Abstract
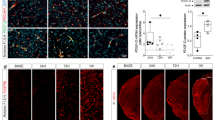
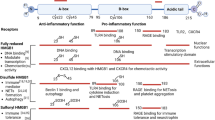
Microglial cells are activated in response to different types of injuries or stress in the CNS. Such activation is necessary to get rid of the injurious agents and restore tissue homeostasis. However, excessive activation of microglial cells is harmful and contributes to secondary injury. Pertinently, microglial cell activity was targeted in many preclinical and clinical studies but such strategy failed in clinical trials. The main reason behind the failed attempts is the complexity of the injury mechanisms which needs either a combination therapy or targeting a process that is involved in multiple pathways. Cofilin is a cytoskeleton-associated protein involved in actin dynamics. In our previous study, we demonstrated the role of cofilin in mediating neuronal apoptosis during OGD conditions. Previous studies on microglia have shown the involvement of cofilin in ROS formation and phagocytosis. However, additional studies are needed to delineate the role of cofilin in microglial cell activation. Therefore, in the current study, we investigated the role of cofilin in LPS-induced microglial cell activation using cofilin siRNA knockdown paradigms. The viability of differentiated PC12 cells was used as a measure of the neurotoxic potential of conditioned medium derived from cofilin siRNA-transfected and LPS-activated microglial cells. Cofilin knockdown significantly inhibited LPS-induced microglial cell activation through NF-κB and JAK–STAT pathways. The release of proinflammatory mediators (NO, TNF-α, iNOS, and COX2) as well as microglial proliferation and migration rates were significantly reduced by cofilin knockdown. Furthermore, differentiated PC12 cells were protected from the neurotoxicity induced by conditioned medium derived from cofilin-transfected and LPS-activated microglial cells. In conclusion, we demonstrated that cofilin is involved in the cascade of microglial cell activation and further validates our previous study on cofilin’s role in mediating neuronal apoptosis. Together, our results suggest that cofilin could present a common target in neurons and microglial cells and might prove to be a promising therapy for different brain injury mechanisms including stroke.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olson JK, Miller SD (2004) Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J Immunol 173(6):3916–3924
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 17(7):796–808. doi:10.1038/nm.2399
Hur J, Lee P, Kim MJ, Kim Y, Cho YW (2010) Ischemia-activated microglia induces neuronal injury via activation of gp91phox NADPH oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(3):1526–1530. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.114
Dolga AM, Letsche T, Gold M, Doti N, Bacher M, Chiamvimonvat N, Dodel R, Culmsee C (2012) Activation of KCNN3/SK3/K(Ca)2.3 channels attenuates enhanced calcium influx and inflammatory cytokine production in activated microglia. Glia 60(12):2050–2064. doi:10.1002/glia.22419
Lee DY, Oh YJ, Jin BK (2005) Thrombin-activated microglia contribute to death of dopaminergic neurons in rat mesencephalic cultures: dual roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Glia 51(2):98–110. doi:10.1002/glia.20190
Lin S, Yin Q, Zhong Q, Lv FL, Zhou Y, Li JQ, Wang JZ, Su BY et al (2012) Heme activates TLR4-mediated inflammatory injury via MyD88/TRIF signaling pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 9:46. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-46
Jana M, Palencia CA, Pahan K (2008) Fibrillar amyloid-beta peptides activate microglia via TLR2: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Immunol 181(10):7254–7262
Rozenfeld C, Martinez R, Seabra S, Sant’anna C, Goncalves JG, Bozza M, Moura-Neto V, De Souza W (2005) Toxoplasma gondii prevents neuron degeneration by interferon-gamma-activated microglia in a mechanism involving inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and transforming growth factor-beta1 production by infected microglia. Am J Pathol 167(4):1021–1031
Zeng KW, Yu Q, Liao LX, Song FJ, Lv HN, Jiang Y, Tu PF (2015) Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of MC13, a novel coumarin compound from condiment Murraya, through inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced TRAF6-TAK1-NF-kappaB, P38/ERK MAPKS and Jak2-Stat1/Stat3 pathways. J Cell Biochem 116(7):1286–1299. doi:10.1002/jcb.25084
Babu R, Bagley JH, Di C, Friedman AH, Adamson C (2012) Thrombin and hemin as central factors in the mechanisms of intracerebral hemorrhage-induced secondary brain injury and as potential targets for intervention. Neurosurg Focus 32(4):E8. doi:10.3171/2012.1.FOCUS11366
Taylor RA, Sansing LH (2013) Microglial responses after ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:746068. doi:10.1155/2013/746068
Colton C, Wilcock DM (2010) Assessing activation states in microglia. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9(2):174–191
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Anne Stetler R, Yang QW (2014) Inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage: from mechanisms to clinical translation. Prog Neurobiol 115:25–44. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.11.003
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69. doi:10.1038/nrn2038
Rangarajan P, Eng-Ang L, Dheen ST (2013) Potential drugs targeting microglia: current knowledge and future prospects. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 12(6):799–806
Bernstein BW, Bamburg JR (2010) ADF/cofilin: a functional node in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol 20(4):187–195. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.01.001
Van Troys M, Huyck L, Leyman S, Dhaese S, Vandekerkhove J, Ampe C (2008) Ins and outs of ADF/cofilin activity and regulation. Eur J Cell Biol 87(8–9):649–667. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.04.001
Cichon J, Sun C, Chen B, Jiang M, Chen XA, Sun Y, Wang Y, Chen G (2012) Cofilin aggregation blocks intracellular trafficking and induces synaptic loss in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 287(6):3919–3929. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.301911
Posadas I, Perez-Martinez FC, Guerra J, Sanchez-Verdu P, Cena V (2012) Cofilin activation mediates Bax translocation to mitochondria during excitotoxic neuronal death. J Neurochem 120(4):515–527. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07599.x
Madineni A, Alhadidi Q, Shah ZA (2014) Cofilin inhibition restores neuronal cell death in oxygen-glucose deprivation model of ischemia. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9056-3
Hong ZY, Shi XR, Zhu K, Wu TT, Zhu YZ (2014) SCM-198 inhibits microglial overactivation and attenuates Aβ(1-40)-induced cognitive impairments in rats via JNK and NF-κB pathways. J Neuroinflammation 11:147. doi:10.1186/s12974-014-0147-x
Alhadidi Q, Bin Sayeed MS, Shah ZA (2016) Cofilin as a promising therapeutic target for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Translational Stroke Research 7(1):33–41. doi:10.1007/s12975-015-0438-2
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 308(5726):1314–1318. doi:10.1126/science.1110647
Parkhurst CN, Yang G, Ninan I, Savas JN, Yates JR 3rd, Lafaille JJ, Hempstead BL, Littman DR et al (2013) Microglia promote learning-dependent synapse formation through brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Cell 155(7):1596–1609. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.030
Sierra A, Encinas JM, Deudero JJ, Chancey JH, Enikolopov G, Overstreet-Wadiche LS, Tsirka SE, Maletic-Savatic M (2010) Microglia shape adult hippocampal neurogenesis through apoptosis-coupled phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 7(4):483–495. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.08.014
Yenari MA, Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA (2010) Microglial activation in stroke: therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):378–391. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2010.07.005
Luo XG, Chen SD (2012) The changing phenotype of microglia from homeostasis to disease. Transl Neurodegener 1(1):9. doi:10.1186/2047-9158-1-9
Frick LR, Williams K, Pittenger C (2013) Microglial dysregulation in psychiatric disease. Clinical & Developmental Immunology 2013:608654. doi:10.1155/2013/608654
Merrill JE, Ignarro LJ, Sherman MP, Melinek J, Lane TE (1993) Microglial cell cytotoxicity of oligodendrocytes is mediated through nitric oxide. J Immunol 151(4):2132–2141
Kacimi R, Giffard RG, Yenari MA (2011) Endotoxin-activated microglia injure brain derived endothelial cells via NF-kappaB, JAK-STAT and JNK stress kinase pathways. J Inflamm (Lond) 8:7. doi:10.1186/1476-9255-8-7
Yenari MA, Xu L, Tang XN, Qiao Y, Giffard RG (2006) Microglia potentiate damage to blood-brain barrier constituents: improvement by minocycline in vivo and in vitro. Stroke 37(4):1087–1093. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000206281.77178.ac
Kim JY, Kim N, Yenari MA (2015) Mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications of microglial activation after brain injury. CNS Neurosci Ther 21(4):309–319. doi:10.1111/cns.12360
Kim JS, Huang TY, Bokoch GM (2009) Reactive oxygen species regulate a slingshot-cofilin activation pathway. Mol Biol Cell 20(11):2650–2660. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-02-0131
Wang Y, Shibasaki F, Mizuno K (2005) Calcium signal-induced cofilin dephosphorylation is mediated by slingshot via calcineurin. J Biol Chem 280(13):12683–12689. doi:10.1074/jbc.M411494200
Huang TY, Minamide LS, Bamburg JR, Bokoch GM (2008) Chronophin mediates an ATP-sensing mechanism for cofilin dephosphorylation and neuronal cofilin-actin rod formation. Dev Cell 15(5):691–703. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.017
Gouix E, Buisson A, Nieoullon A, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Tauskela JS, Blondeau N, Had-Aissouni L (2014) Oxygen glucose deprivation-induced astrocyte dysfunction provokes neuronal death through oxidative stress. Pharmacol Res 87:8–17. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2014.06.002
Verdijk P, van Veelen PA, de Ru AH, Hensbergen PJ, Mizuno K, Koerten HK, Koning F, Tensen CP et al (2004) Morphological changes during dendritic cell maturation correlate with cofilin activation and translocation to the cell membrane. Eur J Immunol 34(1):156–164. doi:10.1002/eji.200324241
Freeman SA, Jaumouille V, Choi K, Hsu BE, Wong HS, Abraham L, Graves ML, Coombs D et al (2015) Toll-like receptor ligands sensitize B-cell receptor signalling by reducing actin-dependent spatial confinement of the receptor. Nat Commun 6:6168. doi:10.1038/ncomms7168
Isowa N, Xavier AM, Dziak E, Opas M, McRitchie DI, Slutsky AS, Keshavjee SH, Liu M (1999) LPS-induced depolymerization of cytoskeleton and its role in TNF-alpha production by rat pneumocytes. Am J Phys 277(3 Pt 1):L606–L615
Freeman SA, Lei V, Dang-Lawson M, Mizuno K, Roskelley CD, Gold MR (2011) Cofilin-mediated F-actin severing is regulated by the Rap GTPase and controls the cytoskeletal dynamics that drive lymphocyte spreading and BCR microcluster formation. J Immunol 187(11):5887–5900. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102233
Pollard TD, Cooper JA (2009) Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. Science 326(5957):1208–1212. doi:10.1126/science.1175862
Jonsson F, Gurniak CB, Fleischer B, Kirfel G, Witke W (2012) Immunological responses and actin dynamics in macrophages are controlled by N-cofilin but are independent from ADF. PLoS One 7(4):e36034. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036034
Maizels Y, Oberman F, Miloslavski R, Ginzach N, Berman M, Yisraeli JK (2015) Localization of cofilin mRNA to the leading edge of migrating cells promotes directed cell migration. J Cell Sci 128(10):1922–1933. doi:10.1242/jcs.163972
Samstag Y, Eckerskorn C, Wesselborg S, Henning S, Wallich R, Meuer SC (1994) Costimulatory signals for human T-cell activation induce nuclear translocation of pp19/cofilin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91(10):4494–4498
van Rheenen J, Condeelis J, Glogauer M (2009) A common cofilin activity cycle in invasive tumor cells and inflammatory cells. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 3):305–311. doi:10.1242/jcs.031146
Heng YW, Koh CG (2010) Actin cytoskeleton dynamics and the cell division cycle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42(10):1622–1633. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2010.04.007
Nagaoka R, Abe H, Kusano K, Obinata T (1995) Concentration of cofilin, a small actin-binding protein, at the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 30(1):1–7. doi:10.1002/cm.970300102
Abe H, Obinata T, Minamide LS, Bamburg JR (1996) Xenopus laevis actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilin: a phosphorylation-regulated protein essential for development. J Cell Biol 132(5):871–885
Kiuchi T, Nagai T, Ohashi K, Mizuno K (2011) Measurements of spatiotemporal changes in G-actin concentration reveal its effect on stimulus-induced actin assembly and lamellipodium extension. J Cell Biol 193(2):365–380. doi:10.1083/jcb.201101035
Kwan W, Trager U, Davalos D, Chou A, Bouchard J, Andre R, Miller A, Weiss A et al (2012) Mutant huntingtin impairs immune cell migration in Huntington disease. J Clin Invest 122(12):4737–4747. doi:10.1172/JCI64484
May RC, Machesky LM (2001) Phagocytosis and the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 6):1061–1077
Adachi R, Takeuchi K, Suzuki K (2002) Antisense oligonucleotide to cofilin enhances respiratory burst and phagocytosis in opsonized zymosan-stimulated mouse macrophage J774.1 cells. J Biol Chem 277(47):45566–45571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207419200
Gitik M, Kleinhaus R, Hadas S, Reichert F, Rotshenker S (2014) Phagocytic receptors activate and immune inhibitory receptor SIRPalpha inhibits phagocytosis through paxillin and cofilin. Front Cell Neurosci 8:104. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00104
Hadas S, Spira M, Hanisch UK, Reichert F, Rotshenker S (2012) Complement receptor-3 negatively regulates the phagocytosis of degenerated myelin through tyrosine kinase Syk and cofilin. J Neuroinflammation 9:166. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-166
Kustermans G, El Benna J, Piette J, Legrand-Poels S (2005) Perturbation of actin dynamics induces NF-kappaB activation in myelomonocytic cells through an NADPH oxidase-dependent pathway. Biochem J 387(Pt 2):531–540. doi:10.1042/BJ20041318
Rivas FV, O’Keefe JP, Alegre ML, Gajewski TF (2004) Actin cytoskeleton regulates calcium dynamics and NFAT nuclear duration. Mol Cell Biol 24(4):1628–1639
Kustermans G, Piette J, Legrand-Poels S (2008) Actin-targeting natural compounds as tools to study the role of actin cytoskeleton in signal transduction. Biochem Pharmacol 76(11):1310–1322. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.05.028
Shen A, Puente LG, Ostergaard HL (2005) Tyrosine kinase activity and remodelling of the actin cytoskeleton are co-temporally required for degranulation by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunology 116(2):276–286. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02222.x
Fazal F, Bijli KM, Minhajuddin M, Rein T, Finkelstein JN, Rahman A (2009) Essential role of cofilin-1 in regulating thrombin-induced RelA/p65 nuclear translocation and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 284(31):21047–21056. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.016444
Bielig H, Lautz K, Braun PR, Menning M, Machuy N, Brugmann C, Barisic S, Eisler SA et al (2014) The cofilin phosphatase slingshot homolog 1 (SSH1) links NOD1 signaling to actin remodeling. PLoS Pathog 10(9):e1004351. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004351
Mayo L, Stein R (2007) Characterization of LPS and interferon-gamma triggered activation-induced cell death in N9 and primary microglial cells: induction of the mitochondrial gateway by nitric oxide. Cell Death Differ 14(1):183–186. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401989
Dai XJ, Li N, Yu L, Chen ZY, Hua R, Qin X, Zhang YM (2015) Activation of BV2 microglia by lipopolysaccharide triggers an inflammatory reaction in PC12 cell apoptosis through a toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 20(2):321–331. doi:10.1007/s12192-014-0552-1
Ivanenkov YA, Balakin KV, Lavrovsky Y (2011) Small molecule inhibitors of NF-kB and JAK/STAT signal transduction pathways as promising anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 11(1):55–78
Socodato R, Portugal CC, Domith I, Oliveira NA, Coreixas VS, Loiola EC, Martins T, Santiago AR et al (2015) c-Src function is necessary and sufficient for triggering microglial cell activation. Glia 63(3):497–511. doi:10.1002/glia.22767
Chen YJ, Hsieh MY, Chang MY, Chen HC, Jan MS, Maa MC, Leu TH (2012) Eps8 protein facilitates phagocytosis by increasing TLR4-MyD88 protein interaction in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Biol Chem 287(22):18806–18819. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.340935
Leonard A, Marando C, Rahman A, Fazal F (2013) Thrombin selectively engages LIM kinase 1 and slingshot-1L phosphatase to regulate NF-kappaB activation and endothelial cell inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 305(9):L651–L664. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00071.2013
Acknowledgements
The study was partly funded by a grant from NIH-National Complimentary and integrative health (R00AT004197) and start-up funds from The University of Toledo to ZAS. Qasim Alhadidi was supported by the Higher Committee for Education Development in Iraq (www.hcediraq.org). We would like to thank Dr. Kumi Nagamoto-Combs from the University of North Dakota for the generous gift of SIM-A9 cells. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhadidi, Q., Shah, Z.A. Cofilin Mediates LPS-Induced Microglial Cell Activation and Associated Neurotoxicity Through Activation of NF-κB and JAK–STAT Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 55, 1676–1691 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0432-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0432-7