Abstract
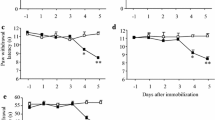
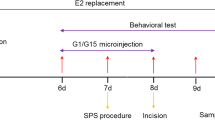
Clinically, preoperative anxiety adversely affected postoperative hyperalgesia. As stress-induced glucocorticoids (GCs) were reported to sensitize the activation of microglia, the present study investigated whether and how GCs and microglia played in the process of preoperative anxiety-induced postoperative hyperalgesia. The study used an animal model that exposed rats to single prolonged stress (SPS) procedure to induce preoperative anxiety-like behaviors 24 h before the plantar incisional surgery. Behavioral testing revealed that preoperative SPS enhanced the mechanical allodynia induced by plantar incision. SPS was also found to induce elevated circulating corticosterone levels, potentiate the activation of spinal microglia, and increase the expression of spinal proinflammatory cytokines. Inhibition of microglia by pretreatment with minocycline attenuated the SPS-enhanced mechanical allodynia, and this was accompanied by decreased activation of spinal microglia and expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Another experiment was conducted by administering RU486, the GC receptor (GR) antagonist, to rats. The results showed that RU486 suppressed SPS-induced and SPS-potentiated proinflammatory activation of spinal microglia and revealed analgesic effects. Together, these data indicated that inhibition of stress-induced GR activation attenuated the preoperative anxiety-induced exacerbation of postoperative pain, and the suppression of spinal microglia activation may underlie this anti-hyperalgesia effect. Pending further studies, these findings suggested that GR and spinal microglia may play important roles in the development of preoperative anxiety-induced postoperative hyperalgesia and may serve as novel targets to prevent this phenomenon.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jawaid M, Mushtaq A, Mukhtar S, Khan Z (2007) Preoperative anxiety before elective surgery. Neurosciences (Riyadh) 12(2):145–148
Nigussie S, Belachew T, Wolancho W (2014) Predictors of preoperative anxiety among surgical patients in Jimma University Specialized Teaching Hospital, South Western Ethiopia. BMC Surg 14:67
Yilmaz M, Sezer H, Gurler H, Bekar M (2012) Predictors of preoperative anxiety in surgical inpatients. J Clin Nurs 21(7-8):956–964
Perks A, Chakravarti S, Manninen P (2009) Preoperative anxiety in neurosurgical patients. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 21(2):127–130
Theunissen M, Peters ML, Bruce J, Gramke HF, Marcus MA (2012) Preoperative anxiety and catastrophizing: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the association with chronic postsurgical pain. Clin J Pain 28(9):819–841
Ali A, Altun D, Oguz BH, Ilhan M, Demircan F, Koltka K (2014) The effect of preoperative anxiety on postoperative analgesia and anesthesia recovery in patients undergoing laparascopic cholecystectomy. J Anesth 28(2):222–227
Ip HY, Abrishami A, Peng PW, Wong J, Chung F (2009) Predictors of postoperative pain and analgesic consumption: a qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology 111(3):657–677
Petrovic NM, Milovanovic DR, Ignjatovic Ristic D, Riznic N, Ristic B, Stepanovic Z (2014) Factors associated with severe postoperative pain in patients with total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 48(6):615–622
Raichle KA, Osborne TL, Jensen MP, Ehde DM, Smith DG, Robinson LR (2015) Preoperative state anxiety, acute postoperative pain, and analgesic use in persons undergoing lower limb amputation. Clin J Pain 31(8):699–706
Jennings EM, Okine BN, Roche M, Finn DP (2014) Stress-induced hyperalgesia. Prog Neurobiol 121:1–18
Crettaz B, Marziniak M, Willeke P, Young P, Hellhammer D, Stumpf A, Burgmer M (2013) Stress-induced allodynia—evidence of increased pain sensitivity in healthy humans and patients with chronic pain after experimentally induced psychosocial stress. PLoS ONE 8(8), e69460
Tramullas M, Finger BC, Moloney RD, Golubeva AV, Moloney G, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 regulates chronic stress-induced visceral pain in mice. Biol Psychiatry 76(4):340–348
Akagi T, Matsumura Y, Yasui M, Minami E, Inoue H, Masuda T, Tozaki-Saitoh H, Tamura T et al (2014) Interferon regulatory factor 8 expressed in microglia contributes to tactile allodynia induced by repeated cold stress in rodents. J Pharmacol Sci 126(2):172–176
Alexander JK, DeVries AC, Kigerl KA, Dahlman JM, Popovich PG (2009) Stress exacerbates neuropathic pain via glucocorticoid and NMDA receptor activation. Brain Behav Immun 23(6):851–860
Bradesi S, Svensson CI, Steinauer J, Pothoulakis C, Yaksh TL, Mayer EA (2009) Role of spinal microglia in visceral hyperalgesia and NK1R up-regulation in a rat model of chronic stress. Gastroenterology 136(4):1339–1348, e1331-1332
Qi J, Chen C, Lu YC, Zhang T, Xu H, Cui YY, Chen YZ, Wang W et al (2014) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 in the medial prefrontal cortex contributes to stress-induced hyperalgesia. Mol Neurobiol 50(3):1013–1023
Fu R, Shen Q, Xu P, Luo JJ, Tang Y (2014) Phagocytosis of microglia in the central nervous system diseases. Mol Neurobiol 49(3):1422–1434
Lu C, Liu Y, Sun B, Sun Y, Hou B, Zhang Y, Ma Z, Gu X (2015) Intrathecal injection of JWH-015 attenuates bone cancer pain via time-dependent modification of pro-inflammatory cytokines expression and astrocytes activity in spinal cord. Inflammation
Hu JH, Yang JP, Liu L, Li CF, Wang LN, Ji FH, Cheng H (2012) Involvement of CX3CR1 in bone cancer pain through the activation of microglia p38 MAPK pathway in the spinal cord. Brain Res 1465:1–9
Wang XW, Li TT, Zhao J, Mao-Ying QL, Zhang H, Hu S, Li Q, Mi WL et al (2012) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in spinal astrocytes and microglia contributes to cancer-induced bone pain in rats. Neuroscience 217:172–181
Wang D, Couture R, Hong Y (2014) Activated microglia in the spinal cord underlies diabetic neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 728:59–66
Sun YE, Peng L, Sun X, Bo J, Yang D, Zheng Y, Liu C, Zhu B et al (2012) Intrathecal injection of spironolactone attenuates radicular pain by inhibition of spinal microglia activation in a rat model. PLoS ONE 7(6), e39897
Ito N, Obata H, Saito S (2009) Spinal microglial expression and mechanical hypersensitivity in a postoperative pain model: comparison with a neuropathic pain model. Anesthesiology 111(3):640–648
Obata H, Eisenach JC, Hussain H, Bynum T, Vincler M (2006) Spinal glial activation contributes to postoperative mechanical hypersensitivity in the rat. J Pain 7(11):816–822
Wen YR, Tan PH, Cheng JK, Liu YC, Ji RR (2011) Microglia: a promising target for treating neuropathic and postoperative pain, and morphine tolerance. J Formos Med Assoc 110(8):487–494
de Pablos RM, Villaran RF, Arguelles S, Herrera AJ, Venero JL, Ayala A, Cano J, Machado A (2006) Stress increases vulnerability to inflammation in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 26(21):5709–5719
Espinosa-Oliva AM, de Pablos RM, Villaran RF, Arguelles S, Venero JL, Machado A, Cano J (2011) Stress is critical for LPS-induced activation of microglia and damage in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 32(1):85–102
Frank MG, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2011) Stress- and glucocorticoid-induced priming of neuroinflammatory responses: potential mechanisms of stress-induced vulnerability to drugs of abuse. Brain Behav Immun 25(Suppl 1):S21–S28
Weber MD, Frank MG, Sobesky JL, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2013) Blocking toll-like receptor 2 and 4 signaling during a stressor prevents stress-induced priming of neuroinflammatory responses to a subsequent immune challenge. Brain Behav Immun 32:112–121
Wohleb ES, Fenn AM, Pacenta AM, Powell ND, Sheridan JF, Godbout JP (2012) Peripheral innate immune challenge exaggerated microglia activation, increased the number of inflammatory CNS macrophages, and prolonged social withdrawal in socially defeated mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37(9):1491–1505
Alexander JK, Cox GM, Tian JB, Zha AM, Wei P, Kigerl KA, Reddy MK, Dagia NM et al (2012) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is essential for inflammatory and neuropathic pain and enhances pain in response to stress. Exp Neurol 236(2):351–362
Frank MG, Thompson BM, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2012) Glucocorticoids mediate stress-induced priming of microglial pro-inflammatory responses. Brain Behav Immun 26(2):337–345
Munhoz CD, Lepsch LB, Kawamoto EM, Malta MB, Lima Lde S, Avellar MC, Sapolsky RM, Scavone C (2006) Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J Neurosci 26(14):3813–3820
Bellavance MA, Rivest S (2014) The HPA-immune axis and the immunomodulatory actions of glucocorticoids in the brain. Front Immunol 5:136
Frank MG, Miguel ZD, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2010) Prior exposure to glucocorticoids sensitizes the neuroinflammatory and peripheral inflammatory responses to E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Brain Behav Immun 24(1):19–30
Kelly KA, Miller DB, Bowyer JF, O’Callaghan JP (2012) Chronic exposure to corticosterone enhances the neuroinflammatory and neurotoxic responses to methamphetamine. J Neurochem 122(5):995–1009
O’Callaghan JP, Kelly KA, Locker AR, Miller DB, Lasley SM (2015) Corticosterone primes the neuroinflammatory response to DFP in mice: potential animal model of Gulf War Illness. J Neurochem 133(5):708–721
Hong S, Zheng G, Wu X, Snider NT, Owyang C, Wiley JW (2011) Corticosterone mediates reciprocal changes in CB 1 and TRPV1 receptors in primary sensory neurons in the chronically stressed rat. Gastroenterology 140(2):627–637, e624
Liu Y, Hou B, Zhang W, Sun YE, Li L, Ma Z, Gu X (2015) The activation of spinal astrocytes contributes to preoperative anxiety-induced persistent post-operative pain in a rat model of incisional pain. Eur J Pain 19(5):733–740
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16(2):109–110
Rojewska E, Korostynski M, Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B, Mika J (2014) Expression profiling of genes modulated by minocycline in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 10:47
Rossi S, De Chiara V, Musella A, Kusayanagi H, Mataluni G, Bernardi G, Usiello A, Centonze D (2008) Chronic psychoemotional stress impairs cannabinoid-receptor-mediated control of GABA transmission in the striatum. J Neurosci 28(29):7284–7292
Liberzon I, Krstov M, Young EA (1997) Stress-restress: effects on ACTH and fast feedback. Psychoneuroendocrinology 22(6):443–453
Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF (1996) Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain 64(3):493–501
Liu X, Wu G, Shi D, Zhu R, Zeng H, Cao B, Huang M, Liao H (2015) Effects of nitric oxide on notexin-induced muscle inflammatory responses. Int J Biol Sci 11(2):156–167
Gregus AM, Doolen S, Dumlao DS, Buczynski MW, Takasusuki T, Fitzsimmons BL, Hua XY, Taylor BK et al (2012) Spinal 12-lipoxygenase-derived hepoxilin A3 contributes to inflammatory hyperalgesia via activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(17):6721–6726
Wen YR, Suter MR, Ji RR, Yeh GC, Wu YS, Wang KC, Kohno T, Sun WZ et al (2009) Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in spinal microglia contributes to incision-induced mechanical allodynia. Anesthesiology 110(1):155–165
Milligan ED, Watkins LR (2009) Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(1):23–36
Yasui M, Yoshimura T, Takeuchi S, Tokizane K, Tsuda M, Inoue K, Kiyama H (2014) A chronic fatigue syndrome model demonstrates mechanical allodynia and muscular hyperalgesia via spinal microglial activation. Glia 62(9):1407–1417
Suarez-Roca H, Quintero L, Avila R, Medina S, De Freitas M, Cardenas R (2014) Central immune overactivation in the presence of reduced plasma corticosterone contributes to swim stress-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res Bull 100:61–69
Anacker C, Cattaneo A, Luoni A, Musaelyan K, Zunszain PA, Milanesi E, Rybka J, Berry A et al (2013) Glucocorticoid-related molecular signaling pathways regulating hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(5):872–883
Egeland M, Zunszain PA, Pariante CM (2015) Molecular mechanisms in the regulation of adult neurogenesis during stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(4):189–200
Epel ES (2009) Psychological and metabolic stress: a recipe for accelerated cellular aging? Hormones (Athens) 8(1):7–22
Chen DY, Bambah-Mukku D, Pollonini G, Alberini CM (2012) Glucocorticoid receptors recruit the CaMKIIalpha-BDNF-CREB pathways to mediate memory consolidation. Nat Neurosci 15(12):1707–1714
Suri D, Vaidya VA (2013) Glucocorticoid regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: relevance to hippocampal structural and functional plasticity. Neuroscience 239:196–213
Zunszain PA, Anacker C, Cattaneo A, Carvalho LA, Pariante CM (2011) Glucocorticoids, cytokines and brain abnormalities in depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(3):722–729
Myers B, McKlveen JM, Herman JP (2014) Glucocorticoid actions on synapses, circuits, and behavior: implications for the energetics of stress. Front Neuroendocrinol 35(2):180–196
Wang S, Lim G, Zeng Q, Sung B, Ai Y, Guo G, Yang L, Mao J (2004) Expression of central glucocorticoid receptors after peripheral nerve injury contributes to neuropathic pain behaviors in rats. J Neurosci 24(39):8595–8605
Zhang J, Zhang W, Sun Y, Liu Y, Song L, Ma Z, Gu X (2014) Activation of GRs-Akt-nNOs-NR2B signaling pathway by second dose GR agonist contributes to exacerbated hyperalgesia in a rat model of radicular pain. Mol Biol Rep 41(6):4053–4061
Wang S, Lim G, Yang L, Sung B, Mao J (2006) Downregulation of spinal glutamate transporter EAAC1 following nerve injury is regulated by central glucocorticoid receptors in rats. Pain 120(1-2):78–85
Myers B, Greenwood-Van Meerveld B (2012) Differential involvement of amygdala corticosteroid receptors in visceral hyperalgesia following acute or repeated stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 302(2):G260–G266
Frank MG, Hershman SA, Weber MD, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2014) Chronic exposure to exogenous glucocorticoids primes microglia to pro-inflammatory stimuli and induces NLRP3 mRNA in the hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 40:191–200
Hermoso MA, Matsuguchi T, Smoak K, Cidlowski JA (2004) Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor alpha cooperatively regulate toll-like receptor 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 24(11):4743–4756
Chinenov Y, Rogatsky I (2007) Glucocorticoids and the innate immune system: crosstalk with the toll-like receptor signaling network. Mol Cell Endocrinol 275(1-2):30–42
Busillo JM, Cidlowski JA (2013) The five Rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore. Trends Endocrinol Metab 24(3):109–119
Cruz-Topete D, Cidlowski JA (2015) One hormone, two actions: anti- and pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 22(1-2):20–32
Frank MG, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2015) The permissive role of glucocorticoids in neuroinflammatory priming: mechanisms and insights. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 22(4):300–305
Ding Y, Gao ZG, Jacobson KA, Suffredini AF (2010) Dexamethasone enhances ATP-induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 335(3):693–702
Nair A, Bonneau RH (2006) Stress-induced elevation of glucocorticoids increases microglia proliferation through NMDA receptor activation. J Neuroimmunol 171(1-2):72–85
Taves S, Berta T, Liu DL, Gan S, Chen G, Kim YH, Van de Ven T, Laufer S, Ji RR (2015) Spinal inhibition of p38 MAP kinase reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain in male but not female mice: Sex-dependent microglial signaling in the spinal cord. Brain Behav Immun
Sorge RE, Mapplebeck JC, Rosen S, Beggs S, Taves S, Alexander JK, Martin LJ, Austin JS et al (2015) Different immune cells mediate mechanical pain hypersensitivity in male and female mice. Nat Neurosci 18(8):1081–1083
Myers B, Greenwood-Van Meerveld B (2010) Elevated corticosterone in the amygdala leads to persistent increases in anxiety-like behavior and pain sensitivity. Behav Brain Res 214(2):465–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471129, 81171048, 81171047) and a grant from the Department of Health of Jiangsu Province of China (XK201140, RC2011006).
Additional information
Rao Sun and Zhibin Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, R., Zhao, Z., Feng, J. et al. Glucocorticoid-Potentiated Spinal Microglia Activation Contributes to Preoperative Anxiety-Induced Postoperative Hyperalgesia. Mol Neurobiol 54, 4316–4328 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9976-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9976-1