Abstract
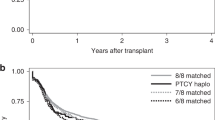
We retrospectively compared transplant outcomes for related bone marrow transplantation (rBMT), related peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (rPBSCT), unrelated bone marrow transplantation (uBMT), and unrelated cord blood transplantation (CBT) in 1,062 patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) aged 20 years or over between January 1, 2000 and December 31, 2009 in Japan. The disease status was as follows: chronic phase 1 (CP1, n = 531), CP 2 or later including accelerated phase (CP2-AP, n = 342) and blastic crisis (BC, n = 189). Graft sources (GS) were rBMT (n = 205), uBMT (n = 507), rPBSCT (n = 226) or CBT (n = 124). In multivariate analysis in CP1, lower overall survival (OS) (relative risk [RR]: 6.01, 95 % confidence interval [CI]: 1.20–29.97, P = 0.029) and leukemia-free survival (LFS) (RR: 4.26, 95 % CI: 1.24–14.62, P = 0.021) were observed in uBMT compared with those in rBMT. For patients in the advanced phase of CML beyond CP1, GS had no significant impact on OS or LFS. Our results support the use of rBMT for adults with CML in CP1, but in contrast to previous reports, the superiority of rPBSCT in advanced stage of CML was not confirmed in our cohorts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cortes J, H Kantarjian. How I treat newly diagnosed chronic phase CML. Blood. 2012;120:1390–7.
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6041–51.
Hehlmann R, Berger U, Pfirrmann M, et al. Drug treatment is superior to allografting as first line therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2007;109:4686–92.
Saussele S, Lauseker M, Gratwohl A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era: evaluation of its impact within a subgroup of the randomized German CML Study IV. Blood. 2010;115:1880–5.
Radich J. Stem cell transplant for chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era. Semin Hematol. 2010;47:354–61.
Venepalli N, Rezvani K, Mielke S, et al. Role of allo-SCT for CML in 2010. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2010;45:1579–86.
Cortes JE, Kantarjian H, Shah NP, et al. Ponatinib in refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2075–88.
O’Hare T, Shakespeare WC, Zhu X, et al. AP24534, a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor for chronic myeloid leukemia, potently inhibits the T315I mutant and overcomes mutation-based resistance. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:401–12.
Atsuta Y, Suzuki R, Yoshimi A, et al. Unification of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation registries in Japan and establishment of the TRUMP System. Int J Hematol. 2007;86:269–74.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1995;15:825–8.
Sullivan KM, Agura E, Anasetti C, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease and other late complications of bone marrow transplantation. Semin Hematol. 1991;28:250–9.
Kanda J. Effect of HLA mismatch on acute graft-versus-host disease. Int J Hematol. 2013;98:300–8.
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Apperley J, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in Europe 2006: transplant activity, long-term data and current results. An analysis by the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Haematologica. 2006;91:513–21.
Khoury HJ, Kukreja M, Goldman JM, et al. Prognostic factors for outcomes in allogeneic transplantation for CML in the imatinib era: a CIBMTR analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012;47:810–6.
Champlin RE, Schmitz N, Horowitz MM, et al. Blood stem cells compared with bone marrow as a source of hematopoietic cells for allogeneic transplantation. IBMTR Histocompatibility and Stem Cell Sources Working Committee and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Blood. 2000;95:3702–9.
Oehler VG, Radich JP, Storer B, et al. Randomized trial of allogeneic related bone marrow transplantation versus peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:85–92.
Lee SJ, Kukreja M, Wang T, et al. Impact of prior imatinib mesylate on the outcome of hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;112:3500–7.
Oehler VG, Gooley T, Snyder DS, et al. The effects of imatinib mesylate treatment before allogeneic transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2007;109:1782–9.
Perz JB, Khorashad JS, Marin D, et al. Imatinib preceding allogeneic stem cell transplantation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2006;91:1145–6.
Giralt SA, Arora M, Goldman JM, et al. Chronic Leukemia Working Committee, Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Impact of imatinib therapy on the use of allogeneic haematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2007;137:461–7.
Deininger M, Schleuning M, Greinix H, et al. The effect of prior exposure to imatinib on transplant-related mortality. Haematologica. 2006;91:452–9.
Gluckman E, Rocha V, Boyer-Chammard A, et al. Outcome of cord-blood transplantation from related and unrelated donors. Eurocord Transplant Group and the European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:373–81.
Rubinstein P, Carrier C, Scaradavou A, et al. Outcomes among 562 recipients of placental-blood transplants from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1565–77.
Sanz GF, Saavedra S, Jimenez C, et al. Unrelated donor cord blood transplantation in adults with chronic myelogenous leukemia: results in nine patients from a single institution. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2001;27:693–701.
Nagamura-Inoue T, Kai S, Azuma H, et al. Unrelated cord blood transplantation in CML: Japan Cord Blood Bank Network analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;42:241–51.
Acknowledgments
We thank all of the physicians and nurses who cared for patients in this study. We also thank all the data managers and officers of the JSHCT, JMDP, and JCBBN.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
On behalf of Choric Myeloid Leukemia Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Ohashi, K., Nagamura-Inoue, T., Nagamura, F. et al. Effect of graft sources on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcome in adults with chronic myeloid leukemia in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a Japanese Society of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation retrospective analysis. Int J Hematol 100, 296–306 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1632-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1632-9