of recombinant PFA in E. coli. The results indicate that co-expression of PFA with the molecular chaperone prefoldin alone significantly increased the soluble expression of PFA. Although, co-expression of other main chaperone components from P. furiosus, such as the small heat shock protein (sHSP) or chaperonin (HSP60), was also able to improve the soluble expression of PFA to a certain extent. Co-expression of chaperonin or sHSP in addition to prefoldin did not further increase the soluble expression of PFA. This finding emphasizes the biotechnological potentials of the molecular chaperone prefoldin from P. furiosus, which may facilitate the production of recombinant PFA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atomi H, Sato T, Kanai T (2011) Application of hyperthermophiles and their enzymes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(5):618–626
Ben-Zvi AP, Goloubinoff P (2001) Review: mechanisms of disaggregation and refolding of stable protein aggregates by molecular chaperones. J Struct Biol 135(2):84–93
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases, α and β. Methods Enzymol 1:149–158
Carvalho H, Meneghini R (2008) Increased expression and purification of soluble iron-regulatory protein 1 from Escherichia coli co-expressing chaperonins GroES and GroEL. Braz J Med Bio Res 41(4):270–276
Chen HY, Chu ZM, Zhang Y, Yang SL (2006) Over-expression and characterization of the recombinant small heat shock protein from Pyrococcus furiosus. Biotechnol Lett 28(14):1089–1094
Chen HY, Chu ZM, Ma YH, Zhang Y, Yang SL (2007) Expression and characterization of the chaperonin molecular machine from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Basic Microbiol 47(2):132–137
Chen H, Yang LD, Zhang Y, Yang SL (2010) Over-expression and characterization of recombinant prefoldin from hyperthermophilic archaeum Pyrococcus furiosus in E. coli. Biotechnol Lett 32:429–434
de Marco A (2007) Protocol for preparing proteins with improved solubility by co-expressing with molecular chaperones in Escherichia coli. Nat Protoc 2(10):2632–2639
de Marco A, Vigh L, Diamant S, Goloubinoff P (2005) Native folding of aggregation-prone recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by osmolytes, plasmid- or benzyl alcohol-overexpressed molecular chaperones. Cell Stress Chaperones 10(4):329–339
Dong G, Vieille C, Savchenko A, Zeikus JG (1997) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene encoding extracellular alpha-amylase from Pyrococcus furiosus and biochemical characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(9):3569–3576
Ellis J (1987) Proteins as molecular chaperones. Nature 328(6129):378–379
Emmanuel L, Stefan J, Bernard H, Abdel B (2000) Thermophilic archaeal amylolytic enzymes. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:3–14
Grzybowska B, Szweda P, Synowiecki J (2004) Cloning of the thermostable α-amylase gene from Pyrococcus woesei in Escherichia coli. Mol Biotechnol 26:101–109
Haki GD, Rakshit SK (2003) Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: a review. Bioresour Technol 89:17–34
Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M (2002) Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: from nascent chain to folded protein. Science 295(5561):1852–1858
Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M (2011) Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 475(7356):324–332
Hongo K, Itai H, Mizobata T, Kawata Y (2012) Varied effects of Pyrococcus furiosus prefolding and P. furiosus chaperonin on the refolding reactions of substrate proteins. J Biochem 151(4):383–390
Iizuka R, Sugano Y, Ide N, Ohtaki A, Yoshida T, Fujiwara S, Imanaka T, Yohda M (2008) Functional characterization of recombinant prefoldin complexes from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Thermococcus sp. strain KS-1. J Mol Biol 377:972–983
Jørgensen S, Vorgias CE, Antranikian G (1997) Cloning, sequencing, characterization, and expression of an extracellular a-amylase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 268:16335–16342
Kim KK, Kim R, Kim SH (1998) Crystal structure of a small heat-shock protein. Nature 394(6693):595–599
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Lakanalamai P, Whitehead TA, Rbobb FT (2004) Minimal protein-folding systems in hyperthermophilic archaea. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(4):315–324
Laksanalamai P, Maeder DL, Robb FT (2001) Regulation and mechanism of action of the small heat shock protein from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Bacteriol 183(17):5198–5202
Laksanalamai P, Pavlov AR, Slesarev AI, Robb FT (2006) Stabilization of Taq DNA polymerase at high temperature by protein folding pathways from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Pyrococcus furiosus. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:1–5
Leroux MR, Fandrich M, Klunker D, Siegers K, Lupas AN, Brown JR, Schiebel E, Dobson CM, Hartl FU (1999) MtGimC, a novel archaeal chaperone related to the eukaryotic chaperonin cofactor GimC/prefoldin. EMBO J 18:6730–6743
Lund P (2011) Insights into chaperonin function from studies on archaeal thermosomes. Biochem Soc Trans 39(1):94–98
Lundin VF, Stirling PC, Gomez-Rein J, Mwenifumbo JC, Obst JM, Valpuesta JM, Leroux MR (2004) Molecular clamp mechanism of substrate binding by hydrophobic coiled-coil residues of the archaeal chaperone prefoldin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:4367–4372
Martinez-Alonso M et al (2009) Rehosting of bacterial chaperones for high-quality protein production. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(24):7850–7854
Nishihara K, Kanemori M, Yanagi H, Yura T (2000) Overexpression of trigger factor prevents aggregation of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:884–889
Okochi M, Yoshida T, Maruyama T, Kawarabayasi Y, Kikuchi H, Yohda M (2002) Pyrococcus prefoldin stabilizes protein-folding intermediates and transfers them to chaperonins for correct folding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:769–774
Okochi M, Kanie K, Kurimoto M, Yohda M, Honda H (2008) Overexpression of prefoldin from hyperthermophilic archaeum Pyrococcus horokoshii OT3 endowed Escherichia coli with organic solvent tolerance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:443–449
Rutherford SL, Lindquist S (1998) Hsp90 as a capacitor for morphological evolution. Nature 396:336–342
Siegers K, Waldmann T, Leroux MR, Grein K, Shevchenko A, Schiebel E, Hartl FU (1999) Compartmentation of protein folding in vivo: sequestration of non-native polypeptide by the chaperonin-GimC system. EMBO J 18:75–84
Tokuriki N, Tawfik DS (2009) Chaperonin overexpression promotes genetic variation and enzyme evolution. Nature 459:668–671
Wang LS, Zhou Q, Chen H, Chu Z, Lu J, Zhang Y et al (2007) Efficient solubilization, purification of recombinant extracellular alpha-amylase from Pyrococcus furiosus expressed as inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 4(3):187–192
Yan X, Hu S, Guan YX, Yao SJ (2012) Coexpression of chaperonin GroEL/GroES markedly enhanced soluble and functional expression of recombinant human interferon-gamma in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93(3):1065–1074
Zhang J, Baker ML, Schroder GF, Douglas NR et al (2010) Mechanism of folding chamber closure in a group II chaperonin. Nature 463(7279):379–383
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) No. 2012CB721103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Chu, Z., Lu, J. et al. Co-expression of chaperones from P. furiosus enhanced the soluble expression of the recombinant hyperthermophilic α-amylase in E. coli . Cell Stress and Chaperones 21, 477–484 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0675-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0675-7