Abstract
Aims
To prospectively assess the use of microwave ablation (MWA) to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and to evaluate factors that significantly affect treatment outcomes.
Methods
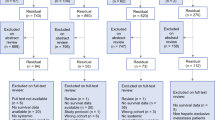
Sixty patients with HCC [55 male, 5 female; mean age, 54.1 ± 10.2 (range 36–77) years] + PVTT were enrolled. Patients were treated with MWA after TACE. Results were compared with those of 54 patients treated by TACE alone in another retrospective study. Data analyzed included patient demographics, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, liver cirrhosis, liver volume, Child-Pugh class, Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score, and imaging findings. Survival time (from occurrence of PVTT to last follow-up) and predictive factors and their correlation with survival were statistically evaluated.
Results
The median 3-year overall survival (OS) duration was 13.5 months, and the 1- and 3-year OS rates were 48 and 23 %, respectively. Cox hazards regression analysis revealed that change in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, CLIP score, and treatment efficacy were the only independent predictive factors for outcome (p = 0.035, 0.024, and 0.000, respectively).
Conclusions
Combination therapy with MWA after TACE may provide a substantial benefit for patients with HCC + PVTT type I, II, or partial III and Child-Pugh class A or B by reducing the tumor burden.
Trial registration number
Chinese Clinical Trial Register (ChiCTR): ChiCTR-ONC-12002689.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- CLIP:
-
Cancer of the Liver Italian Program
- TACE:
-
Transarterial chemoembolization
- CT:
-
Computerized tomography
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- PVTT:
-
Portal vein tumor thrombosis
- RLV:
-
Remnant liver volume
- FRLV:
-
Functional remnant liver volume
- TLV:
-
Total liver volume
- CR:
-
Complete response
- PR:
-
Partial response
- BCLC:
-
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Group
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- HAIC:
-
Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy
- TTV:
-
Total tumor volume
- NLR:
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
References
Takizawa D, Kaizaki S, Sohara N, Sato K, Takagi H, Arai H, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with vein tumor thrombosis: clinical characteristics, prognosis, and patient survival analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52:3290–3295.
Luo J, Guo RP, Lai EC, Zhang YJ, Lau WY, Chen MS, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a prospective comparative study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:413–420.
Shirai S, Sato M, Suwa K, Kishi K, Shimono C, Sonomura T, et al. Feasibility and efficacy of single photon emission computed tomography-based three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma 8 cm or more with portal vein tumor thrombus in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:1037–1044.
Peng BG, He Q, Li JP, Zhou F. Adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization improves efficacy of hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus. Am J Surg. 2009;198:313–318.
Lau WY, Lai EC, Leung TW. Current role of selective internal irradiation with yttrium-90 microspheres in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:460–467.
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF, Mahvi DM, Lee FT Jr. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology. 2005;1:132–139.
Liu C, Liang P, Liu F, Wang Y, Li X, Han Z, et al. MWA combined with TACE as a combined therapy for unresectable large-sized hepotocellular carcinoma. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011;27:654–662.
Hirooka M, Koizumi Y, Kisaka Y, Abe M, Murakami H, Matsuura B, et al. Mass reduction by radiofrequency ablation before hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy improved prognosis for patients with huge hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombus. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194:221–226.
Chen T-M, Lin C-C, Huang P-T, Wen C-F. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio associated with mortality in early hepatocellular carcinoma patients after radiofrequency ablation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:553–561.
Dan J, Zhang Y, Peng Z, Huang J, Gao H, Xu L, et al. Postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio change predicts survival of patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing radiofrequency ablation. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e58184.
Chen Shuqun, Menchao Wu, Chen Han, Shen Feng, Yang Jiahe, Cong Wenming, et al. Significance of typing of tumor thrombi in determination of treatment and assessment of prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the portal vein. Natl Med J China. 2004;84:3–5.
Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:52–60.
European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–943.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53:1020–1022.
Georgiades CS, Hong K, D′Angelo M, Geschwind JF. Safety and efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005;16:1653–1659.
Obi S, Yoshida H, Toune R, Unuma T, Kanda M, Sato S, et al. Combination therapy of intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and systemic interferon-alpha for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous invasion. Cancer. 2006;106:1990–1997.
Kim DY, Park W, Lim DH, Lee JH, Yoo BC, Paik SW, et al. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein thrombosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:2419–2426.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390.
Hata M, Tokuuye K, Sugahara S, Kagei K, Igaki H, Hashimoto T, et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Cancer. 2005;104:794–801.
Qi WX, Fu S, Zhang Q, Guo XM. Charged particle therapy versus photon therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114:289–295.
Gerald DD, Michael CS, Robert AK, Livraghi T, Lees WR, Yamashita Y, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of malignant hepatic tumors: at the threshold of a major breakthrough. Radiographics. 2000;20:9–27.
Toyosaka A, Okamoto E, Mitsunobu M, Oriyama T, Nakao N, Miura K. Intrahepatic metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence for spread via the portal vein as an efferent vessel. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1610–1615.
Zheng RQ, Kudo M, Minami Y, Inui K, Chung H. IV hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous tumor thrombus: complete response after combined therapy of repeated arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:406–409.
Chua W, Clarke SJ, Charles KA. Systemic inflammation and prediction of chemotherapy outcomes in patients receiving docetaxel for advanced cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20:1869–1874.
Jung MR, Park YK, Jeong O, Seon JW, Ryu SY, Kim DY, et al. Elevated preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts poor survival following resection in late stage gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104:504–510.
Halazun KJ, Hardy MA, Rana AA, Woodland DC 4th, Luyten EJ, Mahadev S, et al. Negative impact of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio on outcome after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2009;250:141–151.
Zhang L, Wang JN, Tang JM, Kong X, Yang JY, Zheng F, et al. VEGF is essential for the growth and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:5085–5093.
Wang R, Zhao N, Li S, Fang JH, Chen MX, Yang J, et al. MicroRNA-195 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of VEGF, VAV2 and CDC42. Hepatology. 2013;58:642–653.
Wu Y, Liu C, Sun M, Shen H, Guo D, Gao B. A specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope presentation system for antitumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:2373–2386.
Wang H-T, Lee H-I, Guo J-H, Chen SH, Liao ZK, Huang KW, et al. Calreticulin promotes tumor lymphocyte infiltration and enhances the antitumor effects of immunotherapy by up-regulating the endothelial expression of adhesion molecules. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:2892–2902.
Motomura T, Shirabe K, Mano Y, Muto J, Toshima T, Umemoto Y, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio reflects hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation via inflammatory microenvironment. J Hepatol. 2013;58:58–64.
Sanchez-Ortiz RF, Tannir N, Ahrar K, Wood CG. Spontaneous regression of pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma after radio frequency ablation of primary tumor: an in situ tumor vaccine? J Urol. 2003;170:178–179.
Rao P, Escudier B, de Baere T. Spontaneous regression of multiple pulmonary metastases after radiofrequency ablation of a single metastasis. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2011;134:424–430.
Fagnoni FF, Zerbini A, Pelosi G, Missale G. Combination of radiofrequency ablation and immunotherapy. Front Biosci. 2008;13:369–381.
den Brok MH, Sutmuller RP, vander Voort R, Bennink EJ, Figdor CG, Ruers TJ, et al. In situ tumor ablation creates an antigen source for the generation of antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4024–4029.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Jia-sheng Zheng received a grant from the National Science and Technology Support Project (2010-2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jiang Long, Jia-sheng Zheng, Bin Sun, Ningning Lu declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
The study complied with the standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and current ethical guidelines, and was approved by our institutional ethics board.
Informed Consent
Patient consent was obtained
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Zheng, Js., Sun, B. et al. Microwave ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis after transarterial chemoembolization: a prospective study. Hepatol Int 10, 175–184 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9673-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-015-9673-6