Abstract
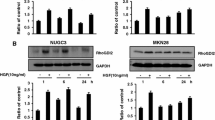
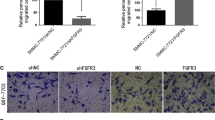
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a crucial role in tumor angiogenesis. VEGF induces new vessel formation and tumor growth by inducing mitogenesis and chemotaxis of normal endothelial cells and increasing vascular permeability. However, little is known about VEGF function in the proliferation, survival or migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC). In the present study, we have found that VEGF receptors are expressed in HCC line BEL7402 and human HCC specimens. Importantly, VEGF receptor expression correlates with the development of the carcinoma. By using a comprehensive approaches including TUNEL assay, transwell and wound healing assays, migration and invasion assays, adhesion assay, western blot and quantitative RT-PCR, we have shown that knockdown of VEGF165 expression by shRNA inhibits the proliferation, migration, survival and adhesion ability of BEL7402. Knockdown of VEGF165 decreased the expression of NF-κB p65 and PKCα while increased the expression of p53 signaling molecules, suggesting that VEGF functions in HCC proliferation and migration are mediated by P65, PKCα and/or p53.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taro Y, Kaneko S (2010) Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 37(1):14–17
Zhang Y, Xia HHX (2008) Novel therapeutic approaches for hepatocellulcar carcinoma: Fact and fiction. World J Gastroenterol 14(11):1641–1642
Ferrara N (2002) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol 29(6 Suppl 16):10–14
Fernando NH, Hurwitz HI (2003) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol 30(3 Suppl 6):39–50
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J (2000) Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 407(6801):242–248
Santos SC, Dias S (2004) Internal and external autocrine VEGF/KDR loops regulate survival of subsets of acute leukemia through distinct signaling pathways. Blood 103(10):3883–3889
Dias S, Hattori K, Heissig B, Zhu Z, Wu Y, Witte L et al (2001) Inhibition of both paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathways is essential to induce long-term remission of xenotransplanted human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10857–10862
Chartier C, Degryse E, Gantzer M, Dieterle A, Pavirani A, Mehtali M (1996) Efficient generation of recombinant adenovirus vectors by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. J Virol 70:4805–4810
Tang J, Wang J, Guo L, Kong X, Yang J, Zheng F et al (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells modified with stromal cell-derived factor 1α improve cardiac remodeling via paracrine activation of hepatocyte growth factor in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cells 29(1):9–19
Tang J, Wang J, Kong X, Yang J, Guo L, Zheng F et al (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes cardiac stem cell migration via the PI3 K/Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res 315(20):3521–3531
Hu Y, Lehrach H, Janitz M (2010) Apoptosis screening of human chromosome 21 proteins reveals novel cell death regulators. Mol Biol Rep 37(7):3381–3387
Shaw LM (2005) Tumor cell invasion assays. Methods Mol Biol 294:97–105
Nagasaki A, Kanada M, Uyeda TQ (2009) Cell adhesion molecules regulate contractile ring-independent cytokinesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Res 19(2):236–246
Wang L, Xue L, Yan H, Li J, Lu Y (2010) Effects of ROCK inhibitor, Y-27632, on adhesion and mobility in esophageal squamous cell cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 37(4):1971–1977
Deli G, Jin CH, Mu R, Yang S, Liang Y, Chen D et al (2005) Immunohistochemical assessment of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding cirrhotic liver tissues. World J Gastroenterol 11(7):960–963
Fragoso R, Elias AP, Dias S (2007) Autocrine VEGF loops, signaling pathways, and acute leukemia regulation. Leuk Lymphoma 48(3):481–488
Danilova N, Sakamoto KM, Lin S (2008) p53 family in development. Mech Dev 125(11–12):919–931
Molchadsky A, Rivlin N, Brosh R, Rotter V, Sarig R (2010) p53 is balancing development, differentiation and de-differentiation to assure cancer prevention. Carcinogenesis 31(9):1501–1508
Guan Y-H, He Q, La Z (2006) Roles of p53 in carcinogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Mol 2:191–197
Aaltonen V, Peltonen J (2010) PKCalpha/beta I inhibitor Go6976 induces dephosphorylation of constitutively hyperphosphorylated Rb and G1 arrest in T24 cells. Anticancer Res 30(10):3995–3999
Wu TT, Hsieh YH, Hsieh YS, Liu JY (2008) Reduction of PKC alpha decreases cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of human malignant hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 103(1):9–20
Deeds L, Teodorescu S, Chu M, Yu Q, Chen CY (2003) A p53-independent G1 cell cycle checkpoint induced by the suppression of protein kinase C alpha and theta isoforms. J Biol Chem 278(41):39782–39793
Coutinho I, Pereira G, Leão M, Gonçalves J, Côrte-Real M, Saraiva L (2009) Differential regulation of p53 function by protein kinase C isoforms revealed by a yeast cell system. FEBS Lett. 583(22):3582–3588
Frankel AE, Gill PS (2004) VEGF and myeloid leukemias. Leuk Res 28:675
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis. Therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Wang R, Chadalavada K, Wilshire J, Kowalik U, Hovinga KE, Geber A, et al. (2010) Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour endothelium. Nature 468: 829–833
Geva R, Prenen H, Topal B, Aerts R, Vannoote J, Van Cutsem E (2010) Biologic modulation of chemotherapy in patients with hepatic colorectal metastases: the role of anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR antibodies. J Surg Oncol 102(8):937–945
Dias S, Hattori K, Zhu Z, Heissig B, Choy M, Lane W et al (2000) Autocrine stimulation of VEGFR-2 activates human leukemic cell growth and migration. J Clin Invest 106(4):511–521
Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, Sherman D, Liang XH, Meng G et al (2002) VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature 417:954–958
Podar K, Anderson KC (2007) Inhibition of VEGF signaling pathways in multiple myeloma and other malignancies. Cell Cycle 6(5):538–542
Ramakrishnan V, Timm M, Haug JL, Kimlinger TK, Wellik LE, Witzig TE et al (2010) Sorafenib, a dual Raf kinase/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor has significant anti-myeloma activity and synergizes with common anti-myeloma drugs. Oncogene 29(8):1190–1202
Ulivi P, Arienti C, Amadori D, Fabbri F, Carloni S, Tesei A et al (2009) Role of RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, p-STAT-3 and Mcl-1 in sorafenib activity in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol 220(1):214–221
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from National natural Science Foundation of China (81170095; 30700306), Hubei Health Department Science Foundation (JX5B24), Hubei Education Department Science Foundation (T2008010,T201112, Q200524003), China; And National Institutes of Health (HL093429 and HL107526).
Conflicts of interest
All authors have read and approved the manuscript, and there is no ethical problem or conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, JN., Tang, JM. et al. VEGF is essential for the growth and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 39, 5085–5093 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1304-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1304-2