Abstract
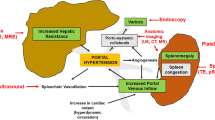
Portal hypertension is the central driver of complications in patients with chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis. The diagnosis of portal hypertension has important prognostic and clinical implications. In particular, screening for varices in patients with portal hypertension can effectively reduce the morbidity and mortality of variceal bleeding. In this article, we review the invasive and non-invasive methods to assess portal hypertension. Hepatic venous pressure gradient remains the gold standard to measure portal pressure but is invasive and seldom performed outside expert centers and research settings. In recent years, a number of non-invasive tests of fibrosis have shown good correlation with liver histology. They also show promise in identifying patients with portal hypertension and large varices. As a result, the latest Baveno VI consensus guidelines endorse the use of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography and platelet count as initial assessment to select patients for varices screening. On the other hand, the performance of non-invasive tests in assessing the response to non-selective beta-blockers or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting is either suboptimal or unclear.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- APRI:
-
AST-to-platelet ratio index
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- AUROC:
-
Area under the receiver-operating characteristics curve
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- FHVP:
-
Free hepatic vein pressure
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HVPG:
-
Hepatic vein pressure gradient
- IVCP:
-
Inferior vena cava pressures
- MRE:
-
Magnetic resonance elastography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- TIPSS:
-
Transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt
- WHVP:
-
Wedged hepatic vein pressure
References
Rincon D, Lo Iacono O, Ripoll C, Gomez-Camarero J, Salcedo M, Catalina MV, Hernando A, et al. Prognostic value of hepatic venous pressure gradient for in-hospital mortality of patients with severe acute alcoholic hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:841–8.
Garg H, Kumar A, Garg V, Kumar M, Kumar R, Sharma BC, Sarin SK. Hepatic and systemic hemodynamic derangements predict early mortality and recovery in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:1361–7.
Sarin SK, Khanna R. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis. 2014;18:451–76.
Kedar RP, Merchant SA, Malde HH, Patel VH. Multiple reflective channels in the spleen: a sonographic sign of portal hypertension. Abdom Imaging. 1994;19:453–8.
Elsayes KM, Narra VR, Mukundan G, Lewis JS Jr, Menias CO, Heiken JP. MR imaging of the spleen: spectrum of abnormalities. Radiographics. 2005;25:967–82.
Lee CM, Jeong WK, Lim S, Kim Y, Kim J, Kim TY, Sohn JH. Diagnosis of clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis: splenic arterial resistive index versus liver stiffness measurement. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42:1312–20.
Aagaard J, Jensen LI, Sorensen TI, Christensen U, Burcharth F. Recanalized umbilical vein in portal hypertension. Am J Roentgenol. 1982;139:1107–10.
Schabel SI, Rittenberg GM, Javid LH, Cunningham J, Ross P. The, “bull’s-eye” falciform ligament: a sonographic finding of portal hypertension. Radiology. 1980;136:157–9.
Subramanyam BR, Balthazar EJ, Madamba MR, Raghavendra BN, Horii SC, Lefleur RS. Sonography of portosystemic venous collaterals in portal hypertension. Radiology. 1983;146:161–6.
Saddekni S, Hutchinson DE, Cooperberg PL. The sonographically patent umbilical vein in portal hypertension. Radiology. 1982;145:441–3.
Lafortune M, Constantin A, Breton G, Legare AG, Lavoie P. The recanalized umbilical vein in portal hypertension: a myth. Am J Roentgenol. 1985;144:549–53.
Cho KC, Patel YD, Wachsberg RH, Seeff J. Varices in portal hypertension: evaluation with CT. Radiographics. 1995;15:609–22.
Eisen GM, Eliakim R, Zaman A, Schwartz J, Faigel D, Rondonotti E, Villa F, et al. The accuracy of PillCam ESO capsule endoscopy versus conventional upper endoscopy for the diagnosis of esophageal varices: a prospective three-center pilot study. Endoscopy. 2006;38:31–5.
de Franchis R, Eisen GM, Laine L, Fernandez-Urien I, Herrerias JM, Brown RD, Fisher L, et al. Esophageal capsule endoscopy for screening and surveillance of esophageal varices in patients with portal hypertension. Hepatology. 2008;47:1595–603.
Banerjee R, Pavlides M, Tunnicliffe EM, Piechnik SK, Sarania N, Philips R, Collier JD, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J Hepatol. 2014;60:69–77.
Pavlides M, Banerjee R, Sellwood J, Kelly CJ, Robson MD, Booth JC, Collier J, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging predicts clinical outcomes in patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:308–15.
Jansen C, Bogs C, Verlinden W, Thiele M, Moller P, Gortzen J, Lehmann J, et al. Shear-wave elastography of the liver and spleen identifies clinically significant portal hypertension: a prospective multicentre study. Liver Int. 2017;37:396–405.
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Garcia-Pagan JC. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:573–82.
Lin HC, Tsai YT, Lee FY, Chang TT, Wang SS, Lay CS, Lee SD, et al. Comparison between portal vein pressure and wedged hepatic vein pressure in hepatitis B-related cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1989;9:326–30.
Perello A, Escorsell A, Bru C, Gilabert R, Moitinho E, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bosch J. Wedged hepatic venous pressure adequately reflects portal pressure in hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1999;30:1393–7.
Thalheimer U, Leandro G, Samonakis DN, Triantos CK, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Assessment of the agreement between wedge hepatic vein pressure and portal vein pressure in cirrhotic patients. Dig Liver Dis. 2005;37:601–8.
Tandon P, Ripoll C, Assis D, Wongcharatrawee S, Groszmann RJ, Garcia-Tsao G. The interpretation of hepatic venous pressure gradient tracings—excellent interobserver agreement unrelated to experience. Liver Int. 2016;36:1160–6.
Zipprich A, Winkler M, Seufferlein T, Dollinger MM. Comparison of balloon vs. straight catheter for the measurement of portal hypertension. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:1351–6.
Ripoll C, Banares R, Rincon D, Catalina MV, Lo Iacono O, Salcedo M, Clemente G, et al. Influence of hepatic venous pressure gradient on the prediction of survival of patients with cirrhosis in the MELD Era. Hepatology. 2005;42:793–801.
Kim TY, Lee JG, Sohn JH, Kim JY, Kim SM, Kim J, Jeong WK. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts long-term mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57:138–45.
D’Amico G, Garcia-Pagan JC, Luca A, Bosch J. Hepatic vein pressure gradient reduction and prevention of variceal bleeding in cirrhosis: a systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1611–24.
Villanueva C, Aracil C, Colomo A, Hernandez-Gea V, Lopez-Balaguer JM, Alvarez-Urturi C, Torras X, et al. Acute hemodynamic response to beta-blockers and prediction of long-term outcome in primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:119–28.
Garcia-Tsao G. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of refractory ascites. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2005;22:278–86.
Bruix J, Castells A, Bosch J, Feu F, Fuster J, Garcia-Pagan JC, Visa J, et al. Surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: prognostic value of preoperative portal pressure. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:1018–22.
Nagoshi S. Osteopontin: versatile modulator of liver diseases. Hepatol Res. 2014;44:22–30.
Bruha R, Jachymova M, Petrtyl J, Dvorak K, Lenicek M, Urbanek P, Svestka T, et al. Osteopontin: a non-invasive parameter of portal hypertension and prognostic marker of cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:3441–50.
Ferlitsch M, Reiberger T, Hoke M, Salzl P, Schwengerer B, Ulbrich G, Payer BA, et al. von Willebrand factor as new noninvasive predictor of portal hypertension, decompensation and mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2012;56:1439–47.
Hametner S, Ferlitsch A, Ferlitsch M, Etschmaier A, Schofl R, Ziachehabi A, Maieron A. The VITRO score (Von Willebrand Factor Antigen/Thrombocyte Ratio) as a new marker for clinically significant portal hypertension in comparison to other non-invasive parameters of fibrosis including ELF test. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0149230.
Abdi W, Millan JC, Mezey E. Sampling variability on percutaneous liver biopsy. Arch Intern Med. 1979;139:667–9.
Piccinino F, Sagnelli E, Pasquale G, Giusti G. Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy. A multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. J Hepatol. 1986;2:165–73.
Zhou K, Lu LG. Assessment of fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. J Dig Dis. 2009;10:7–14.
European Association for Study of the Liver. Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado. EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. J Hepatol. 2015;63:237–64.
Afdhal NH, Nunes D. Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1160–74.
Wong GL, Espinosa WZ, Wong VW. Personalized management of cirrhosis by non-invasive tests of liver fibrosis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015;21:200–11.
Hajian-Tilaki K. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Caspian J Intern Med. 2013;4:627–35.
Lin ZH, Xin YN, Dong QJ, Wang Q, Jiang XJ, Zhan SH, Sun Y, et al. Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2011;53:726–36.
Papastergiou V, Tsochatzis E, Burroughs AK. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2012;25:218–31.
Suzuki A, Angulo P, Lymp J, Li D, Satomura S, Lindor K. Hyaluronic acid, an accurate serum marker for severe hepatic fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2005;25:779–86.
Gressner OA, Weiskirchen R, Gressner AM. Biomarkers of liver fibrosis: clinical translation of molecular pathogenesis or based on liver-dependent malfunction tests. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;381:107–13.
Naveau S, Poynard T, Benattar C, Bedossa P, Chaput JC. Alpha-2-macroglobulin and hepatic fibrosis. Diagnostic interest. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:2426–32.
Imbert-Bismut F, Ratziu V, Pieroni L, Charlotte F, Benhamou Y, Poynard T, Group M. Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: a prospective study. Lancet. 2001;357:1069–75.
Shaheen AA, Wan AF, Myers RP. FibroTest and FibroScan for the prediction of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: a systematic review of diagnostic test accuracy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2589–600.
Cales P, Boursier J, Oberti F, Hubert I, Gallois Y, Rousselet MC, Dib N, et al. FibroMeters: a family of blood tests for liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2008;32:40–51.
Leroy V, Sturm N, Faure P, Trocme C, Marlu A, Hilleret MN, Morel F, et al. Prospective evaluation of FibroTest(R), FibroMeter(R), and HepaScore(R) for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: comparison with hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2014;61:28–34.
Friedrich-Rust M, Rosenberg W, Parkes J, Herrmann E, Zeuzem S, Sarrazin C. Comparison of ELF, FibroTest and FibroScan for the non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010;10:103.
Cales P, Oberti F, Michalak S, Hubert-Fouchard I, Rousselet MC, Konate A, Gallois Y, et al. A novel panel of blood markers to assess the degree of liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2005;42:1373–81.
Rossi E, Adams LA, Bulsara M, Jeffrey GP. Assessing liver fibrosis with serum marker models. Clin Biochem Rev. 2007;28:3–10.
Madhotra R, Mulcahy HE, Willner I, Reuben A. Prediction of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;34:81–5.
Pilette C, Oberti F, Aube C, Rousselet MC, Bedossa P, Gallois Y, Rifflet H, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of esophageal varices in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol. 1999;31:867–73.
Ng FH, Wong SY, Loo CK, Lam KM, Lai CW, Cheng CS. Prediction of oesophagogastric varices in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;14:785–90.
Silva G. New serum markers for predicting esophageal varices: is it a reality? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:4–5.
Rockey DC, Elliott A, Lyles T. Prediction of esophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in patients with acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. J Investig Med. 2016;64:745–51.
Sebastiani G, Tempesta D, Fattovich G, Castera L, Halfon P, Bourliere M, Noventa F, et al. Prediction of oesophageal varices in hepatic cirrhosis by simple serum non-invasive markers: results of a multicenter, large-scale study. J Hepatol. 2010;53:630–8.
Thabut D, Trabut JB, Massard J, Rudler M, Muntenau M, Messous D, Poynard T. Non-invasive diagnosis of large oesophageal varices with FibroTest in patients with cirrhosis: a preliminary retrospective study. Liver Int. 2006;26:271–8.
Poca M, Puente A, Graupera I, Villanueva C. Prognostic markers in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension who have not bled. Dis Markers. 2011;31:147–54.
Mao W, Sun Q, Fan J, Lin S, Ye B. AST to platelet ratio index predicts mortality in hospitalized patients with hepatitis b-related decompensated cirrhosis. Med (Baltimore). 2016;95:e2946.
Qi X, Li H, Chen J, Xia C, Peng Y, Dai J, Hou Y, et al. Serum liver fibrosis markers for predicting the presence of gastroesophageal varices in liver cirrhosis: a retrospective cross-sectional study. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:274534.
Bari K, Garcia-Tsao G. Treatment of portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:1166–75.
Thabut D, Imbert-Bismut F, Cazals-Hatem D, Messous D, Muntenau M, Valla DC, Moreau R, et al. Relationship between the Fibrotest and portal hypertension in patients with liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:359–68.
Chan TT, Wong VW. In search of new biomarkers for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2016;8:19–23.
Wong VW, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Foucher J, Chan HL, Le Bail B, Choi PC, et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:454–62.
Leung VY, Shen J, Wong VW, Abrigo J, Wong GL, Chim AM, Chu SH, et al. Quantitative elastography of liver fibrosis and spleen stiffness in chronic hepatitis B carriers: comparison of shear-wave elastography and transient elastography with liver biopsy correlation. Radiology. 2013;269:910–8.
Cui J, Heba E, Hernandez C, Haufe W, Hooker J, Andre MP, Valasek MA, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography is superior to acoustic radiation force impulse for the Diagnosis of fibrosis in patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study. Hepatology. 2016;63:453–61.
Imajo K, Kessoku T, Honda Y, Tomeno W, Ogawa Y, Mawatari H, Fujita K, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(626–637):e627.
Wong GL, Wong VW, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, Chan FK, et al. Increased liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography in severe acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1002–7.
Millonig G, Friedrich S, Adolf S, Fonouni H, Golriz M, Mehrabi A, Stiefel P, et al. Liver stiffness is directly influenced by central venous pressure. J Hepatol. 2010;52:206–10.
Millonig G, Reimann FM, Friedrich S, Fonouni H, Mehrabi A, Buchler MW, Seitz HK, et al. Extrahepatic cholestasis increases liver stiffness (FibroScan) irrespective of fibrosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:1718–23.
Mederacke I, Wursthorn K, Kirschner J, Rifai K, Manns MP, Wedemeyer H, Bahr MJ. Food intake increases liver stiffness in patients with chronic or resolved hepatitis C virus infection. Liver Int. 2009;29:1500–6.
Loustaud-Ratti VR, Cypierre A, Rousseau A, Yagoubi F, Abraham J, Fauchais AL, Carrier P, et al. Non-invasive detection of hepatic amyloidosis: fibroScan, a new tool. Amyloid. 2011;18:19–24.
Wong GL, Chan HL, Choi PC, Chan AW, Lo AO, Chim AM, Wong VW. Association between anthropometric parameters and measurements of liver stiffness by transient elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11(295–302):e291–3.
Petta S, Maida M, Macaluso FS, Di Marco V, Camma C, Cabibi D, Craxi A. The severity of steatosis influences liver stiffness measurement in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2015;62:1101–10.
Petta S, Wong VW, Camma C, Hiriart JB, Wong GL, Marra F, Vergniol J, et al. Improved noninvasive prediction of liver fibrosis by liver stiffness measurement in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease accounting for controlled attenuation parameter values. Hepatology. 2017;65:1145–55.
Bureau C, Metivier S, Peron JM, Selves J, Robic MA, Gourraud PA, Rouquet O, et al. Transient elastography accurately predicts presence of significant portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:1261–8.
Colecchia A, Montrone L, Scaioli E, Bacchi-Reggiani ML, Colli A, Casazza G, Schiumerini R, et al. Measurement of spleen stiffness to evaluate portal hypertension and the presence of esophageal varices in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:646–54.
Zykus R, Jonaitis L, Petrenkiene V, Pranculis A, Kupcinskas L. Liver and spleen transient elastography predicts portal hypertension in patients with chronic liver disease: a prospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015;15:183.
Takuma Y, Nouso K, Morimoto Y, Tomokuni J, Sahara A, Toshikuni N, Takabatake H, et al. Measurement of spleen stiffness by acoustic radiation force impulse imaging identifies cirrhotic patients with esophageal varices. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(92–101):e102.
Kazemi F, Kettaneh A, N’Kontchou G, Pinto E, Ganne-Carrie N, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M. Liver stiffness measurement selects patients with cirrhosis at risk of bearing large oesophageal varices. J Hepatol. 2006;45:230–5.
Castera L, Le Bail B, Roudot-Thoraval F, Bernard PH, Foucher J, Merrouche W, Couzigou P, et al. Early detection in routine clinical practice of cirrhosis and oesophageal varices in chronic hepatitis C: comparison of transient elastography (FibroScan) with standard laboratory tests and non-invasive scores. J Hepatol. 2009;50:59–68.
Vermehren J, Polta A, Zimmermann O, Herrmann E, Poynard T, Hofmann WP, Bojunga J, et al. Comparison of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging with transient elastography for the detection of complications in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2012;32:852–8.
Stefanescu H, Radu C, Procopet B, Lupsor-Platon M, Habic A, Tantau M, Grigorescu M. Non-invasive menage a trois for the prediction of high-risk varices: stepwise algorithm using lok score, liver and spleen stiffness. Liver Int. 2015;35:317–25.
Wong GL, Kwok R, Chan HL, Tang SP, Lee E, Lam TC, Lau TW, et al. Measuring spleen stiffness to predict varices in chronic hepatitis B cirrhotic patients with or without receiving non-selective beta-blockers. J Dig Dis. 2016;17:538–46.
Robic MA, Procopet B, Metivier S, Peron JM, Selves J, Vinel JP, Bureau C. Liver stiffness accurately predicts portal hypertension related complications in patients with chronic liver disease: a prospective study. J Hepatol. 2011;55:1017–24.
de Franchis R, Baveno VIF. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2015;63:743–52.
Maurice JB, Brodkin E, Arnold F, Navaratnam A, Paine H, Khawar S, Dhar A, et al. Validation of the Baveno VI criteria to identify low risk cirrhotic patients not requiring endoscopic surveillance for varices. J Hepatol. 2016;65:899–905.
Gao J, Ran HT, Ye XP, Zheng YY, Zhang DZ, Wang ZG. The stiffness of the liver and spleen on ARFI Imaging pre and post TIPS placement: a preliminary observation. Clin Imaging. 2012;36:135–41.
Chang TT, Liaw YF, Wu SS, Schiff E, Han KH, Lai CL, Safadi R, et al. Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;52:886–93.
Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, Washington MK, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013;381:468–75.
Mallet V, Gilgenkrantz H, Serpaggi J, Verkarre V, Vallet-Pichard A, Fontaine H, Pol S. Brief communication: the relationship of regression of cirrhosis to outcome in chronic hepatitis C. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:399–403.
Lampertico P, Invernizzi F, Vigano M, Loglio A, Mangia G, Facchetti F, Primignani M, et al. The long-term benefits of nucleos(t)ide analogs in compensated HBV cirrhotic patients with no or small esophageal varices: a 12-year prospective cohort study. J Hepatol. 2015;63:1118–25.
Tsochatzis EA, Bosch J, Burroughs AK. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2014;383:1749–61.
Zironi G, Gaiani S, Fenyves D, Rigamonti A, Bolondi L, Barbara L. Value of measurement of mean portal flow velocity by Doppler flowmetry in the diagnosis of portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 1992;16:298–303.
Pollard JJ, Nebesar RA. Catheterization of the splenic artery for portal venography. N Engl J Med. 1964;271:234–7.
Sheppard DG, Moss J, Miller M. Imaging of the portal vein during transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures: a comparison of carbon dioxide and iodinated contrast. Clin Radiol. 1998;53:448–50.
Khanna R, Sarin SK. Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension—diagnosis and management. J Hepatol. 2014;60:421–41.
Colley DG, Bustinduy AL, Secor WE, King CH. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet. 2014;383:2253–64.
Smalberg JH, Arends LR, Valla DC, Kiladjian JJ, Janssen HL, Leebeek FW. Myeloproliferative neoplasms in Budd-Chiari syndrome and portal vein thrombosis: a meta-analysis. Blood. 2012;120:4921–8.
Sarin SK, Kumar A, Chawla YK, Baijal SS, Dhiman RK, Jafri W, Lesmana LA, et al. Noncirrhotic portal fibrosis/idiopathic portal hypertension: APASL recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Hepatol Int. 2007;1:398–413.
Pohl A, Behling C, Oliver D, Kilani M, Monson P, Hassanein T. Serum aminotransferase levels and platelet counts as predictors of degree of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:3142–6.
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, Fontaine H, et al. FIB-4: an inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007;46:32–6.
Sirli R, Sporea I, Bota S, Popescu A, Cornianu M. A comparative study of non-invasive methods for fibrosis assessment in chronic HCV infection. Hepat Mon. 2010;10:88–94.
Koda M, Matunaga Y, Kawakami M, Kishimoto Y, Suou T, Murawaki Y. FibroIndex, a practical index for predicting significant fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2007;45:297–306.
Zaman A, Rosen HR, Ingram K, Corless CL, Oh E, Smith K. Assessment of FIBROSpect II to detect hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. Am J Med. 2007;120:e280–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest
Vincent Wong has served as an advisory board member for Perspectum Diagnostics and a speaker for Echosens. The other authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable because this is a review article.
Informed consent
Not applicable because this is a review article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leung, J.CF., Loong, T.CW., Pang, J. et al. Invasive and non-invasive assessment of portal hypertension. Hepatol Int 12 (Suppl 1), 44–55 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-017-9795-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-017-9795-0