Abstract
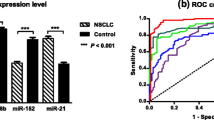
microRNA (miR)-138 has been recognized as a potential tumor suppressor via regulating 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. The aim of this study was to investigate miR-138 and PDK1 mRNA expression in serum of NSCLC and their associations with patients’ prognosis. miR-138 and PDK1 mRNA expressions in 100 NSCLCs and 100 healthy control sera were detected by quantitative real-time PCR. miR-138 expression level was significantly lower in NSCLC serum samples than in healthy control serum samples (P < 0.001), while PDK1 mRNA expression level was significantly increased in NSCLC serum samples compared to healthy control serum samples (P < 0.001). In addition, miR-138 downregulation and PDK1 upregulation were both significantly associated with advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (both P = 0.002) and positive lymph node metastasis (both P = 0.01) of NSCLC patients. Moreover, the overall survival of NSCLC patients with low miR-138 expression or high PDK1 mRNA expression was obviously shorter than those with high miR-138 expression or low PDK1 mRNA expression (both P < 0.001). Notably, NSCLC patients with combined miR-138 downregulation and PDK1 upregulation (miR-138-low/PDK1-high) had shortest overall survival (P < 0.001). Furthermore, multivariate analysis showed that miR-138 expression (P = 0.01), PDK1 expression (P = 0.01), and combined expression of miR-138 and PDK1 (miR-138/PDK1, P = 0.001) were all independent prognostic factors for overall survival in NSCLC patients. Deregulation of miR-138/PDK1 cascade may be implicated in carcinogenesis and cancer progression of human NSCLC. More importantly, miR-138 and PDK1 may synergistically predict patients’ prognosis and their combination may represent a promising prognostic biomarker of human NSCLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
López-González A, Millán PI, Cantos B, Provencio M. Surveillance of resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2012;14:721–5.
Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Baade PD. The international epidemiology of lung cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:819–31.
Zarogoulidis K, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Boutsikou E, Machairiotis N, Tsakiridis K, et al. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Thorac Dis. 2013;5:S389–96.
Filipits M, Pirker R. Predictive markers in the adjuvant therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2011;74:355–63.
Indovina P, Marcelli E, Maranta P, Tarro G. Lung cancer proteomics: recent advances in biomarker discovery. Int J Proteomics. 2011;2011:726869.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Li PY, He FC, Zhou GQ. Association of human microRNA related genetic variations with cancer. Yi Chuan. 2011;33:870–8.
Zhang H, Li W, Nan F, Ren F, Wang H, Xu Y, Zhang F. MicroRNA expression profile of colon cancer stem-like cells in HT29 adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;404:273–8.
de Krijger I, Mekenkamp LJ, Punt CJ, Nagtegaal ID. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol. 2011;224:438–47.
Munker R, Calin GA. MicroRNA profiling in cancer. Clin Sci. 2011;121:141–58.
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, O’Hara B, Liu CG, Palazzo JP, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol. 2009;219:214–21.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol. 2002;12:735–9.
Weber MJ. New human and mouse microRNA genes found by homology search. FEBS J. 2005;272:59–73.
Obernosterer G, Leuschner PJ, Alenius M, Martinez J. Post-transcriptional regulation of microRNA expression. RNA. 2006;12:1161–7.
Jin Y, Wang C, Liu X, Mu W, Chen Z, Yu D, Wang A, Dai Y, Zhou X. Molecular characterization of the microRNA-138-Fos-like antigen 1 (FOSL1) regulatory module in squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:40104–9.
Qiu S, Huang D, Yin D, Li F, Li X, Kung HF, Peng Y. Suppression of tumorigenicity by microRNA-138 through inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832:1697–707.
Jin Y, Chen D, Cabay RJ, Wang A, Crowe DL, Zhou X. Role of microRNA-138 as a potential tumor suppressor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013;303:357–85.
Liu X, Wang C, Chen Z, Jin Y, Wang Y, Kolokythas A, Dai Y, Zhou X. MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem J. 2011;440:23–31.
Wang Q, Zhong M, Liu W, Li J, Huang J, Zheng L. Alterations of microRNAs in cisplatin-resistant human non-small cell lung cancer cells (A549/DDP). Exp Lung Res. 2011;37:427–34.
Wang Q, Tang H, Yin S, Dong C. Downregulation of microRNA-138 enhances the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the upregulation of RhoC/p-ERK/MMP-2/MMP-9. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:2046–52.
Yeh YM, Chuang CM, Chao KC, Wang LH. MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer. 2013;133:867–78.
Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhao M, Lv Z, Zhang X, Qin X, Wang H, Wang S, Su J, Lv X, Liu H, Du W, Zhou W, Chen X, Fei K. MiR-138 inhibits tumor growth through repression of EZH2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31:56–65.
Yang H, Tang Y, Guo W, Du Y, Wang Y, Li P, Zang W, Yin X, Wang H, Chu H, Zhang G, Zhao G. Up-regulation of microRNA-138 induce radiosensitization in lung cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2014;35:6557–65.
Ye XW, Yu H, Jin YK, Jing XT, Xu M, Wan ZF, Zhang XY. miR-138 inhibits proliferation by targeting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Respir J. 2014. doi:10.1111/crj.12100.
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, Xu S, Hu K, Wu M, Liang Y, Liu P, Tang J, Lu WH, Feng QS, Chen LZ, Qian CN, Bei JX, Kang T, Zeng YX. MiR-138 suppressed nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:2495–506.
Long L, Huang G, Zhu H, Guo Y, Liu Y, Huo J. Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting TWIST2. J Transl Med. 2013;11:275.
Medina JR. Selective 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) inhibitors: dissecting the function and pharmacology of PDK1. J Med Chem. 2013;56:2726–37.
Bayascas JR. PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;346:9–29.
Raimondi C, Falasca M. Targeting PDK1 in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2011;18:2763–9.
Li Y, Yang KJ, Park J. Multiple implications of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in human cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2010;1:239–47.
Bayascas JR, Leslie NR, Parsons R, Fleming S, Alessi DR. Hypomorphic mutation of PDK1 suppresses tumorigenesis in PTEN(±) mice. Curr Biol. 2005;15:1839–46.
Yu J, Chen KS, Li YN, Yang J, Zhao L. Silencing of PDK1 gene expression by RNA interference suppresses growth of esophageal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:4147–51.
Liu Y, Wang J, Wu M, Wan W, Sun R, Yang D, Sun X, Ma D, Ying G, Zhang N. Down-regulation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 levels inhibits migration and experimental metastasis of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:944–54.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Zhang, G., Zhang, N. et al. Prognostic potential of microRNA-138 and its target mRNA PDK1 in sera for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol 31, 129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0129-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0129-y